* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 4d Models of the Solar System
Kepler (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Galileo affair wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
De revolutionibus orbium coelestium wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Patronage in astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Galilean moons wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Celestial spheres wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
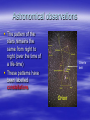
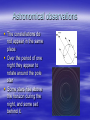
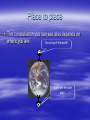
Do now! We will have Wednesday in the computer suite to finish the presentations and you will do the presentations on FRIDAY Development of models of the Solar system/universe You are here Astronomical observations The pattern of the stars remains the same from night to night (over the time of a life-time) These patterns have been labelled constellations Orion’s belt Astronomical observations The constellations do not appear in the same place Over the period of one night they appear to rotate around the pole star Some stars rise above the horizon during the night, and some set behind it. Astronomical Observations This same movement is continued during the day. The sun rises in the east and sets in the west. Maximum height at midday (in the south in the Northern hemisphere. Place to place The constellation you can see also depends on where you are I’m on top of the world! I can’t see the pole star! Constellation position The location of the pole star varies from night to night as we go through the year, so different constellations may be visible at different times of the year. View toward horizon from 59°54'N 11°E, azimuth 0° (N) Planets Some objects that we can see a night behave differently! Their position DOES change relative to the background of stars. These objects are called planets (derived from the Greek word for “wanderer”). Planets The planets can sometimes exhibit retrograde motion over the course of several nights. The moon The moon’s observed motion across the night sky is different again. It takes part in the nightly rotation around the pole star, but it also wanders. Phases The moon’s appearance changes over the course of a month. We say it has phases. The Moon's Phases Models of the Universe Aristotle (384-322 BC) Wisdom is the reward you get for a lifetime of listening when you'd rather have been talking. Aristotle’s Universe Earth at centre (geocentric) Other objects attached to concentric perfect crystal spheres turning at slightly different speeds All “fixed” stars were attached to the final sphere Aristotle’s Universe Ptolemy’s (AD 85 – 165) adaption of Aristotle’s ideas To explain the retrograde motion of some planets, he allowed each planet to move in a small circle (an epicycle) The centre of the epicycle moved on a bigger circle called a deferent. Earth is still at the centre (geocentric) Ptolemy’s adaption of Aristotle’s ideas The Universe of Aristotle and Ptolemy Heliocentric models Sun-centred (heliocentric) First proposed by Aristarchus (2nd century BC), but it has come to be associated with Copernicus (1473-1543) Orbits are still taken to be circular Explains retrograde motion of planets Heliocentric models The Copernican Model: A Sun-Centered Solar System This model also explains why Mercury and Venus always appear close to the sun in the sky To account for slight differences between the model and actual observations, Copernicus was forced to add epicycles too! Galileo "All truths are easy to understand once they are discovered; the point is to discover them." Galileo His observations with one of the first telescopes added further support to the Copernican view Galileo’s observations There are mountains on the moon Venus has phases (like the moon) and appears to change size Jupiter has objects orbiting it (moons) There are dark spots on the sun The sun rotates and the spots on the surface move Galileo in trouble In 1633 he was tried by the catholic Church and forced to recant his ideas. He remained under house arrest for the rest of his life Kepler At the same time as Galileo, Johannes Kepler (1571-1642) was adapting Copernicus’s model His new model gave very good agreement with observations Kepler’s model Each planet orbits the sun in an ellipse, with the sun at one focus Universal Gravitation If I have ever made any valuable discoveries, it has been owing more to patient attention, than to any other talent. Isaac Newton (1642 – 1727) Universal Gravitation Newton came up with a physical explanation for Kepler’s model Newton proposed that every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force that is proportional to the masses of the objects and inversely proportional to the distance between the objects squared Universal Gravitation This law applies everywhere in the universe It can explain why an apple falls to earth, but also why the moon stays in orbit around the earth That’s it!