* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Life2
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Flatness problem wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic microwave background wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Big Bang nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
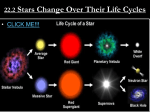
Nucleosythesis Life: DNA – proteins – amino acids - water Question - where did they come from in the first place ? Need to take a step back Waaaaaaay back……..to The Big Bang!!!! Big Bang Basics Universe emerged from a single spot out of nothing. Universe is currently thought to be 13.7 billion years old. Decoupling of matter from radiation at about 379,000 years to form protons and electrons Radiation seen today as microwave background radiation Most of early universe made of about ¾ hydrogen, ¼ helium and trace (.000,000,001) of lithium. No elements produced with an atomic number higher than lithium !!!!!! Heterogeneous universe from a homogenous one ? Quantum fluctuations in early universe produced “framework” of galaxy formation. Attracted gas and dark matter that coalesced to form first galaxies at only 500 million years. Formed in “cosmic web”. Large Scale Structure of Universe How did we get here from there? Nuclear Fusion - nucleosynthesis Stars form mutual gravitational attraction of original matter from Big Bang into clumps called protostars. Hysdrostatic equilibrium is established where outward radiation pressure balances gravity. A Star is born! Early stars had very little metallicity (i.e. no heavy elements). Stellar evolution - (main sequence) – Life cycle of a star depends on it’s size Small stars – last a long time – perhaps longer than the universe. Larger stars – burn through their fuel faster – most of the first stars were large stars that burned up quickly and then exploded. Creation of the “heavy” elements Star will fuse elements into different elements with higher atomic numbers until it reaches iron. Iron does not “burn” Mediums star (sun) will shed most of its accumulated matter into a planetary nebula. Larger suns will supernova – creates all elements heavier than iron by an intense burst of nuclear reactions that typically last mere seconds during the explosion of the supernova core. Scatters elements into cosmos into giant clouds. All elements heavier than Lithium are formed in the heart of stars. Planetary nebula Supernova You are Stardust Formation of Solar System Solar system began with collapse of a giant molecular cloud approx. 4.5 billion years ago. Disturbance by supernova ? Disturbed equilibrium of cloud. As it collapsed it gained angular momentum. Proto-planets began forming. 10 million Kelvin – fusion reaction started Cleared out inner solar system of volatiles – left the rocky worlds. Frost line at asteroid belt. Gas giants kept their volatiles. Accretion Disk Formation of Planet Earth 4.6 BY - Formation of the approximately homogeneous solid Earth by plantiesmal accretion 4.3 BY - Melting of the Earth due to radioactive and gravitational heating – most heavy elements sink to core. Outgassing of molecules such as water, methane, ammonia, hydrogen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide 4.0 BY - Bombardment of the Earth by planetesimals stops. 3.8 BY – the Earth’s crust solidifies – formation of the oldest rocks found on Earth. 3.5 BY Single cell life develops. Implication was that as soon as life COULD exist it did. Early Earth was a Rough Neighborhood