* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Constellations
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
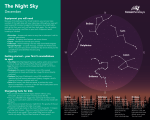
Constellations By: Anna Bracale Constellations A constellation is what astronomers call an asterism. An asterism is a group of celestial bodies (usually stars) that appear to form a visible pattern in the sky. Constellations were created by ancient people to be able to recognize stars in the sky. The shapes of constellations resemble objects familiar to people. Aries Aries also called "The Ram", is an ancient constellation which was very important since the sun passed through it at the vernal equinox. The vernal equinox is the point at which the Sun appears to cross the celestial equator from south to north. Aries' stars are rather faint except for alpha and beta, which are only second magnitude stars. Pegasus Pegasus, the winged horse, flew out of the head of Medusa when Perseus killed her. Pegasus went alone to Olympus, where he was used by Zeus to carry around his thunderbolts. Pegasus is a easy to notice constellation which includes the so-called "Great Square of Pegasus". The stars are generally second and third magnitude. Leo The first on the list of Heracles' jobs was the task of killing the Nemean Lion, a giant beast that roamed the hills and the streets of the Peloponnesian villages, devouring whomever it met. The animal's skin was immune to iron, bronze, and stone and Heracles' arrows bounced off the lion. So Heracles wrestled with the beast and choked it to death. As the story goes, the lion found its way to the heavens to stand for the great battle fought with Heracles. Leo is a very small constellation and, unlike so many other constellations, it is very easy to recognize. Lynx The name Lynx never stood for the animal. Hevelius, the inventor of the constellation, said that anyone who wanted to study the stars here should have eyes like a lynx. As with many other small constellations invented by Hevelius, Lynx is nothing more than a bumpy line. Cygnus Cygnus, The Swan, is one of the more obvious asterisms in the summer skies. Swans occur throughout the Greek myths. Often one of the higher gods had occasion to transform himself into a swan, usually to impress some attractive queen. Cygnus is a very bright constellation , with the stars being generally third and fourth magnitude. Chamaeleon Chamaeleon is one of a dozen constellations created by Johann Bayer in 1603 for his star atlas Uranometria. Like most of these, Chamaeleon is very far to the south. The asterism is supposed to represent a chameleon. Cetus Although Cetus is supposed to be a whale, the constellation was considered to be the monster about to devour Andromeda before Perseus could come to the rescue. Cetus' stars are very faint, but there are a few well known stars here. Such as UV Ceti, which is actually a pair of red dwarfs 9 light years away, and Mira. Bibliography Aries. N.p., n.d. Web. 27 Oct. 2009. <http://www.dibonsmith.com/ari_con.htm>. Cetus. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Oct. 2009. <http://www.dibonsmith.com/cet_con.htm>. Chamaelon. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Oct. 2009. <http://www.dibonsmith.com/cha_con.htm>. Cygnus. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Oct. 2009. <http://www.dibonsmith.com/cyg_con.htm>. Leo. N.p., n.d. Web. 27 Oct. 2009. <http://www.dibonsmith.com/leo_con.htm>. Lynx. N.p., n.d. Web. 27 Oct. 2009. <http://www.dibonsmith.com/lyn_con.htm>. Pegasus. N.p., n.d. Web. 27 Oct. 2009. <http://www.dibonsmith.com/peg_con.htm>.