* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Applying Post-Modern Portfolio Theory to International Performance
Private equity secondary market wikipedia , lookup
Private equity in the 2000s wikipedia , lookup
Socially responsible investing wikipedia , lookup
Environmental, social and corporate governance wikipedia , lookup
Private equity wikipedia , lookup
Early history of private equity wikipedia , lookup
Systemic risk wikipedia , lookup
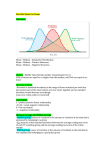
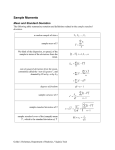
Applying Post-Modern Portfolio Theory to International Performance Measurement Brian M. Rom, President Investment Technologies Outline • Post-Modern Portfolio Theory • Case Studies Post-Modern Portfolio Theory • Downside risk replaces standard deviation • Distributions do not have to be normal or symmetric Downside Risk • The standard deviation of returns below the goal • Differentiates between risk and uncertainty • Naturally incorporates skewness • Recognizes that upside volatility is better than downside volatility • Combines frequency and magnitude of bad outcomes • No single riskless asset Elements of PMPT The Goal • Questions to Identify the Proper Goal: • • • What is at stake here? What are we trying to accomplish? When does it go from good to bad? • Examples of Goals: • • • • • Minimum achievable return Benchmark or index portfolio Comparative universe median Maintain pension contribution below specified amount Achieve target wealth in order to retire Elements of PMPT Sortino Ratio • [Return-Goal]/Downside Risk • PMPT analogue of Sharpe Ratio (Return-Riskfree Rate)/Standard Deviation Elements of PMPT Volatility Skewness [Percent variance above the mean]/ [Percent variance below the mean] Elements of PMPT Downside Frequency Frequency of failure to achieve the goal Elements of PMPT Average Downside Deviation Average deviation below the goal Case Study #1 How Asymmetrical are International Investment Returns? Volatility Skewness Skewness of International Equity Indexes: 1988-1997 1.00 0.00 55 Indexes Sources: Barings, Lipper Analytical, Goldman Sachs, Independence International Associates, Inc., MSCI Volatility Skewness Skewness of International LargeCap Equity Managers: 1993-1997 2.00 1.00 0.00 106 Managers Source: Effron/PSN Volatility Skewness Skewness of International SmallCap Equity Managers: 1993-1997 2.00 1.00 0.00 34 Managers Source: Effron/PSN Volatility Skewness Skewness of International Fixed Income Managers: 1993-1997 1.00 0.00 26 Managers Source: Effron/PSN Case Study #2 Performance analysis of two large-cap international equity investment managers for period 1993-1997 Risk and Return 30 27.0 25 20 18.2 17.6 15 12.5 10 6.9 5 3.6 0 Annualized Compound Average (%) Standard Deviation (%) Downside Deviation @ 10.00% Goal (%) Manager A Manager B Risk-Adjusted Returns 6 5.59 5 4 3 2 1.73 1.73 1.41 1 0 Sortino Ratio @ 10.00% Goal Manager A Sharpe Ratio Manager B Skewness Analysis Manager Volatility Skewness % Upside Volatility % Downside Volatility A 1.30 56.5% 43.5% B 0.65 39.5% 61.5% Manager B Manager A -15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15 Return (%) Manager A Manager B 20 25 30 THE INVESTMENT WORLD IS NOT ALWAYS SYMMETRICAL! Wrap Up • DR is standard deviation of returns below the goal • Differentiates between risk and uncertainty • Naturally incorporates skewness • Recognizes that upside volatility is better than downside volatility • Skewness of returns can be significant • DR handles skewness; SD does not • Concepts are theoretically sound and experimentally validated