* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ancient Greece
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
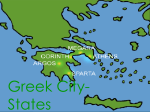
Ancient Greece What do you know about anicent Greece? • Take a quiz: • http://www.mysteryproductions.info/hyper/Hypermedia_2003/ Miller/AM_hypermedia/Artifact/ Greece was famous for: Early Olympics • The Olympic Games began over 2,700 years ago in Olympia, in southwest Greece. • The Games were part of a religious festival. The Greek Olympics, thought to have begun in 776 BC, inspired the modern Olympic Games (begun in 1896). • • The Games were held in honour of Zeus, king of the gods, and were staged every four years at Olympia, a valley near a city called Elis. • People from all over the Greek world came to watch and take part. • At the first one-day Olympic Games, the only event was a short sprint from one end of the stadium to the other. • Gradually more events were added to make four days of competitions. They included wrestling, boxing, long jump, throwing the javelin and discus, and chariot racing. • In the pentathlon, there were five events: running, wrestling, javelin, discus and long jump. • One of the toughest events was the race for hoplites, men wearing armour and carrying shields. • Winners were given a wreath of leaves, and a hero's welcome back home. • Winners might marry rich women, enjoy free meals, invitations to parties, and the best seats in the theatre. • The running track was much wider than a modern one. Twenty people could run at once. Greek Architecture Map of Ancient Greece • Ancient Greece was a collection of Greek city-states. • Because Greece was not yet one country, there was no central government in ancient Greece. • Around 500 BC, villages started to band together to form strong trading centers. • These groups of villages that banded together were called city-states. • Soon, hundreds of city-states had formed in ancient Greece. • TO BE A CITIZEN OF A CITY-STATE: The ancient Greeks referred to themselves as citizens of their individual city-states. • Each city-state (polis) had its own personality, goals, laws and customs. • Ancient Greeks were very loyal to their city-state. • The city-states had many things in common. • They all believed in the same gods. • They all spoke the same language. • Each city-state had its own form of government. • Some city-states, like Corinth, were ruled by kings. • Some, like Sparta, were ruled by a small group of men. • Others, like Athens, experimented with new forms of government. Sometimes these citystates cooperated, sometimes they fought each other. Forms of government • Monarchy: Rule by a king. One city-state whose government was a monarchy was the city-state of Corinth. • Oligarchy: Rule by a small group. One city-state whose government was an oligarchy was the city-state of Sparta. • Democracy: Rule by the citizens, voting in an assembly. One citystate whose government experimented for about a hundred years with democracy was the ancient city-state of Athens. • • What kind of government would you create? Your Project: Create a country • • • • • • • • • Give it a name. Choose a capital. Decide on a form of government. Decide how laws are made. Form a currency. Decide how laws are enforced. Make a flag. Create a map of your country. Make a presentation to share with your class. Lava Land Lava Land’s Currency is • All credit cards. Lava Land’s Flag is blue with gold stars. Lava Land’s government is • A democracy. All leaders are chosen by a majority of the people in a free election. Lava Land’s laws are enforced by • The leaders themselves. They hire local enforcers to keep the peace and deal with those who break the law. • Laws are made by the ruler but the people vote on whether or not they want the law. Elections are held once a year. Majority vote wins.