* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RELATIVITY
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
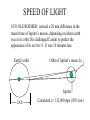
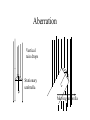
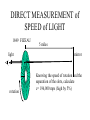
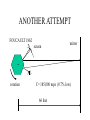
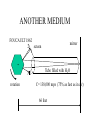
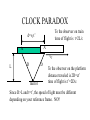
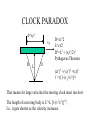
RELATIVITY IN EVERY INERITAL REFERENCE FRAME, THE SPEED OF LIGHT IS A CONSTANT BUT WHAT DOES THIS MEAN? SPEED OF LIGHT LIGHT TRAVELS QUICKLY, AND UNTIL 1676 WAS ASSUMED TO BE INSTANTANEOUS. SPEED OF LIGHT 1676 OLE ROEMER: noticed a 20 min difference in the transit time of Jupiter’s moons, depending on where earth was in its orbit. He challenged Cassini to predict the appearance of Io on Nov 9. It was 10 minutes late. Earth’s orbit Orbit of Jupiter’s moon, Io Jupiter 2AU Calculated c= 132,000 mps (30% low) SPEED OF LIGHT (2) 1728 BRADLEY: WAS MEASURING THE DISTANCE TO NEARBY STARS BY PARALAX. Motion of earth around sun distant stars Earth’s orbit nearby star Aberration Vertical rain drops Stationary umbrella Moving umbrella SPEED OF LIGHT (4) 1728 BRADLEY: WAS MEASURING THE DISTANCE TO NEARBY STARS BY PARALAX. Calculated c= 176,000 mps (only 5% too low) Angle of aberation distant stars Earth’s orbit nearby star DIRECT MEASUREMENT of SPEED of LIGHT 1849 FIZEAU light rotation 5 miles mirror Knowing the speed of rotation and the separation of the slots, calculate c= 196,000 mps (high by 5%) ANOTHER ATTEMPT FOUCAULT 1862 2 screen 1 mirror . rotation C= 185,000 mps (0.7% low) 66 feet ANOTHER MEDIUM FOUCAULT 1862 2 screen 1 mirror . Tube filled with H2O rotation C= 138,000 mps (75% as fast as in air) 66 feet SPEED OF LIGHT MICHELSON 1878 Repeated Foucault’s experiment with rotating mirror, but passed the beam back and forth between two mirrors for a total distance of 22 miles. C= 186,295 mps in air (0.007% too high) When Michelson evacuated the tube, and set up a beam length of 10 miles. c= 186,271 mps (0.006% too low) TODAY WE DO IT DIFFERENTLY We know frequency x wavelength = speed We can measure the frequency of a laser, and its wavelength and multiply to get speed of light. 1972 Nat’l Bureau of Stds c= 186,282.3959 mps in SI: 299,792.4562 km/sec; or close to 3 x 10 8 m/s; or 1 billion kph; or around the world 7.5 times per second One light-year is 1 x 10 13 km; or 6 trillion (1012)miles HOW FAST IS LIGHT? MACH 1: MACH 20: MACH 70: SPEED OF SOUND SPEED OF THE SPACE SHUTTLE SPEED OF THE ASTEROID THAT KILLED OFF THE DINOSAURS MACH 900,000: SPEED OF LIGHT SPECIAL RELATIVITY THE LAWS OF PHYSICS ARE THE SAME IN ALL INERTIAL REFERENCE FRAMES vT c The speed of light is c whether you are on the train or on the platform of the station CLOCK PARADOX To the observer on train time of flight is t=2L/c d=vTt’ A’ A vT L D D mirror To the observer on the platform distance traveled is 2D=ct’ time of flight is t’=2D/c Since D>L and t=t’, the speed of light must be different depending on your reference frame. NO!! CLOCK PARADOX d=vTt’ vT D L D=ct’/2 L=ct/2 D2=L2 + (vTt’/2)2 Pythagorus Theorem D (ct’)2 - (vTt’)2 =(ct)2 t’ = t[1-(vT2/c2)]1/2 That means for large velocities the moving clock must run slow The length of a moving body is L’=L [1-(v2/c2)]1/2, I.e., it gets shorter as the velocity increases. CLOCK PARADOX Clock paradox was predicted by theory and confirmed by experiment. An atomic clock was put aboard a satellite and it lost precisely the amount of time predicted. RELATIVISTIC ENERGY AND MOMENTUM P = mov [1-(v2/c2)]1/2 E = moc2 [1-(v2/c2)]1/2 Where v<<c p= mov E = moc2 + 1/2 mov2 E=moc2 is rest energy even when the object is not moving ASIMOV’S LAWS OF ROBOTICS • A ROBOT MAY NOT INJURE A HUMAN BEING, OR, THROUGH INACTION, ALLOW A HUMAN BEING TO COME TO HARM • A ROBOT MUST OBEY THE ORDERS GIVEN IT BY HUMANS EXCEPT WHERE SUCH ORDERS WOULD CONFLICT WITH THE FIRST LAW. •A ROBOT MUST PROTECT ITS OWN EXISTENCE AS LONG AS SUCH PROTECTION DOES NOT CONFLICT WITH THE FIRST OR SECOND LAW.