* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Interdependence in Living Systems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
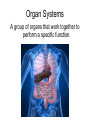
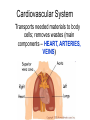
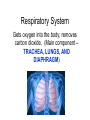
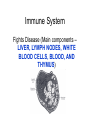
Interdependence in Living Systems Systems Any group of parts that work together as a unit. How the body is organized: • Cells – First level of organization; the basic unit of structure and function. • Tissues – a group of cells that perform the same function. Types of Tissues • • • • Muscle Connective Nerve Epithelial Organs A group of tissues that perform a specific function. Organ Systems A group of organs that work together to perform a specific function. Interactions Within the Human Body Each organ system is dependent on other body systems. Nervous System Obtains and processes information from the body’s internal and external environment; directs most body functions. Main components – BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND NERVES Cardiovascular System Transports needed materials to body cells; removes wastes (main components – HEART, ARTERIES, VEINS) Digestive System Breaks down food and absorbs the broken-down materials (main components – LIVER, STOMACH, GALL BLADDER, SMALL INTESTINE, AND LARGE INTESTINE) Respiratory System Gets oxygen into the body; removes carbon dioxide. (Main component – TRACHEA, LUNGS, AND DIAPHRAGM) Muscular System Enables the body to move Skeletal System Supports and protects the body; works with muscles to enable movement processes Endocrine System Produces chemicals called hormones that help control many body processes (Main components – GLANDS, PANCREAS, AND KIDNEYS THAT PRODUCE HORMONES) Excretory System Removes wastes; helps regulate water in the body (Main component – KIDNEY) Immune System Fights Disease (Main components – LIVER, LYMPH NODES, WHITE BLOOD CELLS, BLOOD, AND THYMUS) Skin (Integumentary) System Protects the body, keeps water inside, and helps sense the external environment Reproductive System Create offspring, determines male and female characteristics (Main Components – OVARIES and TESTES) Interactions in TRANSPORTING OXYGEN • RESPIRATORY – delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide. – Trachea – tube connecting to the lungs – Alveoli –round sacs in the lungs – Moves oxygen from air to blood – Moves carbon dioxide from blood to air •CARDIOVASCULAR – carries oxygen from lungs to bloodstream •MUSCULAR – enables air to enter lungs •Diaphragm – dome shaped muscle Interactions in DIGESTING FOOD • DIGESTIVE – breaks down food into simpler substances to be used by body cells – Mouth and Stomach – begins to break down food – Small Intestine – Completes the breakdown of food and absorbs the nutrients (through villi) – Large Intestine – undigested food passes out of the body as waste Interactions in DIGESTING FOOD •MUSCULAR – moves jaws to break down food. •Absorption of nutrients •Enables you to swallow food •Within the stomach – food is churned and squeezed, broken down into smaller particles Interactions in DIGESTING FOOD •CARDIOVASCULAR – carries nutrients absorbed through the small intestine to the blood. •Nutrients are carried throughout the body. MOVEMENTS: MUSCLES, BONES, AND NERVES •MUSCULAR – produce movement by contracting or shortening •SKELETAL – muscles attached to bones move your body •NERVOUS – involved in movement. Brain and nerves direct muscles to contract. •CARDIOVASCULAR – circulates oxygen and food to cells •RESPIRATORY – brings oxygen into body, removes carbon dioxide •DIGESTIVE – processes food for delivery to cells