* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download press kit - Sanofi Pasteur
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Poliomyelitis eradication wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Thiomersal controversy wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination policy wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
Louis Pasteur wikipedia , lookup
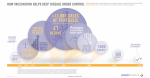
Influenza vaccine wikipedia , lookup
PRESS KIT Sanofi Pasteur – Dedicated to vaccines CONTACT: Global Media Relations Alain Bernal T. +33-4-37-37-50-38 [email protected] www.sanofipasteur.com December 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS SANOFI PASTEUR – DEDICATED TO VACCINES .......................................................... 3 GLOBAL COMMITMENT TO IMPROVE PUBLIC HEALTH ............................................... 6 BROADEST RANGE OF VACCINES .......................................................................... 6 WORLD’S LEADING INFLUENZA VACCINE MANUFACTURER (PANDEMIC AND SEASONAL) .............................................................................................................. 12 VACCINES FOR TOMORROW ................................................................................ 14 PARTNERING WITH THE IMMUNIZATION COMMUNITY ...................................... 17 VACCINATION BASICS ................................................................................................... 20 HISTORY AND HERITAGE............................................................................................... 23 2 PRESS KIT SANOFI PASTEUR – DEDICATED TO VACCINES Sanofi Pasteur is the vaccines division of Sanofi, a leading global pharmaceutical company that discovers, develops and distributes therapeutic solutions focused on patients’ needs. Sanofi Pasteur is the largest company entirely dedicated to vaccines. The company produces more than 1 billion doses of vaccine each year, making it possible to immunize more than 500 million people across the globe. A world leader in the vaccine industry, Sanofi Pasteur offers a broad range of vaccines, protecting against 20 infectious diseases. Sanofi Pasteur’s vision is a world in which no one suffers or dies from a vaccinepreventable disease. Sanofi Pasteur’s mission is to protect and improve human health worldwide by: Providing superior, innovative vaccines for the prevention and treatment of disease Playing an active role in the immunization community to maximize vaccination 3 PRESS KIT SANOFI PASTEUR: A GLOBAL COMPANY Headquarters: Lyon, France Revenue: 3,974 million euros in 2014 Market share: responsible for the provision of approximately 20% of the world’s vaccine market in value, Sanofi Pasteur is amongst the top 3 companies of the industry 15 R&D and industrial sites worldwide France (Marcy l’Etoile, largest industrial site dedicated to vaccines worldwide, Neuville-surSaône and Val de Reuil) United States (Swiftwater, PA; Cambridge and Canton, MA; Rockville, MD; Orlando, FL) Canada (Toronto) Argentina (Pilar), China (Shenzhen), Thailand (Chachoengsao), India (Hyderabad), Ocoyoacac (Mexico) SANOFI PASTEUR: OUR PEOPLE Olivier Charmeil: President and Chief Executive Officer Almost 14,000 employees worldwide SANOFI PASTEUR: CONTINUALLY INVESTING IN RESEARCH AND PRODUCTION CAPACITY A large product range available, against 20 infectious diseases R&D: more than 500 million euros invested in 2014 11 vaccines in development or submitted (entirely new vaccines or improved versions of existing vaccines) Investment milestones: more than 3 billion euros in the last 10 years (2005-2014) 2014: Sanofi Pasteur inaugurated a new yellow fever vaccine production unit in its industrial site in Val-de Reuil, France. The company’s 25 million euros investment will double yellow 4 PRESS KIT fever vaccine production capacity by 2016, making it possible to provide a major portion of the doses required to meet global public health needs for the next decade. 2009: Sanofi Pasteur started the construction of a new vaccine manufacturing center in Neuville-sur-Saône, France investing 300 million euros to produce Sanofi Pasteur’s vaccine against dengue fever. The site is now operational. 2009: Construction of new vaccine production facilities began in China and Mexico to produce seasonal influenza vaccine for the Chinese and Mexican markets. The Mexican production facility has been operational from the end of 2012 and the Chinese facility was certified at the end of 2013. 2009: Sanofi Pasteur was granted licensure from U.S. FDA (Food and Drug Administration) for a new influenza vaccine production facility in the U.S. representing a U.S. 150million investment. Other key investments over the last 5 years include: Increased production capacity for inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) to help polio-free countries implement international health standards to respond to the World Health Organization’s (WHO) strategy to eradicate polio Increased production capacity for quadrivalent conjugate vaccine against four different types of meningococcal meningitis (serogroups A, C, Y and W-135) A new building for visual inspection of vials and syringes New production facility for pediatric vaccines (Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)). New R&D unit in the world’s largest campus dedicated to the research, development and production of vaccines 5 PRESS KIT GLOBAL