* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classical Greece
Ancient Greek architecture wikipedia , lookup
Greek contributions to Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
Spartan army wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek religion wikipedia , lookup
List of oracular statements from Delphi wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Greek Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Eurymedon wikipedia , lookup
Corinthian War wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Persian Wars wikipedia , lookup
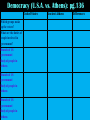
WarmUp #2 • Analyze the map on pg. 137 on the Persian Wars & answer the two respective questions. Democracy (U.S.A. vs. Athens): pg.136 United States Which groups make up the voters? What are the duties of people involved in government? Branch of US government/ Body of people in Athens Branch of US government/ Body of people in Athens Branch of US government/ Body of people in Athens Ancient Athens Differences Classical Greece Athens and the Age of Pericles • time between Persian & Peloponnesian Wars • founded Delian League to protect against invasion – Sparta refused to join – became Athenian Empire • Pericles: dominant force in Athenian politics • center of philosophy, architecture, learning, art, etc. • food came from trade – protected by navy • Golden Age! Greek Drama • Initial writings: drama • Later writings: comedy • masks used for emotion – Oedipus Rex trilogy (Sophocles): tales of a man who becomes king, but with disastrous results – Medea (Euripides): tales of a woman who swears revenge on her unfaithful husband & his new wife the Herodes Atticus Theatre in Athens! History • 1st group of people to try to analyze past events • Herodotus: 1st historian – wrote about Persian Wars – but lots of superstition & subjective bias • Thucydides: looked at human impact, not just divine reasons – found evidence for his historical assertions Art/Architecture • art attempted to express eternal ideals – balance, proportion, harmony • sculpture showed this with perfect human proportions • architecture: mainly temples – Parthenon built in Athens, • showed calmness, clarity & freedom from unnecessary details Greek Philosophy • philosophy: organized system of thought – “love of wisdom” • Socrates: education was key to the improvement of the individual • no writings – his ideas written by students (i.e. Plato, Aristole) • questioned students to help them analyze & learn (Socratic method) • “the unexamined life is not worth living” • got into trouble with Athenian government & was forced to commit suicide by drinking hemlock juice Plato • student of Socrates • fascinated by question of reality – ”how do we know what is real?” • believed that concepts/ideas were true reality • physical objects just “shadows” of reality (cave illustration) • the Republic: his text on government, where he believed that philosopherkings should rule society Aristotle • student of Plato • believed we only know true reality by observation & by study of things • used logic to classify/understand • interested in everything! – wrote thoughts on science, art, etc. • Western scholarship based on his teachings until 1600 AD • concerned more with the nature of the world Answers to Logic Q’s • Valid • Invalid • Argument is valid but the conclusion is not true, because the premises are incorrect Copy the following arguments. Using logic, identify whether the arguments are valid or invalid. • 1. All men are mortal. 2. Socrates is a man. Therefore, Socrates is mortal. 1. Some plants are poisonous. 2. Broccoli is a plant. Therefore, broccoli is poisonous. 1. All doctors are men. 2. My mother is a doctor. Therefore, my mother is a man. The “premise” or phrases within the argument must be true or else, the conclusion might not work, even if you use the correct deductive reasoning. Peloponnesian Wars Peloponnesian Wars 431-404 BC • after the Persian Wars, the 2 main powers in Greece: – Athens with Delian League – Sparta with Peloponnesian League • both wanted to be most powerful! – led to conflict in 431 BC • series of wars fought between: – Spartan army – Athenian navy • finally Spartans defeated Athenians – ironically with the help of the Persians • the infighting weakened ALL the Greek city-states: thus, it was very easy for Macedonia to take over! In-Class Assessment • 1. Which Greek philosopher believed that “the unexamined life is not worth living” & left behind no writings of his own? • 2. Which Greek philosopher believed concepts & ideas were the true reality & that people & humans were mere shadows of reality? • 3. Which Greek philosopher believed true reality could only be uncovered through logic & observation? • 4.What does it mean that Classical Greek art sculpted using idealistic proportions? • 5.What famous Athenian temple was built to the goddess Athena, which portrayed the Greek thought on clean & calm lines without too much unnecessary details? Peloponnesian Wars: Who Are You Supporting?!? (Pgs.140-141) • In pairs (with a partner): – Pick a side in the Peloponnesian Wars. – Create a propaganda poster advertising YOUR league! • 1. On one side: draw a large picture (or several small pictures) that showcases your league’s strengths & add a creative slogan! • 2. On the opposite side: draw a large picture (or several small pictures) that showcases your opponent’s weaknesses & add a creative slogan!