* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch28
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
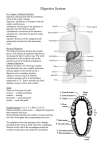
Essentials of Pathophysiology CHAPTER 28 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM PRE LECTURE QUIZ TRUE/FALSE The digestive tract is a single-layered tube. T The gastrointestinal tract is innervated by both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. T The gastrointestinal tract is the largest endocrine organ in the body. T Each day, approximately 7000 mL of fluid is secreted into the gastrointestinal tract. T Absorption is the process of moving nutrients and other materials from the external environment of the gastrointestinal tract into the internal environment. F PRE LECTURE QUIZ Digestion Esophagus Ileum Peristaltic stomach The __________ is a tube that connects the oropharynx with the stomach. The small intestine, which forms the middle portion of the digestive tract, consists of three subdivisions: the duodenum, the jejunum, and the __________. __________ movements are rhythmic propulsive movements that occur when the smooth muscle layer constricts, forming a contractile band that forces the intraluminal contents forward. The __________ serves as a reservoir for ingested solids and liquids. __________ is the process of dismantling foods into their constituent parts. THE JOB OF THE BOWEL Food: Movement Breakdown Absorption Keeping dangerous gut contents out of the blood Keeping blood contents from being lost into the gut lumen Sequentially number parts through which food travels 1 1 2 3 8 4 7 6 9 5 12 10 11 BOWEL AND MESENTERIES Abdomen QUESTION Tell whether the following statement is true or false. The mesentery contains the intestine’s blood supply. ANSWER True An extension of the visceral peritoneum, the mesentery contains blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to (arteries) and eliminate CO2 and waste from (veins) the intestines. PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME It is traditionally characterized by hypotonia, short stature, hyperphagia, obesity, behavioral issues (specifically OCD-like behaviors), small hands and feet, hypogonadism, and mild mental retardation. Plasma ghrelin levels are extremely high Discussion: What are the effects of this disorder? ghrelin a gastrointestinal hormone produced by epithelial cells lining the fundus of the stomach; appears to be a stimulant for appetite and feeding, but is also a strong stimulant of growth hormone secretion from the anterior pituitary Ghrelin levels increase before meals and decrease after meals. It is considered the counterpart of the hormone leptin, PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME This is a picture of a child with Prader-Willi Syndrome, first with a small, undersized figure, then as an obese teenager later in life. SCENARIO A woman has a pancreatic tumor that secretes gastrin- a hormone that stimulates the secretion of gastric juice. Question What complication is likely to develop? Why? SCENARIO A man cannot produce cholecystokinin. Question What problems will this cause him? CARBOHYDRATE DIGESTION Mouth: Salivary amylase Duodenum: pancreatic amylase Polysaccharides disaccharides Brush border enzymes Disaccharides monosaccharides Monsaccharides absorbed into blood PROTEIN DIGESTION Stomach: pepsinogen Activated to pepsin by acid in stomach Breaks proteins into polypeptides Duodenum: pancreatic trypsinogen Activated to trypsin in duodenum Breaks proteins into polypeptides Brush border enzymes Breaks polypeptides into 2–3 amino acid peptides Peptides absorbed into blood FAT DIGESTION Duodenum: bile Emulsifies fats Duodenum: pancreatic lipase Breaks triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids Jejunum Packages digested fats as chylomicrons Passed to the lymph QUESTION Digestion of which substance begins in the mouth? a. Carbohydrates b. Protein c. Fat d. All of the above ANSWER Carbohydrates Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with salivary amylase; protein digestion begins in the stomach with pepsinogen; fat digestion begins in the small intestine with bile and pancreatic lipase. a. DISCUSSION Which is the best choice to reduce fat digestion? Suppress duodenal hormone secretion Suppress the activity of chief cells in the stomach Decrease intrinsic factor secretion Block gall bladder contraction Inactivate pancreatic lipase QUESTION How would fat digestion be affected if bile levels decreased? a. It would increase. b. It would decrease. c. It would have no effect—fat digestion is mainly affected by amylase. d. It would have no effect—fat digestion is mainly affected by lipase. ANSWER It would decrease. Bile emulsifies fat so that it can be more easily digested. Decreased amounts of bile would lead to decreased fat emulsification and decreased ability to break down/digest fats. b.