COMMITMENT TO IMPROVE PUBLIC HEALTH A BROAD RANGE OF VACCINES Today, according to the WHO, vaccines are available to protect against more than 26 infectious diseases. Sanofi Pasteur is committed to the health of the world in the area of infectious diseases with a broad range of vaccines, protecting against 20 infectious diseases: World’s first dengue vaccine paving the way for active immunization against dengue in endemic countries World’s leader of seasonal influenza vaccines: over 220 million doses in 2014 Leading provider of both injectable and oral poliomyelitis vaccines Range of modern pediatric combination vaccines for children throughout the world World’s largest provider of vaccines against meningococcal infections Largest portfolio of vaccines for travelers and people living in endemic areas DENGUE FEVER Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne disease It is estimated that 390 million people are caused by four types of dengue viruses infected annually, of which 96 million (type 1 to 4). The disease is a threat to manifest clinically (with any severity of the almost half of the world’s population — disease)6. Currently, there is no specific more than 100 tropical and subtropical treatment available against dengue fever. countries. 6 PRESS KIT FIRST DENGUE VACCINE Sanofi Pasteur has been investing in the research and development of a dengue vaccine for over 20 years. The company conducted a worldwide clinical study program in which nearly 40,000 volunteers participated. It is the first vaccine candidate to successfully complete phase III clinical studies. In 2014, world’s first phase III dengue vaccine efficacy study including 10,275 participants in Asia demonstrated protection against dengue and dengue hemorrhagic fever. The results were published in The Lancet in July 2014. A second phase III study in more than 20,869 participants conducted in Latin America has met its primary endpoint. The results, announced in September 2014, showed efficacy against each of the four dengue serotypes. The results were published in The New England Journal of Medicine in November 2014. In July 2015, The New England Journal of Medicine published new analyses confirming that Sanofi Pasteur’s vaccine candidate safely protects pre-adolescents to adults against dengue in endemic countries. In December 2015, Sanofi Pasteur’s dengue vaccine was approved in Mexico, making it the first vaccine to be licensed in the world for active immunization against dengue disease in preadolescents, adolescents and adults (9 to 45 years of age) living in endemic areas. This is a historic milestone paving the way to significantly impact dengue burden in endemic countries. More information on www.dengue.info INFLUENZA: MEETING ESCALATING GLOBAL DEMAND INTRADERMAL INFLUENZA VACCINE Current influenza vaccines are generally The WHO estimates that influenza causes up administered intramuscularly (IM). The to 500,000 deaths worldwide every year1; and intradermal (ID) route represents an demand for influenza vaccines is increasing. alternative route of injection: the vaccine is Sanofi Pasteur is the world’s largest provider administered into the dermis, or the top layer of influenza vaccines. It provided over 220 of the skin. In 2010, the first intradermal million doses of influenza vaccine in 2014. In microinjection influenza vaccine produced in May 2009, Sanofi Pasteur announced the France was launched in the European Union licensure from U.S. FDA of a new influenza and in Australia, Argentina and New Zealand. vaccine production in the U.S. In 2011, Sanofi Pasteur’s new intradermal influenza virus vaccine produced in the U.S. was launched in the U.S. market. In December 2014, Sanofi Pasteur’s intradermal Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccine for adults was approved by FDA in the U.S. 7 PRESS KIT QUADRIVALENT INFLUENZA VACCINE TO ENSURE BROADER PROTECTION than one billion doses of IPV and IPVcontaining vaccines. Currently, the annual influenza vaccination targets the three influenza virus strains In March 2014, UNICEF announced it would anticipated to circulate during the influenza purchase significant quantities of IPV from season. Given the evolution in seasonal flu Sanofi Pasteur and make it available based epidemiology, Sanofi Pasteur has initiated the on country needs and vaccination plans in switch to Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccine (two more than120 countries that routinely use A-strains and two B-strains) to ensure a only OPV. To support rapid and widespread broader protection and to provide ever-better adoption of IPV, Sanofi Pasteur and the Bill & vaccine solutions. In June 2013, the new Melinda Gates Foundation have developed a Sanofi Pasteur four-strain influenza vaccine joint price support mechanism, including a was licensed by U.S. FDA for a broad age financial contribution from both organizations. range of children and adults in the U.S. In This mechanism allows Sanofi Pasteur to December 2014, the intradermal version of offer IPV at the lowest price possible to 73 of Sanofi Pasteur’s influenza quadrivalent the world’s poorest countries. Gavi, the vaccine for adults was approved by FDA in Vaccine Alliance, a global immunization the U.S. The new quadrivalent vaccine will partnership, will make IPV available for progressively become the new standard of inclusion in routine immunization schedules in prevention. these countries. Sanofi