* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Client-server database systems and ODBC
Serializability wikipedia , lookup
Tandem Computers wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Team Foundation Server wikipedia , lookup
Database model wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
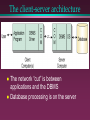
Client-server database systems and ODBC Client-server architecture and components More on reliability and security ODBC standard Database processing functions The client-server architecture The network “cut” is between applications and the DBMS Database processing is on the server DBMS Driver Receive processing requests from applications Format requests and deliver to DBMS Receive responses from DBMS Format responses for application Communication layer on client and server to exchange messages between DBMS and driver Roles of client and server Client » Manage the user interface » Enforce business rules » Process application logic » Generate database requests (SQL) » Transmit database requests to server » Receive results from server » Format results Server » Accept database request from clients » Process database requests » Format results and transmit to client » Enforce business rules » Perform integrity checking » Maintain database overhead data » Provide concurrent access control » Provide recovery and security services Advantages & disadvantages Pro » Applications use client CPUs in parallel – More powerful applications » Network traffic is reduced Con » Concurrency control » Multiple client OS’s Multithreading Client requests Native library calls (API) » DBMS-specific Embedded SQL » Static SQL – SQL structure fixed at compile time – Faster » Dynamic SQL – SQL structure determined at run time – More flexible Business rules: client-enforcement Business rules: server-enforcement Enforcement of business rules Client » Triggers » Duplication » What about using DML directly? Server » All in one place » What if DBMS cannot enforce business rules? Concurrency control Pessimistic locking » Assume things will go wrong » Prevent problems all the time Optimistic locking » Assume things will go well » If problem, do it over Pessimistic locking: same page, different records Optimistic locking: same page, different records What if same record? Concurrency control, take 2 Pessimistic versus optimistic locking, which is better? » Depends on application... » What is the common case? – If conflict is frequent, use pessimistic! – If conflict is rare, use optimistic! ODBC Open DataBase Connectivity Industry-standard interface between client applications and server DBMS products The idea is to write DBMS-independent applications, as long as they conform to the ODBC standard To conform or not to conform? ODBC architecture ODBC components On the server: » Data source(s) - database, DBMS, OS, network platform On the client: » DBMS drivers - one per data source – Receive ODBC request – Process if not standard SQL – Submit to specific data source » Driver manager - one per client – Receive ODBC request from application – Load appropriate driver and forward request ODBC drivers Single-tier: process both ODBC calls and SQL statements Multiple-tier: process ODBC calls and pass SQL statements to data source ODBC conformance levels 3 levels of driver API conformance » Core (connect, commit/rollback, error...) » Level 1 (partial results, catalog, driver gestalt...) » Level 2 (browse, scrollable cursors...) 3 levels of SQL conformance » Minimum (simple select, create, drop, insert, update, delete, simple expressions...) » Core (indices, views, grant, revoke, subqueries, aggregate functions...) » Extended (outer joins, cursors, scalar functions, procedures...)