* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
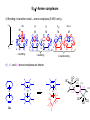
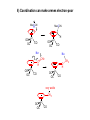
Lecture 33 1) h3-Allyl complexes • • h3-Allyl ligand C3H5- is anionic, donates 4 electrons from its p-system to form one s- and one p-bond with the metal and forms complexes with many transition metals such as Ni(h3-C3H5)2. Allyl is capable of p-backbonding but it is not so important as in the case of olefins or CO. z LUMO M • • M In symmetrical h3-allyl complexes the M-C1 and M-C3 distances are identical and slightly longer than M-C2. In addition, Hmeso and Hsyn are bent 7-130 towards the metal while Hanti are bent 300 away. h3-allyl can easily convert into h1-allyl: M h -allyl 3 12.6 eV M x M HOMO y 0.3 eV H C1 Hanti H C3 Hsyn C2 -4.7 eV Hmeso dyz pz dxz M M s-bonding p-bonding M M h -allyl 1 p-backbonding 2) Coordination can make olefins and allyl electron-poor • Alkenes typically considered in organic chemistry as electron-rich compounds can become electrophilic if coordinated to an electron-poor metal: R R R3N R3N Pd Cl • NR3 Cl R NHR2 R3N Pd NR3 Cl NHR2 Pd NR3 Even anionic allyl can behave as an electrophile if it is attached to PdII: R3P R3P Pd R3P R3P -Pd0 Pd0 CHX2 CHX2 3) p-MO’s of cyclic conjugated ligands For qualitative analysis of bonding between transition metals and p-electron donors such as organic compounds with C=C bonds it is necessary to know how the ligand p-MO’s look like. Frost diagrams allow establish the shape, degeneracy and the energy sequence of the ligand pMO’s for the case of cyclic conjugated species. The diagrams below describe qualitatively the p-MO’s in the n-membered cyclic systems. The number of the nodal surfaces (shown with dashed lines) of the MO’s increases as you move up along the diagram. • • • E Energy levels of resulting p-MO's are indicated with d c energy level of isolated p-orbitals c b n=3 a n=4 b c n=5 a n=6 n=7 Scheme of the p-MO's for benzene molecule: Scheme of the p-MO's for cyclopentadienyl a b a b c d 4) h5-Cyclopentadienyl complexes • p-MOs’ of cyclopentadienyl anion: • And bonding in h5-Cp complexes: z dz2 y M px M py dx2-y2 dxy M M M x s-bonding p-bonding -backbonding 5) h6-Arene complexes h6-Bonding in transition metal – arene complexes (5 MO’s only): z dz2 M px py dxy dx2-y2 M M M M y x b a s-bonding c b c p-bonding -backbonding h6-, h4- and h2-arene complexes are known: CO OC Fe 2 e- Cr Ru0 2+ Ru 1.43 1.41 1.50 D6h 1.31 1.42 CO 1.31 1.45 1.43 1.42 1.38 Fe OC CO CO 6) Coordination can make arenes electron-poor Me2CCN OC OC Me2CCN H Cr OC OC CO Cr CO NuC H OC OC Nu CH2 C H Cr OC OC CO Cr very acidic CH3 OC OC Cr CO CO CH2