Pasteur is also a major provider of OPV. The company has POLIOMYELITIS: WORKING TOWARDS ERADICATION provided more than five billion doses of OPV Sanofi Pasteur, as a leader in providing both 2013, the company announced it would Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) and Inactivated provide 1.7 billion doses of OPV from 2013 to Polio Vaccine (IPV), has been a partner of 2017 for polio eradication. the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) for over 25 years. Since the creation of GPEI in 1988, cases of the disease have fallen by 99%2, with more than 10 million people escaping paralysis. In 1982, Sanofi Pasteur registered the first to UNICEF over last two decades. In April PUBLIC HEALTH COMMITMENT In September 2011, Sanofi Pasteur donated a vaccine strain used for polio eradication to the WHO. With this donation from Sanofi Pasteur, the WHO is in full control of the storage of the vaccine strain and its distribution to vaccine producers worldwide. enhanced-potency Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV), which is now distributed globally as a stand-alone poliovirus vaccine as well as in combination pediatric vaccines to immunize PEDIATRIC COMBINATION VACCINES: PROTECTING AGAINST CHILDHOOD DISEASES against many diseases in a single shot. Since Sanofi Pasteur is committed to providing the then, Sanofi Pasteur has distributed more same standard-of-care combination vaccines 8 PRESS KIT throughout the world, offering protection against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis and against major childhood diseases such as poliomyelitis in children aged 4 to 6 years. diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whooping cough), polio, hepatitis B, and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib). In April 2013, the MENINGOCOCCAL MENINGITIS: TACKLING MAJOR OUTBREAKS European Medicines Agency (EMA) approved Sanofi Pasteur is the world’s leading provider the only fully liquid 6-in-1 pediatric vaccine in of vaccines to fight meningococcal infections. Europe. The vaccine which protects infants Sanofi Pasteur was the first company to against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis provide a quadrivalent conjugate vaccine (whooping cough), hepatitis B, polio and protecting against four different types of invasive infections caused by Haemophilus meningococcal meningitis (serogroups A, C, influenzae type b (Hib), is intended for use in Y and W-135). The vaccine is licensed in the Latin America, Africa, Eastern Europe, Middle U.S. and Canada for people aged 2 to55 East and Asia. In May 2011, the first 5-in-1 years. In September 2013, it was the first combination vaccine (diphtheria, tetanus, quadrivalent meningococcal vaccine acellular pertussis, inactivated poliomyelitis prequalified by the WHO, which makes it vaccine, and Haemophilus influenzae type b eligible to purchase by United Nations conjugate vaccine) from Sanofi Pasteur was Agencies. In April 2011, the U.S. FDA launched in China. This vaccine is also granted licensure to expand the indication for available to infants in Mexico, Turkey and the vaccine to infants aged 9 to23 months. In South Africa through the countries’ national June 2010, the vaccine was registered by the immunization programs since 2007. Health Council for Arab countries in the Gulf. BOOSTERS: PROVIDING LONGERLASTING PROTECTION VACCINES FOR TRAVELERS AND PEOPLE IN ENDEMIC AREAS: OFFERING A BROAD VACCINE PORTFOLIO A booster vaccine is a repeat shot that is used, at intervals, to maintain immunity. Sanofi Pasteur provides the broadest range Sanofi Pasteur’s latest booster vaccine is a of vaccines for travelers, military personnel, combination against tetanus, diphtheria, and populations living in tropical areas where pertussis (whooping cough), and polio. This infectious diseases are endemic. The booster vaccine allows parents and relatives portfolio includes vaccines against cholera, to protect not yet fully immunized newborns diphtheria, hepatitis A and B, Japanese from pertussis by stopping the transmission encephalitis, meningococcal diseases, rabies, cycle of the disease. A quadrivalent booster tetanus, typhoid, yellow fever, and a range of vaccine including diphtheria, tetanus, antivenoms sera. In June 2011, the WHO acelullar pertussis and IPV has been granted prequalification to Sanofi Pasteur’s developed for the U.S. market. In March polysaccharide typhoid vaccine indicated for 2015, the FDA approved use of this active immunization of persons two years of quadrivalent vaccine for active immunization age and older against typhoid fever. It is the 9 PRESS KIT first WHO prequalified typhoid vaccine. Over fever outbreaks in Africa. Reemergence of the past 20 years, nearly 20 million people in yellow fever results in an estimated 200,000 100 countries have been treated against cases and 30,000 deaths every year 3. rabies with Sanofi Pasteur vaccines and immunoglobulins. of yellow fever vaccine for Africa for 60 years VACCINES FOR THE MOST VULNERABLE since the vaccine was discovered by Institut India’s first oral cholera vaccine Pasteur. In the past 20 years, over 200 introduced by Shantha Biotechnics (part million doses of yellow fever vaccines were of Sanofi Pasteur since 2009), was procured. In September 2014, the company prequalified by the WHO, in 2011. The inaugurated a new yellow fever vaccine vaccine is procured to United Nations production unit in its industrial