* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Growth & Division - Whitman
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
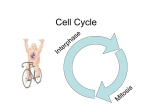
Eukaryotic Cell Division •Stage 1: Mitosis • Stage 2: Cytokinesis Interphase-(the long period) • G1 Phase: Cell grows, makes new proteins and organelles • G0 Phase: Cells “hang out” and perform usual functions • S Phase: DNA is replicated • G2 Phase: Organelles required for division are synthesized •The shortest part of the cell cycle •Lasts from a few minutes to several days •Consists of 4 Phases: -Prophase -Metaphase -Anaphase -Telophase • Nuclear envelope dissolves • Nucleolus disappears • Chromosomes become visible • Centrioles move to poles • Spindle fibers form • Chromosomes line up at the equator (center) • Spindles connect to the centromere of each chromosome • Centrioles split chromosomes into sister chromatids • Phase ends once chromatids reach the poles • Chromosomes uncoil • A nuclear envelope surrounds DNA • Nucleolus re-forms • Spindle fibers break down • Cell division is not complete! •Divides cytoplasm In plants, a cell plate Forms new forms cell wall! between the 2 new cells Meiosis During sexual reproduction, gametes (sperm or eggs) are produced by each parent Gametes contain half the number of chromosomes found in most cells When gametes unite, the zygote then has the normal number of chromosomes Dad’s Mom’s chromosomes chromosomes Dad’s Mom’s gametes gametes zygote Diploid vs. Haploid DIPLOID: Contains BOTH sets of chromosomes (1 from each parent) HAPLOID: Contains 1 set of chromosomes to combine during sexual reproduction with another to form a DIPLOID cell.