* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MIS 431
Tandem Computers wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Relational algebra wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Team Foundation Server wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
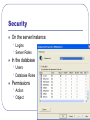
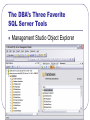
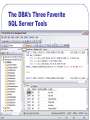
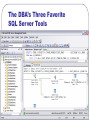
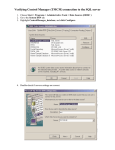
MIS 424 Guest Lecture Welcome MIS 424 Dr. Steve Ross April 30, 2007 Overview of SQL Server Material for this lecture is drawn from SQL Server 2005 Database Essentials, SQL Queries for Mere Mortals, and the professor’s experience. Star Wars sounds from http://www.galaxyfaraway.com/Multimedia/sounds.shtml Presentation Outline Overview of Relational Database Management Introduction to SQL Server Application Architecture Overview of Relational Database Management How do databases “think”? What is a Relational Database Management System? Software Three major parts • Manages storage and retrieval of data • Stored in two-dimensional tables • Data definition language (DDL) • Creation of the database structure • Data manipulation language (DML) • CRUD • Data control language (DCL) • Controls access to the data CRUD? Create new records Read the data in existing records Update the data in existing records Delete records A “complete” business application must accomplish the full range of CRUD on all fields of all tables. CRUD – SQL Commands Create Read Update Delete = INSERT = SELECT = UPDATE = DELETE Sets Tables are treated as sets • A command deals with the entire set or a • • portion thereof determined by a filter No inherent order unless indexed Record-by-record processing requires special methods The result of a SELECT command is another set Relating Data – Joins Field(s) in one table compared to field(s) in another • Inner join … records with matching values • Left/Right outer join … all records of one • • paired with records of the other with matching values Full outer join … all records of both Joins are normally based on equal values, but may be based on any relation between the values of the fields (e.g., <, >, between …) Sample Query SELECT S.TERM,S.SUBJECT,S.COURSE_NUMBER,FIRST_NAME + ' ' + LAST_NAME AS S_NAME FROM dbo.S_SCHEDULE S INNER JOIN dbo.S_HIST_DETAIL HD ON S.TERM=HD.TERM AND S.CRN=HD.CRN INNER JOIN dbo.G_PERSON P ON HD.PIDM=P.PIDM INNER JOIN dbo.S_REG_DETAIL RD ON RD.PIDM=P.PIDM WHERE S.PRIMARY_INSTRUCTOR_PIDM=5120 AND RD.TERM='200720' AND RD.CRN='21070' UNION SELECT S.TERM,S.SUBJECT,S.COURSE_NUMBER,FIRST_NAME + ' ' + LAST_NAME AS S_NAME FROM dbo.S_SCHEDULE S INNER JOIN dbo.S_REG_DETAIL RD0 ON S.TERM=RD0.TERM AND S.CRN=RD0.CRN INNER JOIN dbo.G_PERSON P ON RD0.PIDM=P.PIDM INNER JOIN dbo.S_REG_DETAIL RD ON RD.PIDM=P.PIDM WHERE S.PRIMARY_INSTRUCTOR_PIDM=5120 AND RD.TERM='200720' AND RD.CRN='21070' ORDER BY S.SUBJECT,S.COURSE_NUMBER,S.TERM Result TERM -----200540 200640 200710 200710 200720 200720 SUBJECT ------MIS MIS MIS MIS MIS MIS COURSE_NUMBER ------------320 421 421 421 421 431 (6 row(s) affected) S_NAME --------------------Hyun Park Hyun Park Alexander Nichols Daniel Stead Adam Opitz Alexander Nichols Introduction to SQL Server Is it any different from Access? SQL Server Microsoft Product • Originally developed by Sybase and purchased by Microsoft “Recent” version: SQL Server 2000 “Current” version: SQL Server 2005 • A.k.a. Yukon • Integrated with Whidbey – next version of Visual Studio What about Microsoft Access? Both are DBMS Both allow a lot of records SQL-Server Access • More power in DDL, DML, DCL • Handles more data and more concurrent users • Less expensive • More readily available • Includes user interface tools (forms and reports) Hierarchy of Objects The Server: RELIANT.CBE.WWU.EDU • The Instance: MIS424S05 or (port #) 2767 • The Database: KKPMusicStore Database Objects • Specific Object: tblCustomers Security On the server/instance • • Logins Server Roles In the database • • Users Database Roles Permissions • • Action Object The DBA’s Three Favorite SQL Server Tools Management Studio Object Explorer The DBA’s Three Favorite SQL Server Tools Management Studio Object Explorer • Graphical interface that allows • Creation of database objects (DDL) • • • • Tables Views Stored procedures User-defined functions • • • Logins Server roles Database roles • Specification of rights (DCL) • Allows direct editing of database data • Usually a bad idea! The DBA’s Three Favorite SQL Server Tools The DBA’s Three Favorite SQL Server Tools The DBA’s Three Favorite SQL Server Tools