site in Val-de Agencies. The pentavalent vaccine Reuil, France. The company’s €25 million against diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, investment will double yellow fever vaccine Haemophilus influenza type b and production capacity by 2016, providing the hepatitis B has received prequalification means to better respond to the growing by the WHO on May 5, 2014. Sanofi Pasteur has been the primary supplier global demand and the ability to deal with recurring epidemics in Africa and in South America. Sanofi Pasteur has provided 6 million doses of vaccine for the stockpile funded by the Vaccine Alliance (Gavi) for routine immunization and to control yellow PRODUCTION CAPACITY Sanofi Pasteur has the industrial-scale manufacturing ability to produce vaccines in large quantities, with the highest quality standards, to help fulfill public health needs. To meet the growing demand for vaccines, Sanofi Pasteur is continuously investing to increase production capacity. More than 3 billion euros have been invested between 2005 and 2014. 10 PRESS KIT SANOFI PASTEUR VACCINE PORTFOLIO Cholera Mumps Diphtheria Pertussis Dengue Pneumococcal infections Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) Poliomyelitis infections Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Influenza Japanese encephalitis Measles Rabies Rubella Tetanus Tuberculosis Typhoid fever Yellow fever Meningococcal infections And against one eradicated disease: Smallpox (vaccine produced in response to the threat of bioterrorism) 11 PRESS KIT GLOBAL COMMITMENT TO IMPROVE PUBLIC HEALTH WORLD’S LEADING INFLUENZA VACCINE MANUFACTURER (PANDEMIC AND SEASONAL) Backed by its experience as a world leader in influenza vaccine research, development and production, Sanofi Pasteur is constantly working to save lives through the development of new and innovative influenza vaccines. A WORLD LEADER Sanofi Pasteur is the world’s leading manufacturer of vaccines against seasonal influenza, a disease responsible for up to half-a-million deaths worldwide each year, according to WHO estimates. Sanofi Pasteur has four influenza vaccine production facilities. Two established sites in the U.S. and in France where the company has made large investments to increase production capacity and two new vaccine production This greater production capacity for seasonal influenza vaccines brings both immediate and long-term public health benefits. It enables the expansion of current influenza immunization programs and enhances Sanofi Pasteur’s ability to respond effectively to a potential influenza pandemic. As part of a large industrial network, Sanofi Pasteur also benefits from Sanofi’s industrial assets to respond to the increasing worldwide demand for the influenza vaccine. centers in China and Mexico to meet local needs. The Mexican production facility has been operational since the end of 2012 and the one located in Shenzhen (Southern China) was certified at the end of 2013. LEADING PROVIDER OF SEASONAL INFLUENZA VACCINES Sanofi Pasteur produces approximately 40 percent of influenza vaccines distributed worldwide. The company mainly operates influenza vaccine production facilities in its two established sites, one based in Swiftwater, Pennsylvania, U.S., and the other in Val de Reuil, France. All Sanofi Pasteur influenza vaccine facilities have been designed and built to be able to switch from seasonal influenza vaccine production to pandemic influenza vaccine production. 12 PRESS KIT INDUSTRIAL-SCALE CAPACITY Sanofi Pasteur was the first company to employ its industrial-scale capabilities for the A(H5N1) influenza virus. PANDEMIC PREPAREDNESS manufacture of a vaccine against an A(H5N1) Sanofi Pasteur has been bringing its influenza pandemic. Since 2004, millions of worldwide vaccine expertise to governments, doses have been industrially produced, using international organizations, and working different A(H5N1) and A(H7N9) strains. groups on all aspects of influenza pandemic Industrial and scientific expertise have preparedness and supporting dialogue enabled Sanofi Pasteur to produce A(H5N1) between all partners to define vaccination vaccines for several countries, including the strategies before a pandemic was declared. U.S., France, and Italy for their national prepandemic stockpiles, as part of their In 2007, Sanofi Pasteur was the first to pandemic preparedness programs. In the receive a license for a vaccine against avian A(H1N1) pandemic situation, the company influenza in humans from the U.S. FDA. has produced over 250 million doses of A(H1N1) monovalent vaccine in 2009-2010. Sanofi Pasteur has committed to contribute to WHO pandemic vaccine stockpile in case of a CONTINUAL NEW RESEARCH Sanofi Pasteur has been investing heavily to support a priority research program for pandemic. A(H1N1) PANDEMIC RESPONSE influenza. This program has yielded Sanofi Pasteur’s response to the emergence unprecedented results showing that the of a new A(H1N1) 2009 influenza strain was lowest dose known today of a prototype to maintain maximum flexibility in its influenza H5N1 influenza vaccine, containing a new vaccine production. The company adjuvant, induces a strong immune response, manufactured a new A(H1N1) vaccine while thus allowing for the production of a large maintaining its seasonal influenza vaccine number of doses in the event of a pandemic. production for the 2009/2010 Northern Hemisphere influenza season and for the