* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circular Motion
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Mechanics of planar particle motion wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
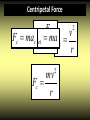
Round and Round 2-2-3 Circular Motion Uniform Circular Motion How in do circular we define motion VELOCITY?have constant Objects traveling Velocity is TANGENT to the speed and constantlyWhat CHANGING velocity – ‘t’ are ‘d’ are we we talking talking about? about? dcircle at all points changing notPERIOD magnitude v in direction but CIRCUMFERENCE (T) t 2r vc T Time for C = one 2πr revolution = πd If this is true, why does ANYTHING move in a circle? Centripetal Force • Inertia causes objects to travel STRAIGHT • Paths can be bent by FORCES • CENTRIPETAL FORCE bends an object’s path into a circle - pulling toward the CENTER Misconception The doors to the “Gravitron” close and it starts to spin. You are pushed against the outside edge of the ride and pinned there, You must be experiencing “centrifugal force” throwing you outward from the ride! Right? What is really happening? As the Gravitron starts to spin, friction F between your body and the ride start you moving v Once you are moving, your body wants to go STRAIGHT … but you can’t… The wall keeps pushing you back in toward the center of the ride! What is the sensation that you feel? • centrifugal (center fleeing) force – A ‘fictitious’ or ‘inertial’ force that is experienced from INSIDE a circular motion system – WHAT YOU FEEL • centripetal (center seeking) force – A true force that pushes or pulls an object toward the center of a circular path – WHAT ACTUALLY HAPPENS Centripetal Acceleration • Centripetal force is a NET FORCE • Causes ACCELERATION • In the SAME DIRECTION AS NET FORCE 2 v ac r Example #1 • What is the centripetal acceleration of a toy ball on the end of a 1.44 meter long string if it is moving at 12 meters per second? ac = v2/r ac = (12 m/s)2/1.44 m ac = 100 m/s2 Centripetal Force 2 Fnet v Fc maFcanet maac m r mv Fc r 2 Example #2 • What is the centripetal force acting on a 2000 kilogram airplane if it turns with a radius of 1000 meters while moving at 300 meters per second? ac = v2/r Fc = mac ac = (300 m/s)2/1000 m Fc = (2000 kg)(90 m/s2) ac = 90 m/s2 Fc = 1.8 x 105 N Example #3 • Is it possible for a 1000 kilogram car to make a turn with a radius of 50 meters while moving at 15 meters per second with rubber tires on dry asphalt? Fc = 4500 N Ff = 8339 N 2/r F F = = mv μF f N F ≥F Yes, asc long as f c 2/ 50 m Fc = (1000 Ff = (0.85)(9810 kg)(15 m/s)N) Fcf = 8339 4500 N End of 2.2.3 - PRACTICE