* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Team 6 Presentation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
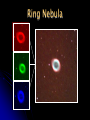
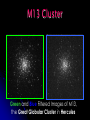
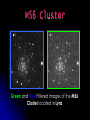
Team Leader: Dr. Sean Hendrick Team Assistant: Jackie Haynicz Teamsters: Swati Antala Salina Bakshi Jeff Barry Kevin Chen Benjamin Hsu Arpan Patel Payal Patel Jena Song Janelle Trinidad Brian Wexler Evolution of the Universe Through the observations of: Planetary Nebulae Globular Clusters Galaxies Ritchey-Chretien Telescope • used a charged coupled device (CCD) camera – Santa Barbara Instrument Group ST-1001E • used red, green, blue, and regular light filters Planetary Nebula Formation After a star has reached its red giant phase… Nebulium? •“nebulium” – named by Sir William Huggins •Forbidden line of doubly-ionized oxygen (OIII) correctly identified by American astrophysicist Ira S. Bowen Dumbbell Nebula Ring Nebula What is a Globular Cluster? Large gravitationally bound groups of stars 10 thousand to 1 million stars In halo around core Very old Why look at Globular Clusters? Stellar and galactic evolution Usually as old as the galaxies in which they are found Studying Milky Way Galaxy globular clusters can yield information about our own galaxy M13 Cluster Green and Blue Filtered Images of M13, the Great Globular Cluster in Hercules M56 Cluster Green and Blue Filtered Images of the M56 Cluster located in Lyra Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram •Two main types of stars •Main sequence •Red giants •Turn-off point dependent on age Our H-R Diagram M13 M56 Globular Cluster Results Our Observations, although valid in analysis, did not match in turn off points with the Main Sequence Diagram. There are a number of possible error sources which include: • Difference in peak wavelength values • The crowded center of M13 •The resolving power of Drew’s Telescope Galaxies M81 Normal Spiral Galaxy M87 Elliptical Galaxy M95 Barred Spiral Galaxy Edwin Hubble –first person to realize these celestial bodies are galaxies Mid eighteenth century3 galaxies detected 1780- Charles Messier recorded 32 galaxies Sir William Herschel, Caroline Herschel, Sir John Herschel discovered thousands more galaxies Galactic Classification Galaxy – massive group of interstellar matter and stars Normal spiral galaxycentral bulge, spiral arms Barred spiral galaxy- bar of stars, spiral arms from end of bar Elliptical galaxy- elliptical shape, older stars Irregular galaxy Galactic Evolution Central Quiescent Theory- large ball of gas fragmented into galaxies Collisional Starburst Scenariouniverse built from small structures, some of which merged to form galaxies Hubble Tuning Fork Galaxy Targets Normal Spiral - M101 Pinwheel, M51 Whirlpool, M81, M64 Elliptical - M86 Other – Stephan’s Quintet, contains three different types of galaxies Target Pictures Whirlpool Pinwheel Our Hubble Tuning Fork Black Eye Pinwheel Whirlpool Stephan’s Quintet The Evolving Universe…