* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FUSION AND FISSION - Science Education at Jefferson Lab
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear reactor wikipedia , lookup
Fusion power wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Fleischmann–Pons experiment wikipedia , lookup
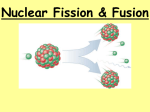
FUSION AND FISSION THE SUN Nuclear Fusion • Nuclear fusion is the process by which multiple nuclei join together to form a heavier nucleus. • It is accompanied by the release or absorption of energy depending on the masses of the nuclei involved.. FUSION NEUTRON DEUTERIUM HELIUM TRITIUM http://fusioned.gat.com Nuclear Fusion • Iron and nickel nuclei have the largest binding energies per nucleon of all nuclei and therefore are the most stable. Nuclear Fusion • The fusion of two nuclei lighter than iron or nickel generally releases energy. • The fusion of nuclei heavier than them absorbs energy. Complete the Reaction 1H element atomic number (protons) 4Be 1H 6C 2He 1H 2He 1H 2He 6C 4Be 2He 8 2He O Energy needed for Fusion The thermal activity of a gas is described by its temperature measurement which is really an indication of its velocity/energy. Thermal energy is represented by the height that the upper magnet. The upper ring has a potential energy given by PE = mgh at its drop point which is converted into kinetic energy (KE = 1/2 mv2) As the magnet falls towards the lower magnet. The two magnets click lightly when the kinetic energy is just greater than the magnetic energy that holds them apart. Since Kinetic Energy = Potential Energy (ignoring frictional components), the gravitational pull and mass of the upper magnet are constant, then the height needed to overcome the magnetic repelling force is proportional to that magnetic repelling force. Energy needed for Fusion PE =mg x h2-h1 PE = KE = Fxh1 F=force of repulsion F=PE/h1 Upper Drop Position Ring Magnets Float Position Lower Magnet Wood Block h2 h1 Fusion Changes Mass to Energy E=mc2 .993 kg Helium 1kg Hydrogen Cookie Fusion • • • • • • • • • • • Procedure Cut 2 squares of wax paper 10 cm on a side Cut 5 cm wide slice of cookie dough (atom) Find the mass of the atom and record on the table Place the atom one cm away from the edge of a wax paper square Repeat step 2 thru 4 for a second atom Place the atoms about 2 cm from each other Place both atoms on a plate and microwave for 1 minute Remove the “new element” and let cool for 2 minutes Find the mass of the “new element” Complete the table Cookie Fusion Mass Before Cooking Atom 1 Atom 2 Total Difference Mass After Cooking Learning Check What process creates energy in the Sun? Fusion of hydrogen into helium in the Sun’s core generates the Sun’s energy. How long ago did fusion generate the energy we now receive as sunlight? Fusion created the energy we receive today about a million years ago. This is the time it takes for photons and then convection to transport energy through the solar interior to the photosphere. Once sunlight emerges from the photosphere, it takes only about 8 minutes to reach Earth. Learning Check NUCLEAR FISSION A reaction in which an atomic nucleus of a radioactive element splits by bombardment from an external source, with simultaneous release of large amounts of energy, used for electric power generation Nuclear Fission Neutron induced in U235 Fission is Exothermic The sum of the masses of the resulting nuclei is less than the original mass (about 0.1% less) The “missing mass” is converted to energy according to E=mc2 Neutrons may: 1 - Cause another fission by colliding with a U235 nucleus • Creates two smaller nuclides and free neutrons • The free neutrons potentially collide with nearby U235 nuclei • May cause the nuclide to split as well Each split (fission) is accompanied by a large quantity of E-N-E-R-G-Y 2 - Be absorbed in other material 3 - Lost in the system If sufficient neutrons are present, we may achieve a chain reaction U.S. Electrical Power Production by Source Source: EIA (2004) Nuclear Fuel Costs • Nuclear Fuel Costs Include – – – – Uranium Enrichment Manufacturing Waste Disposal • Total Nuclear Fuel Cost is Only About 0.5 cents per kilowatt-hour – Uranium accounts for only about 20% of this cost or 0.1 cents per kilowatt-hour – Increasing Uranium Cost has Minimal Impact Review Nuclear fission: A large nucleus splits into several small nuclei when impacted by a neutron, and energy is released in this process Nuclear fusion: Several small nuclei fuse together and release energy. Draw a Double Bubble Map of Fusion and Fission fission fusion Differences Similarities Differences