Results from this program have been applied 2010 Southern Hemisphere influenza season to the development of Sanofi Pasteur’s as recommended by the WHO. Production of adjuvanted pandemic vaccine against A both Northern and Southern hemisphere (H1N1) 2009. seasonal influenza vaccines was considered as a priority by the WHO and the authorities Sanofi Pasteur has also been testing the when the A(H1N1) 2009 pandemic strain ability of its vaccines to generate immune emerged. responses against other types (or strains) of 13 PRESS KIT GLOBAL COMMITMENT TO IMPROVE PUBLIC HEALTH VACCINES FOR TOMORROW The process to develop a new vaccine can take between 14 to 254 years with an overall cost of US$300 million to US$1 billion5. Sanofi Pasteur R&D team is fully committed to the research and development of new vaccines: 11 vaccines are in development or submitted for market authorization, including: New vaccines against endemic diseases, and against hospital-acquired infections (C. difficile), for which no vaccines exist yet Next-generation vaccines such as a meningitis quadrivalent conjugate vaccine New combinations vaccines and new administration systems HOSPITAL-ACQUIRED INFECTIONS Hospital-acquired infections are a major concern for public health in many industrialized countries and cause significant annual costs to healthcare systems. include up to 15,000 adults at 200 sites across ~20 countries. A Phase II study of the vaccine against Clostridium difficile was done in the U.S. The U.S. FDA granted fast-track designation to Sanofi Pasteur's investigational Clostridium difficile vaccine. CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE Sanofi Pasteur’s candidate vaccine against Clostridium difficile takes a toxoid-based approach, which has been used extensively in Sanofi Pasteur’s licensed vaccines against tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis (whooping cough). In August 2013, the company SANOFI PASTEUR’S OPEN INNOVATION initiated its Phase III clinical program called APPROACH Cdiffense to evaluate the safety, immunogenicity and efficacy of its Sixty percent of Sanofi Pasteur’s current investigational vaccine for the prevention of pipeline is the result of external primary symptomatic Clostridium difficile partnerships. infection (CDI). The Cdiffense Phase III clinical program has started recruiting volunteers for an international trial that will 14 PRESS KIT HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS (HIV) Vaccines & Diagnostics and Sanofi Pasteur, with the collaboration of the National Sanofi Pasteur is taking part in the global Department of Health in South Africa) effort to develop an HIV vaccine. Over the committed to building on the success of the last 20 years since Sanofi Pasteur's HIV RV144 HIV vaccine trial and evaluating vaccine development program was potentially improved pox-protein vaccines to established, the company has been determine if they might provide a significant collaborating with a number of leading public-health benefit. The P5 is working on governmental agencies and pharmaceutical follow-up clinical studies using improved companies. These partnerships have led to vaccine regimens in southern Africa and major advances in research, clinical study Thailand. design, and implementation. In February 2015, an HIV vaccine clinical trial was announced by the U.S. NIAID (National Institutes of Allergy & Infectious Diseases) division of the NIH (National Institutes of Health). This includes Sanofi Pasteur’s ALVAC-HIV investigational vaccine as the prime in a prime-boost regimen being studied in what is called the HVTN-100 (HIV Vaccine Trials Network) in South Africa. It is a preventive vaccine regimen similar to that used in the 6-year, HIV vaccine clinical trial in Thailand (RV-144), which was the first HIV vaccine trial to show any efficacy, in September 2009. The new study in South Africa is enrolling participants and is expected to take approximately two years to complete. HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS (HSV) Sanofi Pasteur’s HSV vaccine candidate is currently in Phase I in a trial sponsored by the U.S. NIH, involving 60 volunteers to assess the safety of the vaccine. The vaccine candidate has been shown to be safe and immunogenic in the preclinical stage, with the results supporting entry into Phase I clinical development. The Phase I study is designed to collect safety and immunogenicity data following three doses of the candidate vaccine administered over a period of 6 months in participants with and without HSV infection. Each of the study participants will be followed for one year from the time of the first immunization. More information on the study design can be found on HVTN 100 is the result of the Pox-Protein www.clinicaltrials.gov Public-Private Partnership (P5), a diverse group of organizations (the NIH, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, HVTN, the U.S. Military HIV Research Program, Novartis 15 PRESS KIT AT THE CUTTING EDGE OF VACCINE DEVELOPMENT Sanofi Pasteur continually works to remain at In October 2013, Sanofi Pasteur announced the forefront of vaccine research and a partnership with the Bill & Melinda Gates development. Whether alone or in Foundation to explore and develop new collaboration with partners, Sanofi Pasteur is platforms and methods intended to accelerate seeking new approaches to combat infectious vaccine R&D in areas of global health. In diseases. Several