* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stars
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
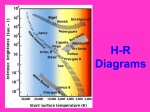
Stars • The apparent twinkling of the stars is a product of the turbulence and motion of the Earth’s atmosphere • Stars have different colors depending on how hot they are. The HOTTEST stars are BLUE, the COLDEST stars are RED. (Note- this is opposite to what we are used to associating with temperature.) • Color is used to determine ages – stages – in life cycle. Spectroscope • A tool that is used to separate light into the visible spectrum. Used to help determine elements in the stars. Absorption Spectroscopy Star Colors • • • • • • • Blue (HOT) 11-40,000C Blue-White White Yellow Orange Red (COLD) 7.5-11,000C 6-7,500C 5-6,000C 3.5-5,000C 3-3,500C (young) Beta Centauri Rigel (supergiant) Vega _____ Aldebaran (old) Betelgeuse Hadar (r) and Alpha Centauri (l) Vega – upper left Star Life Cycle • Nebula: a large cloud of gas and dust in space that is the beginning of a star (PLANETS are also formed this way) • Dwarf: a main sequence star or, the smallest of stars (up to 20 times larger than our sun and up to 20,000 times brighter. Our sun is a dwarf star.) • Red Giant: star is dying (red=cold) and energy is expanding outward • White Dwarf: a dying star that is extremely massive and may soon become a black hole • Supernova: an exploding star; usually occurring after a dying star becomes too dense to be supported • Binary star (double star): a stellar system consisting of two stars orbiting around their center of mass • Our Sun is unusual in that it is NOT part of a binary system Hubble image of the Sirius binary system, in which Sirius B can be clearly seen (lower left) Star forming region in the nebula NCG 604, in the nearby spiral galaxy M33, Diminutive by stellar standards, white dwarf stars are also intensely hot ...but they are cooling. No longer do their interior nuclear fires burn, so they will continue to cool (turn more red) until they fade away E0102-72 is a supernova remnant in the Small Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. This galaxy is 190,000 light years from Earth. E0102 -72, which is approximately a thousand years old, is believed to have resulted from the explosion of a massive star. Stretching across forty light years of space, the multi-million degree source resembles a flaming cosmic wheel. Star Vocabulary • Luminosity: the brightness of a star compared to the brightness of the Sun. In other words, the Sun’s luminosity is 1, Sirius is 23, Adhara is 5,000. Luminosity is measured in ergs per second. – The apparent brightness of the sun is 63 billion times brighter than Arcturus, although intrinsically the Sun is 100 times fainter. • Apparent Magnitude: stars closer to Earth appear brighter than those that are farther away • Absolute Magnitude: big stars are brighter than small stars. This is the ACTUAL brightness of the star – If all the stars were lined up equi-distant from Earth, we would be able to compare their actual brightness Magnitude • The SMALLER the magnitude, the BRIGHTER the star – For example, Vega with an apparent magnitude of +.02 seems about 2 ½ times brighter than Antares whose apparent magnitude is +.98 – Antares is actually almost 100 times as bright as Vega, since Antares has an absolute magnitude of -4.0 and Vega ‘s is +.5 Magnitude cont. • As a comparison, the Sun has an apparent magnitude of -27, but an absolute magnitude of +5. this is because the Sun is so close to Earth. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram • An American, Henry Russell and a Dutchman, Ejnar Hertzsprung noted a relationship between temperature (color) and luminosity (brightness) of the stars. • The significance of the discovery of the “main sequence” is that for any given temperature, there is a preferred radius. Therefore, luminosity is related to temperature. HertzsprungRussell Diagram Sun Page 714 In your book White dwarfs, Very hot, Very dense Cool, bright Hot, bright Hot, dim _______ Very big Very bright cool Our SUN • Age: approx 4.5 billion years old • Diameter: 1.4 X 106 km (medium sized star) • Temperature: 5,800 Kelvin (10,000°F) • Distance from Earth: 1.5 X 108 km (150,000,000) (closer than any other star) • Burns more than 24 billion tons of Hydrogen gas per minute. Sun Vocab • Sunspot: an area of the sun that gives off less light, due to a disturbance in the sun’s magnetic field Sun Vocab • Solar Flare: an area of the sun that erupts Sun Vocab • Corona: the area surrounding the Sun that can be seen during an eclipse • Core: center of the sun where the thermonuclear transmutation of H to He occurs • Photosphere: the visible surface of the Sun – several hundred miles thick (Visible surface) (part of the atmosphere)