* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download I. Reproductive Systems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
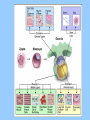
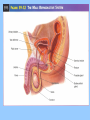
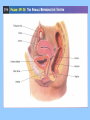
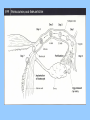
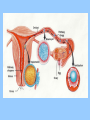
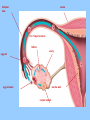
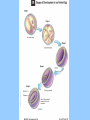
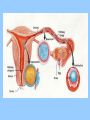
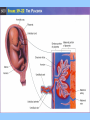
BIOLOGY NOTES GENETICS PART 3 PAGES 151-155, 786-805 Standard: ____ 4.16 Describe the basic anatomy and physiology of the human reproductive system. Describe the process of human development from fertilization to birth and major changes that occur in each trimester of pregnancy. Essential Questions: 1. How does the fetus develop from fertilization to birth? I. Reproductive Systems In order for a species to continue, reproduction of new individuals must occur. Each individual cell and continues to grow begins as a single ____ mitosis until enough through the process of _______ cells have been created to sustain life in the outside world. • Reproductive System = a collection of organs glands and _______ tissues that specialized _______, individual being help to produce a new _________ • In humans, reproductive organs are not fully puberty functional until ________ growth and puberty = a period of rapid _______ sexual maturation during which the reproductive functional system becomes fully __________ A. The Male Reproductive System • The main function of the male reproductive sperm system is to produce and deliver _______ The testes are the male reproductive organ sperm responsible for the production of _______ scrotum outside of the and stored in the ________ body FSH and ____ LH stimulate the hormones _____ sperm the testes to produce ______ The testes are outside of body because it is 3° cooler which sperm require for about ___ formation proper __________ tubules inside the testes Seminiferous ________ actually make the sperm For sperm to exit the organism, it must move vas into the ___________, epididymis through the ____ penis deferens and out of the ______ There are approximately _____ 2.5 million sperm per drop in semen B. The Female Reproductive System • The main function of the female reproductive ova (egg) AND provide a system is to produce ____ embryo nourishing environment for an ________ sperm • Unlike males who produce _______ continuously throughout their lifetime, females only produce one mature ____ ova or egg each month (about every ___ 28 days) _______ Eggs are stored in the ______ ovary or the female reproductive organ • Each egg has clusters of ________ follicles attached to mature before it which help the egg become _______ leaving the ______ ovary • ovulation = the release of a mature egg from the ______ ovary • For eggs to exit the ovary, it must move into the uterus cavity _________ fallopian tube and into the______ • if the egg is _________ fertilized then it will implant in uterus and an embryo will form the _______ • if the egg is NOT ________ fertilized then it will exit the uterus through the ______ cervix and out of the _______ vagina fallopian tube uterus 5 to 7 days to uterus follicle ovary egg cell egg released uterine wall corpus luteum Remember, the function of the female reproductive system is NOT just to make eggs environment but to also provide a nourishing ____________ uterus which comes from the _______ every time an egg is released, the uterus embryo prepares for an implanted ________ if the egg is not fertilized, then the lining of the uterus will ______ shed and exit with the cervix and out unfertilized egg through the _______ of the vagina • Menstruation = the phase of the menstrual ______ cycle in which unfertilized _____ eggs and the uterus actually _____ lining of the ________ exits the female body C. Stages of Pregnancy fertilized by sperm in • Eggs usually become _________ fallopian tubes the _________ egg • Zygote = a fertilized _____ • as soon as the zygote is formed, it undergoes _________ mitosis which increases the number of cells 4 days after the formation of the zygote, • about __ the embryo is approximately ___ 64 cells large and morula called a ________ blastocyst is what implants or embeds • the ___________ uterus itself in the wall of the _______ • from here the embryo will continue to grow in differentiate or size and the cells will ____________ _____ become specialized until the fetus is born (this 9 months in humans) takes approximately __ 1. FIRST TRIMESTER (WEEKS 1-13) neurulation = the beginning development of the _________ nervous system the placenta forms placenta = the connection between a mother and a developing ________ embryo through _______ wastes are passed which nutrients and _______ diffusion (through the process of _________!!!!) eye formation, jaws, arms, legs, fingers, hands, toes become __________ noticeable fetus = name of embryo at week __ 8 of pregnancy forms from placenta to umbilical cord ______ mother ________ 11 the baby has all the major by week ___, organ systems partially developed ______ fetal heartbeat develops 2. SECOND TRIMESTER (WEEKS 14-27) skeleton bone formation begins and early _________ develops fetus hair covers the ______ movement that can be felt the fetus begins ___________ mother by the ________ developed and there is hearing is well __________ eye movement evident rapid ____ 3. THIRD TRIMESTER (WEEKS 28-40) mature and the fetus organ systems _______ doubles in mass ________ temperature is now regulation of body ___________ possible the central nervous system and lungs complete their development the fetus moves into head down into the ______ pelvis and awaits birth II. Cell Differentiation = the process by which forms unspecialized cells develop into mature ______ functions and __________ • The function of a cell will be determined by its location within an embryo ________ once a cell’s function is determined, the cell DNA needed to will only use parts of the _____ help with that particular function • Stem cells = a cell that can divide for long periods of time while remaining _______________ undifferentiated stem cells are classified according to which type of cell they can become: _____ a. totipotent stem cell = a type of stem cell any type of cell which can become ____ e.g. fertilized egg b. pluripotent stem cell = a type of stem cell which can become ____ any type of cell EXCEPT a totipotent stem cell e.g. embryonic stem cell c. multipotent stem cell = a type of stem cell closely related cells that can only grow into _______ e.g. adult stem cell First, an egg is fertilized by a sperm cell in a petri dish. The egg divides, forming an inner cell mass. These cells are then removed and grown with nutrients. Scientists try to control how the cells specialize by adding or removing certain molecules.