* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Inflation (cosmology) wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic microwave background wikipedia , lookup
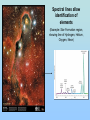
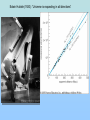
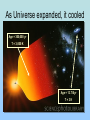
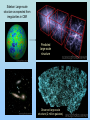
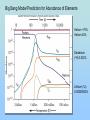
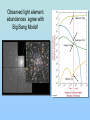
The Scientific Case for The Standard Big Bang Cosmological Model: A 30 minute synopsis And the Lord said, “Let there be light….” (Genesis 1:2) The Big Bang (inaccurate artist’s conception!! Is the Big Bang ‘just a theory’? George Deutsch, a presidential appointee in NASA headquarters, told a Web designer [October 2005] working for the agency to add the word “theory” after every mention of the Big Bang, The Big Bang is “not proven fact; it is opinion” stated Deutsch in a email to NASA scientists (Deutsch later resigned his post after it was discovered that he had misrepresented his education (didn’t graduate from Texas A&M in journalism) on his application to NASA. “Standard Model” of the Universe c.100AD-1600AD Geocentric (Earthcentered) Cosmological Model • Valid scientific model (testable, falsifiable) • Not in conflict with observations until Galileo (c. 1610) Galileo’s discovery (1610) of Jupiter’s moons with his telescope showed that Earth was not the center of all orbits strongly supported a heliocentric (Sun-centered) model The Three Observational Foundations of the Big Bang Theory 1. Hubble Expansion of the Universe (1920’s)_ 2. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (1965) 3. Elemental Abundances (1960’s – 1980’s) First, we need a tutorial on spectral analysis… Importance of stellar spectra 1: : Lines determine what are stars made of (like fingerprints) Spectral lines allow identification of elements (Example: Star Formation region, showing line of Hydrogen, Helium, Oxygen, Neon) Importance of spectra, 2: Line Shifts Determines speeds of stars (and galaxies) State’s Evidence 1: Expansion of the Universe Speed (km/s) Edwin Hubble (1920): “Universe is expanding in all directions” Distance to galaxy • Three bike racers: – Lance: 30 mph – Bob: 20 mph – Fred: 10 mph – Start race at time = 0 • Slope of line determines time since race started Time = D/V, ‘age’ of race!) • • Edwin Hubble (1920’s) measured speed (Doppler shift) and distance for galaxies –got a straight line • Slope determines age of Universe: 13.7 Billion yrs Speed (mph) Hubble expansion: Implies finite age of Universe: Bike race analogy Oldest detected object in Universe (Quasar, 12.5 billion light-yrs distance) Infrared Historical origins of the Big Bang model • Georges LeMaitre, a Belgian priest and mathematician, proposed (1927) that the expansion of the universe can be traced to an exceedingly dense ‘primeval atom’ • … when the whole universe exploded in “fireworks of unimaginable beauty” and with a “big noise” • Einstein, after listening to a lecture by LeMaitre said ‘This is the most beautiful and satisfactory explanation of creation to which I have ever listened.” • LeMaitre used the term ‘Cosmic Egg’. Now known as the Big Bang theory State’s Evidence 2: Cosmic Background Radiation Penzias and Wilson (Discoverers of CMB Radiation (1965) As Universe expanded, it cooled Age = 300,000 yr T = 3,000 K Age = 13.7 Byr T=3K CBR spectrum is exactly thermal, as expected from Big Bang model Sidebar: Large-scale structure as expected from irregularities in CBR Predicted large-scale structure Observed large-scale structure (2 million galaxies) State’s Evidence 3: Csomic Abundance of Elements What is Universe made of? Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin (1925) determines that Sun (and all stars) are primarily: • Hydrogen (75%) • Helium (25%), • All other elements <2% Payne-Gaposchkin: “Hydrogen, helium dominate solar abundance” (1925 Ph.D. thesis) Professor Russell: “Clearly impossible” Payne-Gaposchkin adds “almost certainly not real” to her final Ph. D. draft Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin (First Harvard PhD. in Astronomy 1923) Prof. Henry Norris Russell Harvard College Observatory Director Edward Pickering and his ‘computers’ c. 1912 I’m the boss! Big Bang Model Prediction for Abundance of Elements Helium ~75% Helium 24% Deuterium (2H) 0.002% Lithium (7Li) 0.00000002% Observed light element abundances agree with Big Bang Model! What is still uncertain? Plenty! For example… 1. Why did inflation occur? 2. Standard model doesn’t predict fundamental constants (masses, charges, speed of light, etc) • 3. Anthropic principle: If constants were even a little different, we wouldn’t be here to puzzle about them! Why is energy density of the vacuum so close to the energy density of matter? • Particle physics predicts ratio should be ~10120 !) Is there only one Universe or are there ‘many Universe bubbles?’ 4. • 5. Inflation allow for such disconnected space-time ‘bubbles’ What was before the Big Bang? • String theory avoids singularity at t=0 [in 10-dimensional space-time]