* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
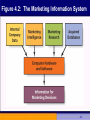
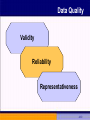
MARKETING CHAPTER 4 Marketing Information and Research: Analyzing the Business Environment Off-line and Online Knowledge is Power • A Marketing Information System (MIS) determines what information managers need and then gathers, sorts, analyzes, stores, and distributes relevant and timely marketing information to system users • 3 components of MIS – data – computer hardware and software – MIS experts 4-2 Figure 4.2: The Marketing Information System 4-3 Marketing Decision Support System • Includes analysis and interactive software that allows managers to conduct their own analyses 4-4 Search for Gold: Data Mining Customer Acquisition Customer Retention Customer Abandonment Market Basket Analysis 4-5 Figure 4.4: Steps in the Research Process Define the Problem Determine Research Design Choose Data Collection Method Design the Sample Collect the Data Analyze and Interpret Data Prepare the Research Report 4-6 Step 1: Define the Problem • Specify the research objectives • Identify the consumer population of interest • Place the problem in an environmental context 4-7 Step 2: Determine the Design • Can the information be acquired from existing data? – If so, secondary data sources will be utilized – If not, primary research will be necessary 4-8 Step 3: Choose the Data Collection Method • Communication – Mail questionnaires – Telephone – Face to face – Online questionnaires • Observation 4-9 Data Quality Validity Reliability Representativeness 4-10 Probability Samples Simple Random Systematic Random Stratified 4-11 Non-Probability Samples Convenience Quota 4-12 Garbologists Search for Clues 4-13 Step 5: Collect the Data • Implementation phase • Special issues in data collection – Gathering Data in Foreign Countries – Single-Source Data 4-14 Checkout Scanners Checkout scanners enable marketers to collect singlesource data 4-15 Step 6: Analyze and Interpret Data • Enter, clean, and code data • Choose appropriate techniques for analysis • Interpret analysis 4-16 Step 7: Prepare the Research Report Executive Summary Description of Research Methods Discussion Limitations Conclusions/ Recommendations 4-17 Online Research - Online Tracking • The Internet offers the ability to track and monitor consumers while they surf • Several behaviors can be monitored – What sites are visited? – How long did the visitor stay? – What types of information did they collect at the site? – Where did they go after they left? 4-18 Coremetrics Coremetrics specializes in tracking the online behavior of all visitors to their clients’ Web sites 4-19 Cookies • Cookies are text files inserted on a user’s hard drive by an Internet site • Cookies allow for details of a Web visit to be stored and tracked with future visits • For marketers, cookies allow a way of observing behavior and customizing Web sites and offerings to specific users • For consumers, cookies represent a tradeoff between privacy and customization 4-20 MCI In focus groups and interviews about online shopping, consumers consistently rate security their number one concern 4-21 Online Activities/Experiments 4-22 Purposes of Internet Research Develop new products Estimate market response Test markets Assess attitudes 4-23 Limitations of Online Research • • • • Representativeness of the population Self-selection bias Influence from hackers Threats of competitive intelligence 4-24 Issues for Discussion • What is the impact on legitimate researchers when marketers disguise themselves as market researchers in order to attempt to sell something? • Should marketers be allowed to conduct research with young children? • Are you willing to share personal information with marketing researchers? How much are you willing to tell? 4-25 Issues for Discussion • What is your overall attitude toward marketing research? Is it beneficial from the consumer’s perspective? • Some firms use data mining to identify and abandon customers who are not profitable. What do you think of such practices? Is it ethical? 4-26 Issues for Discussion • Do consumers have the right to “own” data about themselves? Should governments limit the use of the Internet for data collection? • Do you think marketers should have the right to go through consumers’ or competitors’ garbage? Is it ethical? 4-27