* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 - Tracy Jubenville Nearing
Chromium(III) picolinate wikipedia , lookup
Adipose tissue wikipedia , lookup
Oral rehydration therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dietary fiber wikipedia , lookup
Food choice wikipedia , lookup
Human nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbohydrate diet wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
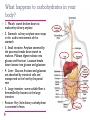
Chapter 5 Carbohydrates Carbohydrates Class of nutrients that is a major source of energy foe the body Monosaccharides: simple sugar that is the basic molecule of carbohydrates Glucose, fructose, galactose -ose Glucose: primary fuel for muscles and other cells Fructose: in fruits, fruit sugar and levulose Most important monosaccharide in the body Naturally found in fruits, honey and some vegetables Body has little need for fructose, most converted to glucose or fat Galactose: component of lactose Not commonly found in foods Disaccharides: simple sugar comprised of two monosaccharide's. Maltose: comprised of 2 glucose molecules, malt sugar Sucrose: comprised of 1 glucose and 1 fructose molecule Few foods naturally contain maltose Sugar cane and sugar beets “junk food” Lactose: comprised of 1 glucose and 1 galactose molecule Nutritive and Nonnutritive Sweeteners Nutritive sweetener: sweetener that contributes energy to foods Added sugars: sugars and syrups added to foods during processing or preparation Alternative sweeteners: substance that sweeten foods while providing few or no kilocalories Nonnutritive sweeteners: group of synthetic compounds that are intensely sweet tasting compared to sugars Complex Carbohydrates (polysaccharides) Comprised of 10 or more monosaccharides bonded together Starch: storage polysaccharide in plants Glycogen: storage of polysaccharide in animals Fiber: indigestible plant material, most are polysaccharides Soluble Insoluble What happens to carbohydrates in your body? 1. Mouth: starch broken down to maltose by salivary amylase 2. Stomach: salivary amylase soon stops in the acidic environment of the stomach 3. Small intestine: Amylase secreted by the pancreas breaks down starch to maltose. Maltase digest maltose into glucose and fructose. Lacatase breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose 4. Liver: Glucose, fructose and galactose are absorbed by intestinal cells and transported to the liver by the portal vein 5. Large intestine: some soluble fiber is ferment3ed by bacteria in the large intestine Rectum: Very little dietary carbohydrate is excreted in feces. Maintaining blood glucose levels Glucose is an important cellular fuel Pancreas Beta cells and alpha cells Insulin Glucagon 70-100 mg/dL of blood Glucose for energy Brain and nervous system burn glucose Ketones: chemicals that result from incomplete fat breakdown Ketosis RDA 130 g/day Carbohydrate consumption patters Developing nations: 70% unprocessed carbs, especially complex carbs Industrial nations: eat more refined sugars and added sugars. Carbs supply 50% of energy for Americans. Should be 45-65% Reducing your refined carbs intake Avoid vending machines Avoid fast food Cut up fruit Are carbs fatting? Atkins, low glycemic index, zone Energy intake matches your energy output Refined carbs curb hunger less then protein and fat Fiber rich foods more filling Percentages of overweight people has risen in the past 35 yrs. Children and obesity Liquid candy Diabetes Group of serious chronic characterized by abnormal glucose, fat and protein metabolism. Type 1 5-10% Usually diagnosed as a child, but can be any age Autoimmune disease Body does not recognize own beta cells, immune system attach and destroy them Type 2 Adult on set Beta cells produce insulin but not as well Genetics, obesity, lack of exercise Diabetes cont… Hyperglycemia: abnormally high blood glucose level Primary sign of diabetes Fasting blood test, 12 hours Normal is 70-100 mg/dl Pre-diabetes: 100-125 >125, person has diabetes Beta cells don’t produce insulin Other signs: excessive thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, poor wound healing, yeast infections, impotence Other signs, type 1 only: increased appetite with weight loss, fatigue easily, breath smells like fruit, confusion Diabetes cont… Complications: kidney failure, organ failure, damages nerves, blood vessels. 200,000 Americans die from the complications annually, 6th leading cause of death Diabetes increasing at alarming rate: 1980: 1985: 1990: 1995: 2000: 2005: 5.6 million 6.2 6.6 8.0 12.0 15.8 Controlling diabetes Testing, monitor, shots, eating right Doctor appointment A1c: blood test to determine how well someone is controlling their diabetes Glycemic index Glycemic index and load: standards that indicate that body’s insulin response to a carbohydrate containing food Different carbs undergo a different rate and digestion and absorption GI <70 may promote satiety (feeling that enough food has been eaten to delay the next eating episode and or reduce subsequent food intake). Hypoglycemia Condition that occurs when the blood glucose level is abnormally low. <70 mg/dl blood test after 12 hour fast Declining blood sugar levels, your body produces epinephrine Symptoms: head ache, irritable, restless, shaky, sweaty, loss of consciousness, dizzy. Metabolic Syndrome Condition that increases risk of type 2 diabetes People with this condition: 2x risk of heart disease and CDV Genetic factors Excess abdominal fat Insulin resistant Poor diet Smokes No physical activity Large waist circumference Hypertension High elevated fasting blood fats High fasting blood glucose Low fasting high-density lipoprotein cholesterol People can reduce their risk of Metabolic and CVD: Exercise 3x a week Eat more fruits and veggies Lose weight Reduce intake of saturated fat, cholesterol and simple sugars What has sugar done for you? Hyperactivity in children? FALSE Promote ADHD? False Lactose intolerance Inability to digest lactose properly 30-50 million Americans suffer from it Does not produce enough lactase Not same as milk allergy, 5% of population Disaccharide is not completely digested and absorbed by the time it enters the large intestine Symptoms Within a couple of hours Cramps Bloating Gas diarrhea Usually able to eat yogurt, hard cheese Milk pretreated with lactase, pills also available What fiber can do and not do for you Is not a nutrient because your body can live with out it Reduce your risk of obesity, diabetes, intestinal track disorders, CDV Reduce constipation, diverticulitis, hemorrhoids Increase regularity Does not effect chances of getting colon cancer Diets rich in soluble fiber can reduce risk of CVD, by reducing cholesterol Helps you feel full AI: 38-25g/day