* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Milky Way Galaxy
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
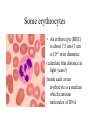
How Big is the Universe? The observable Universe is greater than 12 x 109 light years in radius. (12 x 109 years)(365 days) (24 hr) (60 min) (60 sec) (3 x 108 m ) ( 1 km ) ( year = ) (day ) ( hr ) ( min ) ( sec ) ( 103 m ) 2 x 1021 km !!!! (20000000000000000000000 km) That’s big! Photo of Universe not available. The Milky Way • As a galaxy, the Milky Way is actually a giant, as its mass is probably between 750 billion (750000000000, 750 x 109) and one trillion (750 x 1010) solar masses, and its diameter is about 100,000 light years • The Milky Way is a gravitationally bound collection of roughly a hundred billion stars. Our Sun is one of these stars and is located roughly 24,000 light years (or 8000 parsecs) from the center of our the Milky Way. COBE image of the Milky Way: (Courtesy of Ned Wright The Sun • The Sun is an ordinary G2 star, one of more than 100 x 109 stars in our galaxy. • Diameter: • • Mass: 1.989 x 1030 Temperature: 5800 K (surface) 1,390,000 km. kg • 15,600,000 K (core) • The Sun is the largest object in the solar system. It contains more than 99.8% of the total mass of the Solar System (Jupiter contains most of the rest). The Earth • Orbit: 149,600,000 km (1.00 AU) from Sun • Diameter: 12,756.3 km • (0.0000000015 light yrs) • Mass: 5.9736e24 kg Mt Mansfield from my Pasture • The summit of Mt. Mansfield; 4,393' above sea level; 4393 ft(12 in/ft)(2.54 cm/in)(1 m/100 cm)(1 km/1000 m) (1 sec/30000 km)(1 min/60 sec)(1 hr/60 min)(1 day/24 hr)(1 yr/365 days) = 0.0000000000001415 light years high. Klaque • As previously mentioned, The mass of the galaxy is 2 x 1042 kg. The mass of the sun, 2 x 1030 kg. The mass of earth, 6 x 1024. Kg. The mass of Klaque: 0.05 kg. Some erythrocytes • An erthyrocyte (RBC) is about 7.5 um (1 um is 10-6 m in diameter. (calculate that distance in light years!) Inside each avian erythocyte is a nucleus which contains molecules of DNA A Piece of DNA • This piece of DNA is 20 Å (1 Å is 0.1 x 10-9 m). wide. It can be up to 5 x 106 Å long. Looking at DNA another way Cells are a collection of larger molecules in a water environment: Of course, not all molecules live in cells This is DEET Molecular Formula: C12H17NO Synonymes: Detamide; Metadelphene; MGK; Off; Diethyltoluamide; Deet; Delphene; N,N-diethylm-toluamide; diethyl-m-toluamide; 3-methyl-N,Ndiethylbenzamide; m-toluic acid diethylamide; ai 3-22542 This is pure carbon, in the form of diamond Some water molecules • Each water molecule is 3 Å across. Each one weighs 3 x 10-23 g. Beyond water • Each water molecule is made up of 2 hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. • Each H atom weighs 1.7 x 10-24 g. & has a radius of 1.2 Å A way to visualize the Hydrogen atom Another way to view a Hydrogen atom Another way to view atoms • STM image of the Si(111)5x5 reconstructed surface • (Randall Feenstra’s group, Carnegie Mellon U http://stm1.phys.cmu.e du/stm/) Oh Where, Oh Where Has My Xenon Gone? Oh Where, Oh Where Can He Be? Media : Xenon on Nickel (110) Au atoms Another way to visualize an atom Atomic orbitals…regions in space where the electrons hang out. http://courses.chem.psu.e du/chem38/molgallery/orbitals/orbital s.html A way to visualize a negative twist of nothingness The mass of an electron is 9.1 x 10-31 kg. It is not possible to know precisely where an electron is now and where it is going at the same time Beyond Teeny • Quantum chromodynamics (QCD) is the proposed theory of the so-called strong interactions that bind quarks and gluons together to form hadrons-the constituents of nuclear matter such as the proton and neutron.