* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mountain-building processes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
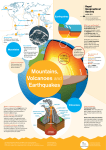
CE - Mountain-building processes © Oxford University Press 2001 S2 - The unstable earth © Oxford University Press 2001 Mountain-building © Oxford University Press 2001 Vs Unstable earth The unstable earth What makes up the earth’s crust Where are the unstable zones on the earth? Why does the crust move? What are the causes of volcanic eruptions & earthquakes? Volcanic eruptions © Oxford University Press 2001 Earthquakes Fold mountains What makes up the earth’s crust? The earth is made up of 3 layers: crust mantle core The earth’s crust is made up of __________ and rocks continents and __________. They form the __________ soil ocean __________ floors. © Oxford University Press 2001 Where are the unstable zones on the earth? There are 3 major zones of earthquakes and volcanic activities: Mediterranean belt Mid-Atlantic zone © Oxford University Press 2001 CicumPacific belt Why does the crust move? The earth’s crust is made up of __________. plates Name the plates marked 1 to 7 in the map below. Eurasian Plate African Plate North American Plate Pacific Plate Indo-Australian Plate Antarctic Plate © Oxford University Press 2001 South American Plate Why does the crust move? The plates are moving very slowly along _________________. plate boundaries © Oxford University Press 2001 Why does the crust move? The movement of plates is caused by the _______________ convection of magma in the mantle. Destructive plate boundary Two plates move __________ towards each other Constructive plate boundary Plates move __________ apart magma Convection of __________ This process is explained in the theory of _________________. plate tectonics © Oxford University Press 2001 What are the causes of volcanic eruptions? magma Hot __________, volcanic __________ and __________ are ash gases thrown out to the earth surface. When there is a line of __________ weakness in the earth’s crust, magma escapes to the surface from the mantle. This is called volcanic __________. eruption Magma in the mantle is under great heat and high pressure. __________ © Oxford University Press 2001 What are the causes of earthquakes? The earth will shake. This is called _______________. earthquake The plates will break and energy is released. __________ When the plates move, __________ pressure builds up in them. © Oxford University Press 2001 What are the harmful effects of earthquakes? Collapse of dams may flooding cause __________ Landslide __________ Fire __________ may break out Big waves — tsunamis __________ Buildings, bridges, roads and railways collapse __________ © Oxford University Press 2001 killed People are __________ and injured How to reduce the negative impact of earthquakes? __________ Prediction Scientific methods have been developed to predict when and where hazards will occur. Protection measures Build earthquake-__________ buildings. proof wider parks Build __________ roads and open ________. Preparation drills Carry out earthquake __________. Relief __________ work Better planning for emergency work. © Oxford University Press 2001 What are fold mountains? The rocks may be folded up into high mountains. fold They are known as __________ mountains. When plates move together, some rocks in between are folding compressed and bent. This is called __________. © Oxford University Press 2001 Where are the fold mountains? 1. Name the fold mountains 1 to 4. plate boundaries 2. Fold mountains are usually found at _______________. Alps Himalayas Rockies Andes © Oxford University Press 2001 How are fold mountains formed? The weight changes them into __________. rocks Sand and mud are left between two plates. © Oxford University Press 2001 How are fold mountains formed? The rocks are folded up into high __________ fold mountains. The fold mountain formed Himalayas here is the ____________. plate The rocks in between are compressed by __________ movement. © Oxford University Press 2001