* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 5
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
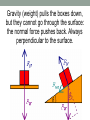
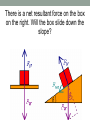
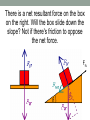
“If at first you don't succeed, then skydiving definitely isn't for you.” Anonymous Course web page http://sdbv.missouristate.edu/mreed/CLASS/PHY12 3 Cell phones put away when class begins please. Announcements Reading: Chapter 2, sections 1-3; Chapter 3 section 1; and Chapter 4, all. HW2 is on WileyPlus now and due Friday by 5pm. Sample problems also on WileyPlus. Test 1 is a week from Wednesday. Chapter 4: Forces and Newton's Laws of Motion Newton’s 2nd Law F = ma where: •F = force in Newtons •m = mass in kilograms •a = acceleration in 2 m/s Forces have direction. What is the net force on this box? What's the first thing to do? Forces have direction. What is the net force on this box? Decide on axes and break into components. +Y 162 +X Forces have direction. What is the net force on this box? Break everything into components. +Y F1x=-258.7 F2x=263.3 F3x=0 162 F1y=84.1 +X F2y=282.3 F3y=-441 Forces have direction. What is the net force on this box? Solve the components +Y 162 Fx= -258.7+262.2+0=4.9 Fy= 84.1+282.3-441=-74.9 +X Forces have direction. What is the net force on this box? Combine into resultant force (vector). +Y 162 F = (4.92+(-74.9)2)1/2 =74.8 N +X q = tan-1(-74.9/4.9) = -86.3o Note that Y is negative and X is positive. Forces have direction. What is the net force on this box? What's the acceleration of the box? Use Newton's 2nd law: F=ma → a=F/m +Y 162 F = (4.92+(-74.9)2)1/2 =74.8 N +X q = tan-1(-74.9/4.9) = -86.3o Forces have direction. What is the net force on this box? What's the acceleration of the box? 1.7 m/s2 in the same direction. +Y 162 F = (4.92+(-74.9)2)1/2 =74.8 N +X q = tan-1(-74.9/4.9) = -86.3o •Do heavier objects fall faster since they have a greater mass? No. Galileo proved that g=constant. •For gravity, we write F=mg since 2 g=-9.8m/s for us on Earth, always. •Weight is a force caused by gravity. •Weight depends on the strength of gravity. •Mass is the amount of 'stuff' an object is made of, and does not change when gravity does. Forces • If anything is changing its velocity, it has acceleration and it is being acted upon by a force. • And therefore follows F=ma Fundamental Forces 1) Gravity 2) Strong Nuclear Force 3) Electroweak Force But we will mostly use gravity and other forces which are a result of 3. Forces we will use this semester: 1) Gravity 2) Normal 3) Friction 4) Tension 5) Spring Let's see how they work! Newton’s 3rd Law •For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Thought experiment •Gravity is acting upon you. Why don't you fall through the floor? Catalog of Forces • Weight – gravitational pull of the Earth on an object and is always directed toward the Earth. It is a long-range force. • Normal Force – reaction force of a surface to counter gravity. Normal forces are forces that can oppose other forces acting downward and put the object in equilibrium (in relation to the surface). Identical stickmen stand on the ground. Weight presses them down, the normal force of the ground holds them up. One is supporting some of his weight on a rope. Is the force from the ground the same on each stickman? Identical stickmen stand on the ground. Weight presses them down, the normal force of the ground holds them up. One is supporting some of his weight on a rope. Is the force from the ground the same on each stickman? NO The ground only applies as much force as is necessary. Gravity (weight) pulls the boxes down, but they cannot go through the surface: the normal force pushes back. Always perpendicular to the surface. There is a net resultant force on the box on the right. Will the box slide down the slope? There is a net resultant force on the box on the right. Will the box slide down the slope? Not if there's friction to oppose the net force. Ffs Friction • Friction is the force between an object and the surface it is on. Static friction is the force that keeps objects “stuck” in place and acts in the direction opposite the object would move. Kinetic friction is friction that opposes motion once the object is moving and acts in the opposite direction the object moves. • Friction always acts parallel to the surface.