* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell Cycle - Solon City Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
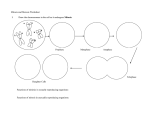
The Cell Cycle Why are cells so small?? • What limits the size of a cell?? – Most cells are between .002 - .2 millimeters What limits the size of a cell? • Diffusion – Very fast and efficient over short distances – Becomes slow and inefficient as the distances become larger – Cells would die before nutrients could reach the organelles if the cell was too big What limits the size of a cell?? • Surface Area – to – Volume Ratio – As cell size increases, its volume increases much faster than surface area – Example: If cell size doubles, the cell would require 8 times more nutrients, but the cell membrane would only increase by 4 times. This would mean that the cell doesn’t have enough room (cell membrane) to diffuse. What limits the size of a cell?? • DNA – There’s a limit to how fast DNA can make proteins – If you have a large cell than the DNA can’t make proteins fast enough for the cell. The Cell Cycle • Cell Reproduction – One cell (parent cell) reproduces to make 2 identical cells (daughter cells) – 5 steps in this process What is Mitosis • Mitosis is…THE PROCESS BY WHICH A CELL’S NUCLEUS DIVIDES! Mitosis • Interphase – This phase is broken down into 3 subphases – G1 = Cell grows in size – S = DNA duplicates itself – Chromatin duplicates – long coily strands of DNA that become wrapped up – G2 = Rapid Growth before dividing – Cells spend most of their time in this phase Interphase Interphase Interphase Interphase Mitosis • Prophase – A.) Chromatin organizes itself into chromosomes made up of 2 sister chromatids attached by a centromere • Sister Chromatids – A chromosome and its duplicated twin • Centromere – rubber band structure that joins the 2 sister chromatids together Prophase – B.) Nuclear membrane breaks down – Nucleus dissolves – C.) Centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell (poles) – Centrioles – cylinder structures that will reel in the chromatids – D.) Spindle fibers form – Spindle fibers – football shaped set of ropes that will attach to the centrioles and the chromatids Prophase Prophase Prophase Prophase Prophase Prophase Prophase Mitosis • Metaphase – Spindle fibers attach to centrioles and sister chromatids at their centromeres. – Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell Metaphase Metaphase Metaphase Metaphase Metaphase Metaphase Metaphase Metaphase Metaphase Metaphase Mitosis • Anaphase – The centromeres split apart and the sister chromatids separate from each other – The spindle fibers pull the chromatids toward the poles Anaphase Anaphase Anaphase Anaphase Anaphase Anaphase Anaphase Anaphase Anaphase Anaphase Anaphase Mitosis • Telophase – Chromatids reach the poles – Chromosomes unwind – Spindle fibers break down – Nucleus reforms – Cell begins to split • Cleavage furrow Telophase Telophase Telophase Telophase Telophase Telophase Telophase Telophase Telophase Telophase Mitosis • Cytokinesis – Cells Separate Cytokinesis The Cell Cycle