vaccines are under June 2011, a U.S. 101 million vaccine development stemming from agreements research and development facility was signed between Sanofi Pasteur and opened at the Connaught’s Campus in north biotechnology industry partners. Toronto. This facility establishes the Connaught Campus as the North American Research into disease epidemiology and Centre of Excellence in analytical and basic immunology is also supported, bioprocessing R&D for Sanofi Pasteur underpinning the scientific rationale for globally. In 2014 and 2010, Sanofi Pasteur vaccine development and improving signed agreements with Valneva (ex-Vivalis) knowledge of when and where vaccines are for the discovery of human monoclonal required most. In March 2014, Sanofi Pasteur antibodies against infectious diseases. In signed a cooperation agreement with SK April 2010, Sanofi Pasteur entered into a Chemicals Co. of South Korea to co-develop partnership with the U.S. Naval Medical an innovative pneumococcal conjugate Research Center (NMRC) to develop a vaccine (PCV). promising new bacterial vaccine against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). ETEC causes nearly 400,000 childhood deaths in the developing world each year. VaxDesign is a U.S. biotechnology company that develops, manufactures and markets in vitro models of the human immune system. VaxDesign is the developer of the Modular Invitro Construct (MIMIC®) technology that melds immunology with engineering to find solutions to complex biological problems. MIMIC®is useful in assessing the potential of Sanofi Pasteur’s vaccine candidates, providing a key filter in the preclinical stage before Phase I clinical trials. In October 2011, Sanofi Pasteur’s VaxDesign Corp. entered a 4-year collaboration in the field of prophylactic and therapeutic vaccines for infectious diseases. The agreement signed by Sanofi Pasteur S.A., Curevac (German global leader in mRNA based vaccination technologies) and In-Cell-Art (French Biotech company specialized in nano-carriers technologies) concerns a project co-funded by the U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA). Sanofi Pasteur acquired VaxDesign in 2010. 16 PRESS KIT GLOBAL COMMITMENT TO IMPROVE PUBLIC HEALTH PARTNERING WITH THE IMMUNIZATION COMMUNITY Sanofi Pasteur works in partnership within the immunization community, including policy makers, donors, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs), to ensure that the largest number of people benefit from vaccination. Immunization Community: Partnerships and co-operation between members of the immunization community are essential if vaccines are to be supplied to those who need them most. Sanofi Pasteur works with many of the institutions represented in this diagram. 17 PRESS KIT INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATIONS Sanofi Pasteur supports Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, which is a public-private partnership focused on increasing children's access to vaccines in poor countries. Partners include national governments, UNICEF (United Nations Children’s Fund), WHO, The World SUPPORTING IMMUNIZATION INFRASTRUCTURE The cost of vaccine administration, weak healthcare infrastructure and in some cases conflict mean that many people living in the world’s poorest countries do not have access to vaccines. Bank, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the vaccine industry, public health institutions, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs). Sanofi Pasteur has developed specially adapted packaging and established tiered pricing policies in order to widen access to Sanofi Pasteur has ongoing partnerships with a number of international organizations, including UNICEF, to supply vaccines where vaccines in developing countries. This strategy helps provide access to vaccines in countries supported by Gavi. they are needed most. Each year, the company provides nearly 400 million doses of vaccine to UNICEF and other international organizations. Since 2003, Sanofi Pasteur has provided 6 million doses of yellow fever vaccine each year for the stockpile funded by Gavi to control outbreaks in Africa. 18 PRESS KIT TRAINING AND KNOWLEDGE SHARING PROGRAMS From 2002 to 2014, EPIVAC has trained and certified nearly 525 doctors. The EPIVAC Program is one of Sanofi Pasteur’s contributions to the Vaccine Alliance (Gavi). It is implemented by the Preventive Medicine Agency (AMP) and aims at strengthening the performance of the national immunization programs in Francophone sub-Saharan Africa. The program was developed in conjunction with the national governments of eleven Gavi This EPIVAC program won the 2014 Gates Vaccines Innovation Award in recognition of the interest of the initiative that helps building countries capabilities and has proven being impactful on vaccination coverage. eligible countries (Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Côte d’Ivoire, Guinea, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, EPIVAC-trained officers positively impacted Senegal, and Togo) and participating an estimated 6 million lives in 2012. In 2014, universities (Cocody-Abidjan in Côte d’Ivoire the EPIVAC program was restructured, and Paris-Dauphine in France), in leading to new university partnerships and collaboration with the WHO, UNICEF and diplomas adapted to reflect the changing others working in Africa. immunization context under the name of EPIVAC PLUS. In the areas of research and knowledge sharing, Sanofi Pasteur maintains privileged partnerships with Fondation Mérieux (a non-profit organization founded in 1967 by Dr Charles Mérieux). The Foundation contributes to medicine and the improvement of public health by organizing scientific events and training courses, publishing reports, and funding research. Since its inception, Sanofi Pasteur has supported many of the Foundation’s events, such as the International Vaccinology Program. 