* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Circumstellar habitable zone wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Exoplanetology wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Directed panspermia wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
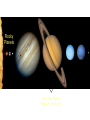
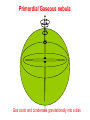
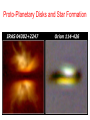
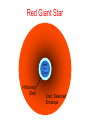
The Formation of the Solar System Planetary motions • The Sun, planets, asteroids, comets, planetesimals all revolve in the same direction with some exceptions. • Rotation axes usually perpendicular to orbital plane Pluto Planet-Planetesimal composition • Terrestrial Planets: • Cores Small & rocky (refractory elements, silicates & iron) • Atmospheres: Thin, no H/He, some ices or volatiles (C, N, O, Ne) •Jovian Planets: • Cores large rocks/metals/ices • Atmospheres H or H-compounds (e.g. CH4) • KBOs: planetesimals and icy bodies: •Small ice & rock mixtures with frozen volatiles. Icy Pluto Rocky Planets Giant Gas Planets Mostly H, He, & Ices Primordial Gaseous nebula Gas cools and condenses gravitationally into a disk Proto-Planetary Disks and Star Formation Primordial Solar Nebula • Rotating solar nebula is composed of • ~74% Hydrogen & 25% Helium • Traces of metals and dust grains • Initially T~2000 K, gas cools to ice and dust according to condensation temperature Condensation Temperatures T(K) Elements Compounds (oxides,silicates) >2000K gases Ions: atoms, molecules 1400K Iron & Nickel 1300K Silicon, Sulfur Metal Grains (e.g. Fe2O3) Silicate grains 300K Carbon Carbonaceous grains 100-300K H, C, N, O Ices (H2O,CO2,NH3,CH4) Snow Line: Separation of Rocks/Metals from Gases/Ices • Rock & Metals form where T < 1300 K • Carbon grains & ices where T(gas) < 300 K • Inner planets and asteroids: Rocky and metallic • Snow line • Outer Jovian systems: Gaseous giants, carbon ices • Dust grains and ices collide, accrete, and eventually grow bigger gravitationally into planetesimals beyond the snow line Life of the Sun • Burns or converts H He via theromonuclear fusion in core • When hydrogen in the core is exhausted, converted into helium, the H-burning shell moves outward and the star expands • H-burning phase for another 5 billion years; inert He-core • Stars in H-burning phase are said to be Main Sequence stars • Sun Red Giant • Eventually He in the core ignites helium flash • He-burning C/O (carbon, oxegen core) • Core separates from the envelope, which is ejected • Hot core and ejected envelope “Planetary Nebula” (star looks like a ring with bright center; nothing to do with planets) • Central core of planetary nebulae cools White Dwarf Red Giant Star Inert He Core H Burning Shell Cool, Extended Envelope Planetary Nebulae Sampler Death of the Sun • Hot core continues as a white dwarf, about 60% mass of the Sun and size of the Earth • Gigantic diamond in the sky! The Death of the Sun