Management Studio Query • Object browser • Command line interface • Create and test statements • Execute statements – DDL, DML, DCL • Execution plan The DBA’s Three Favorite SQL Server Tools The DBA’s Three Favorite SQL Server Tools Books Online • Help facility • Help that’s actually helpful! Application Architecture How do we get the information to and from the user? N-Tier Architecture* * Graphic from P.J. Pratt and J.J. Adamski, Concepts of Database Management, 4th Ed. Primary Concern of the DBA: Maintaining Data Integrity Protect existence Maintain quality Ensure confidentiality • Data are available when needed • Data are accurate, complete, and current • Data are accessed only by those authorized to do so How much access does the database administrator grant the programming staff? DBA Programmer Maintaining Integrity in Tables Field data type, size Check constraints Entity integrity (primary key) Referential integrity (foreign key) Triggers • Procedures that execute on insert, update, or delete actions on the table Using Views to Maintain Integrity (In Access, views are called queries) Specify only certain fields • Output fields can be renamed to “hide” internal structure Filter the records • Conditions can be based on characteristics of the user, e.g., his/her ID, department, status Stored Procedures Similar to sub-routines in other languages Provide all aspects of CRUD, most DDL, DCL • Very good way to return result sets Transact-SQL (T-SQL) programming language Procedural structure • • • Sequence Iteration Condition Stored Procedures Input and output parameters provide a consistent interface between programmer and database administrator • cont’d Facilitates data structure changes Allow a great deal of internal error-checking and validation Stored Procedure Example I CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.uspInsertNewPOS ( @WWUID nchar(10), @CurrID int, @StartQtr int, @Quarter int, @CourseAbbr nchar (4), @CourseNumb nchar(4), @OtherCrs nvarchar(20), @ElectSet smallint, @ElectCrs smallint, @CourseCategory nchar(2) ) AS SET NOCOUNT ON INSERT INTO tblStuPOS (WWUID,CurrID,StartQtr,ElectSet,ElectCrs,CourseAbbr,CourseNumb,Quarter, OtherCrs,CourseCategory) VALUES ( @WWUID, @CurrID, @StartQtr, @ElectSet, @ElectCrs, @CourseAbbr, @CourseNumb, @Quarter, @OtherCrs, @CourseCategory ) SET NOCOUNT OFF GO Stored Procedure Example II CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.uspFoundationCourses ( @CurrID int, @WWUID nchar(10) ) AS SET NOCOUNT ON SELECT * INTO #tblSelectedStuPOS FROM tblStuPOS WHERE WWUID=@WWUID SELECT C.CourseAbbr, C.CourseNumb, C.CurrID, C.DeptAbbr, C.DegreeName, C.Concentration,C.Requirement, isnull(P.Quarter,999999) as Quarter FROM dbo.vueCurrCourses C LEFT OUTER JOIN #tblSelectedStuPOS P ON C.CourseAbbr=P.CourseAbbr AND C.CourseNumb = P.CourseNumb WHERE (C.Requirement='FD') and C.CurrID=@CurrID ORDER BY C.CourseAbbr, C.CourseNumb SET NOCOUNT OFF GO Stored Procedure Example III CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.uspDeleteOldPOS ( @WWUID nchar(10) ) AS SET NOCOUNT ON DELETE FROM tblStuPOS WHERE WWUID=@WWUID SET NOCOUNT OFF GO User-Defined Functions Similar to functions in other languages T-SQL programming language Procedural structure • Parameters for input • Single result returned • Sequence • Iteration • Condition User-Defined Function Example I CREATE FUNCTION dbo.fnPassedCourse ( @dgrade float, @grade nvarchar(3) ) RETURNS bit AS BEGIN DECLARE @output bit IF @dgrade > 1.5 or upper(@grade) = 'S' SET @output = 1 ELSE SET @output = 0 RETURN @output END User-Defined Function Example II CREATE FUNCTION dbo.fnLatestDepartment ( @Person2Edit CHAR(9) ) RETURNS nvarchar(4) AS BEGIN DECLARE @output nvarchar (4) SELECT @output = DeptAbbr FROM dbo.tblAppointment WHERE PersonID=@Person2Edit AND TermCode = (SELECT MAX(TermCode) FROM dbo.tblAppointment WHERE PersonID = @Person2Edit) RETURN @output END Triggers Attached to a table “Fires” on insert, update, or delete Able to access • Old (deleted or updated) values • New (inserted or updated) values Trigger can reference and change other tables Trigger Examples CREATE TRIGGER ut_CreateSale ON [dbo].[tblSaleItem] FOR INSERT, UPDATE AS UPDATE vueProductInventory SET QuantityOnHand = QuantityOnHand - (SELECT QuantitySold FROM INSERTED) WHERE ProductCode = (SELECT ProductCode FROM INSERTED) CREATE TRIGGER ut_DeleteSale ON [dbo].[tblSaleItem] FOR UPDATE, DELETE AS UPDATE vueProductInventory SET QuantityOnHand = QuantityOnHand + (SELECT QuantitySold FROM DELETED) WHERE ProductCode = (SELECT ProductCode FROM DELETED) What are your questions? Thank You for your attention and interest