19 PRESS KIT VACCINATION BASICS THE VALUE OF VACCINES However, it remains important to develop improved vaccines and increase access to Apart from clean, safe drinking water, no human action rivals immunization in preventing infectious diseases and reducing these vaccines, enabling even more lives to be saved. It is also important to recognize that vaccination is an ongoing challenge. mortality rates7. Vaccination saves lives: History shows that a decrease in more than 3 million lives every year8 thanks immunization coverage sets the stage for the to the vast range of vaccines providing protection from over 26 infectious diseases. reappearance of disease in previously protected populations. The resurgence of diphtheria in the 1990s in certain Eastern Vaccination also saves money, being one of the most cost-effective healthcare investments available. For instance, in the U.S., a cost-benefit analysis indicates that every dollar invested in a vaccine dose saves up to US $27 in health-care expenses9. European countries, with more than 125,000 cases and 4,000 deaths reported10, illustrates that continued vigilance is crucial to controlling and eradicating some infectious diseases in the future. More recently, the U.S. experienced a record number of measles cases during 2014, with 668 cases from 27 states reported to the CDC's National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD). This is the greatest number of cases since measles elimination was documented in the U.S. in 2000.11 REDUCING THE BURDEN OF DISEASE Since the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) was launched in 1988, reported cases of polio have fallen by 99% with more than 10 million people escaping paralysis12. 20 PRESS KIT WHAT IS IMMUNIZATION? Infectious diseases are a major cause of death, in particular among children and young adults. Infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms such as viruses, bacteria, parasites or fungi. They are present everywhere and may survive in many types of environments (soil, water, food) or hosts (humans, animals). Vaccines are produced from whole bacteria or viruses, from their components (polysaccharides, proteins), or the substances they secrete (toxins), in which their capacity to provoke a disease has been eliminated while keeping intact their ability to induce a specific immune response. The immune response stimulated by a vaccine is vital to ensure that enough antibodies are made and that the body’s natural defenses Vaccination can protect against these are able to fight off any infection in the future. diseases. It provides an individual with protection from an infection by stimulating an immune reaction and thereby boosting the natural defenses of the body. MAIN VACCINE TYPES LIVE ATTENUATED VACCINES The bacteria or virus is weakened. Its ability to cause disease is removed, either by growing it in a certain way or by using physical or chemical treatments. But the pathogen is still able to produce an immune response. Examples: Mumps, measles, rubella, polio (oral), yellow fever, tuberculosis. INACTIVATED VACCINES Inactivated vaccines can be produced from the whole microorganism or only parts of it. Whole germ vaccines are made from the entire pathogenic agent, which is killed using chemicals or heat, without altering its immunogenicity. Sub-unit vaccines only comprise those parts of the infectious agent necessary to obtain an immune response (antigens). Examples: Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, Hib, meningococcal infections, typhoid fever, pneumococcal infections, influenza, rabies, polio (injectable), hepatitis A, Japanese encephalitis. RECOMBINANT VACCINES Recombinant vaccines are produced by genetic engineering. Other animal cells or yeasts can be used as ‘antigen-factories’ producing large amounts of vaccine antigen, which are then used to produce an immune response. Example: Hepatitis B. 21 PRESS KIT THE VACCINE DEVELOPMENT CYCLE Vaccine research is long, complex and costly. Because a vaccine is a biological product made from living microorganisms, its development cycle is quite different from that of a pharmaceutical product: Exploratory stage: to understand the disease, its epidemiological data and the right proteins (antigens) to use in preventing or treating the disease Pre-clinical stage: to assess antigen safety and select the best candidate vaccine Clinical development: a dozen (Phase I) to thousand people (Phase III) are involved in clinical trials and the first batches are produced (clinical batches and industrial batches for compliance) Regulatory approval: all the data collected through the preceding stages are submitted to the relevant health authorities for approval Manufacturing process: takes 6–22 months to produce a single batch of vaccine Quality control: approximately 70% of production time is dedicated to quality control and pharmacovigilance procedures in the clinical development and production phases 22 PRESS KIT HISTORY