* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download atmospheric extinction
Nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Health threat from cosmic rays wikipedia , lookup
Microplasma wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic microwave background wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
X-ray astronomy detector wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
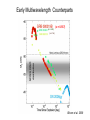
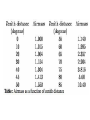
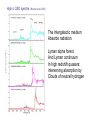
Supporting material for Lecture 3: Gamma-Ray Bursts and their counterparts Light extinction: Atmospheric absorption Galactic extinction by dust and gas GRBs are brief flashes of soft -ray radiation (100 keV), discovered in the 1970’s, the origin of which was not known until 1997 CGRO-BATSE Early Multiwavelength Counterparts (z = 0.937) (z = 6.29) (z = 1.6) Bloom et al. 2008 atmospheric extinction The amount of atmospheric extinction depends on the altitude of an object, being lowest at the zenith and at a maximum near the horizon. It is calculated by multiplying the standard atmospheric extinction curve by the mean airmass calculated over the duration of the observation: Airmass = sec(z), z = zenith angle Spectrum of star HD144470: the only line produced in the Stellar atmosphere is He 7065, the rest are telluric The Milky Way in Infrared (2MASS survey) Note the Galactic Plane QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Extinction curves of our Galaxy and Magellanic Clouds QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. 2175 Å: graphite or PAH? Dust suppression along given sight lines is estimated from COBE Infrared maps: Schlegel, Finkbeiner, Davis 1998, ApJ, 500, 525 Neutral gas in our Galaxy absorbs thru photoelectric effect. This is predominantly neutral hydrogen (HI): the Lyman limit occurs at 912 Å = 13.6 eV At frequencies higher than 13.6 eV part of the X-ray flux is Absorbed, in a frequency-dependent way Morrison & McCammon (1983, ApJ, 270, 119) have computed this dependence in the 0.03 - 10 keV energy interval, taking into account cosmic abundances QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Hydrogen atom One = 21 cm (1420 MHz) photon is emitted when the proton And electron spins flip from parallel to antiparallel. Radio and far infrared images of M81 (3.6 Mpc) QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. The Antennae (22 Mpc) White: optical Blue: radio (21cm) QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. High-z QSO spectra (Becker et al. 2001) The Intergalactic medium Absorbs radiation: Lyman alpha forest And Lyman continuum In high redshift quasars: intervening absorption by Clouds of neutral hydrogen Elihu Boldt The Extreme Universe: Some Views From Here Closing lecture, 3rd INTEGRAL Workshop: The Extreme Universe, Taormina, September 14-18 1998 Astrophysical Letters & Communications Vol. 37, 1999 arXiv:astro-ph/9902040