* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Open Clusters
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Open cluster wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
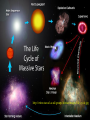
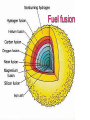
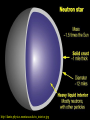
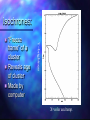
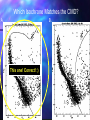
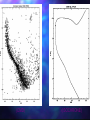
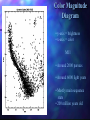
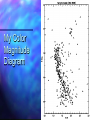
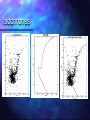
QuickTi me™ and a TIFF ( Uncompressed) decompr essor are needed to see thi s picture. Open Clusters Allan Harrell Edgar Toledo Tenaya Pusley Carmen De Martis What is a star? A giant ball of gas Hydrogen Emits light Different colors and sizes How do stars form? Form from clouds of dust and molecular hydrogen Gravity collapse Why doesn’t a star continue collapsing? Hydrostatic Equilibrium Gravity pushes in…. Pressure pushes out… Create an equilibrium What are open clusters? Young stars Same chemical composition Same Age Distance Bound by gravity Form in spiral and irregular galaxies QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. About Main Sequence Stars Stars spend most of their life in the main sequence, about 90% Our sun is 5 billion years into its main sequence The larger the star, the less time it will spend on the main sequence Main sequence stars maintain brightness and energy through fusion QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Fusion is important!! 1. Fusion creates energy 2. Energy raises temperature 3. Temperature 4. Faster makes atoms move faster moving atoms increase pressure 5. Pressure fights against gravity QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. http://www.star.ucl.ac.uk/groups/hotstar/images/life_cycle.jpg “What happens in a high mass star?” - Shorter lifetimes - Consumes fuel faster Fuses more elements. - Fusion of iron consumes energy instead of giving off energy. - Fuel fusion http://physics.uoregon.edu/~jimbrau/BrauImNew/Chap21/FG21_05.jpg “Supernova explosion” http://imgsrc.hubblesite.org/hu/db/2004/29/videos/d/stills/3/image.jpg “What happens after death” It either becomes a: Black hole or a Neutron star. http://dante.physics.montana.edu/ns_interior.jpg “Black Hole” http://www.wvp-consulting.com/astronomy/images/blackhole.jpg Observations: Used the Lick Nickel 40 inch telescope Observed remotely with the help of Elinor Gates Took images of 4 open clusters QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. http://www.ucolick.org/graphics/nickel_lg.jpg CCDs: Basic tools of astronomical imaging Grids of light buckets Colorblind 3 different filters allow us to see color (red, green, and blue) Same as the digital cameras that you may own Quic kTime™ and a TIFF (Unc ompres sed) decompress or are needed to see this picture. Isochrones: Y=brightness “Freeze frame” of a cluster Reveals age of cluster Made by computer X=color and temp. Which Isochrone Matches the CMD? A. B. This one! Correct! :) (CMD) (ISOCHRONE) How to calculate the distance: Due to dust Apparent Mag. (from CMD) 0.2 ( m-M+5-Ar ) d=10 Distance Absolute Mag. (from isochrone) QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. M11 Color Magnitude Diagram • y-axis = brightness • x-axis = color M11 • Around 2000 parsecs • Around 6000 light years • Mostly main sequence stars • 200 million years old •What I found out : 5095 light years from the earth 1.6 billion years old My Color Magnitude Diagram Open Cluster NGC6939 NGC 6819 Apparent Diameter: 5 arc min. “NGC 6819” Open star cluster According to my results: -It is about 3/4 of the Earth’s lifetime old. -It is about 7,603 light years away from us. -Has a metallicity of about 2%---like Sun “Isochrone” “CMD” for NGC 6819 NGC 6791 Observed and recorded data for NGC 6791 7.6 billion years old Looking at isochrones 4972 parsecs (3.26 light years = 1 parsec) Isochrones Puzzles from NGC 6791 It’s really old Metal rich NGC 6705 NGC 6791 NGC 6819 Sun NGC 6939 We would like to thank: CFAO Laura Chomiuk Kathy Cooksey Daisy Corral Liz Espinoza Emily Freeland Elinor Gate •John Martin •Hilary O’Bryan •Jay Strader •Gene Switkes •Vay Hoang