* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 5 Sec. 4 - J Go World History
Spartan army wikipedia , lookup
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Persian Wars wikipedia , lookup
Liturgy (ancient Greece) wikipedia , lookup
Corinthian War wikipedia , lookup
First Persian invasion of Greece wikipedia , lookup
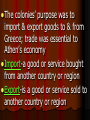
Ch. 5 Sec. 4 Daily Life in Athens The Athenian Economy Most Athenians were farmers who grew olives, grapes, & figs on terraces (terracingcarving small, flat plots of land from hillsides) There was a push for Athenian farmers & workers to set up overseas colonies The colonies’ purpose was to import & export goods to & from Greece; trade was essential to Athen’s economy Import-a good or service bought from another country or region Export-is a good or service sold to another country or region Home & Family Life Athenian famlies lived in simple homes, yet they built magnificent temples & other public buildings Marriage & family life was important to Athenians with parents arranging marriages for girls ages 13 or 14 Main purpose of marriage was to have children If the family could not afford to raise the child, the child was left to die (especially if it was a girl) Sappho was a female Greek poet who wrote “Sleep, Darling” an ode to her daughter Legally & socially women were considered inferior to men; they were citizens, but couldn’t own or inherit property; duties included managing the household, slaves, & raising children Mother took care of children until the age of 6; at age 7, boy came under the care of a pedagogue-a male slave who taught the boy manners Daughters stayed home & learn to run a household (wealthy girls learn to read & write) Education & Military Service Wealthy men took part in politics, gossip in marketplace, athletic activities, but most Greeks were poor & hardworking Athenians placed high value on literacy & education teaching boys reading, writing, grammar, poetry, music, & gymnastics In the 400s B.C., men called Sophists opened schools for older boys where they studied gov’t, mathematics, ethics, & rhetoric Ethics deals w/ what is good & bad, & moral duty Rhetoric was the study of oratory, or public speaking, & debating At age 18, males had a year of military training Wealthy men who could afford armor & weapons became hoplites & served in army for a year; formed the center of the infantry Poorer men served in the army’s flanks Education help spread the Greek language & civilization throughout the Mediterranean world