AND HERITAGE FOUR PATHS, ONE DESTINY The origin of Sanofi Pasteur dates back more than a century and is closely linked with the achievements of Louis Pasteur, the Mérieux family, John FitzGerald and Richard Slee. Although each followed a unique path, they shared one goal – protecting people from infectious diseases. LOUIS PASTEUR: A SCIENTIFIC VISIONARY THE MÉRIEUX FAMILY: THREE GENERATIONS OF INNOVATORS Profoundly influenced by the teaching of Louis Pasteur, Marcel Mérieux established the Institut Biologique Mérieux. Three generations of the Mérieux family—Marcel, son Charles and grandson Alain—dedicated their lives to protecting people from infectious diseases. The most important contribution of the Institut Mérieux was the development of Louis Pasteur made a series of discoveries throughout his career that revolutionized modern medicine and laid the groundwork for the practice of microbiology. His contributions stem from his industrial-scale vaccine production, allowing large numbers of people to be vaccinated in a relatively short period of time. In 1974, techniques developed by the Institute stopped an epidemic of meningococcal meningitis in Brazil, where 90 million people were immunized in nine months. “germ theory of disease” – proving that infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms. Further to this theory, Pasteur found that injecting a weakened form of a microorganism could protect the body from the diseases that it causes. This discovery led to the development of a number of vaccines, including the rabies vaccine, first administered to a human in 1885. Pasteur dedicated the final years of his life to the establishment of Institut Pasteur, a non-profit organization that continues to work on protecting people from infectious diseases. Sanofi Pasteur has maintained a privileged relationship with the Institute. 23 PRESS KIT JOHN FITZGERALD: CANADA’S PUBLIC HEALTH PIONEER RICHARD SLEE: A VACCINE TRAILBLAZER John FitzGerald had a In 1897, Richard Slee vision of producing life- founded the Pocono saving, public-health Biological Laboratories in products at prices Swiftwater, Pennsylvania, within everyone’s to house the production of reach. Founded by FitzGerald in 1914, a new breed of smallpox vaccine. More than Connaught Laboratories grew rapidly, 100 years later, his legacy remains intact— producing vaccines and serums against smallpox has been officially eradicated diphtheria, smallpox, tetanus and meningitis. globally since 1980, and his laboratory has The Laboratories also made an important grown to become the location of Sanofi contribution to the battle against polio. After Pasteur in the U.S. he developed the first injectable polio vaccine, Dr. Jonas Salk used techniques developed by Connaught scientists to produce polio vaccine on a large scale, bringing an end to the epidemics in North America in the 1950s. 24 PRESS KIT SANOFI PASTEUR’S HISTORY 1885 Louis Pasteur creates the rabies vaccine. 1897 Profoundly influenced by the teachings of Louis Pasteur, Marcel Mérieux establishes Institut Biologique Mérieux. Across the Atlantic, Richard Slee opens the Pocono Biological Laboratories, which today houses the U.S. headquarters of Sanofi Pasteur. 1914 In Toronto, John Fitzgerald establishes a laboratory for the production of a diphtheria antitoxin. Formerly known as Connaught Laboratories, this is now the headquarters of Sanofi Pasteur in Canada. 1937 Charles Mérieux succeeds his father, Marcel. He develops a foot and mouth vaccine, which saves six million cattle during a severe epidemic in 1952. Industrial virology is born and applied to human medicine. 1967 Alain Mérieux succeeds his father, Charles, and Institut Mérieux becomes a worldwide player in the field of applied immunology. 1968 Rhône-Poulenc acquires a majority stake in Institut Mérieux. 1973 Institut Pasteur production site is created in Val de Reuil, France. The site will be acquired by Institut Mérieux in 1985. 1985 Institut Mérieux acquires Institut Pasteur production. 1989 Institut Mérieux acquires Connaught Laboratories and becomes the world leader in vaccines. 1990 Institut Mérieux becomes Pasteur Mérieux Sérums & Vaccins. 1994 Pasteur Mérieux Sérums & Vaccins becomes a wholly owned subsidiary of the Rhône-Poulenc Group. 1994 Pasteur Mérieux MSD is founded. Known today as Sanofi Pasteur MSD, it is a joint venture with Merck & Co. covering 19 countries in Europe. 1996 Pasteur Mérieux Sérums & Vaccins and Connaught Laboratories adopt the name Pasteur Mérieux Connaught. 1999 Rhône-Poulenc and Hoechst merge their life sciences activity—pharmaceuticals, animal health and crop science—to form a single company, Aventis. Pasteur Mérieux Connaught changes its name to Aventis Pasteur. 2004 Sanofi-synthelabo acquired Aventis, becoming sanofi-aventis Group. Aventis Pasteur becomes Sanofi Pasteur. 2008 Sanofi Pasteur acquired Acambis plc, a biotech company. 2009 Sanofi Pasteur acquired Shantha Biotechechnics, a vaccine manufacturer based in India. 2010 Sanofi Pasteur acquired VaxDesign, a U.S. biotechnology company. 2011 Sanofi Pasteur acquired Topaz Pharmaceuticals, a pharmaceutical company. 25 PRESS KIT References 1.World Health Organization Fact sheet N°211 Revised March 2003 – Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/2003/fs211/en. Accessed November 20, 2015. 2.World Health Organization Fact sheet N°114 Updated October 2015 – Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs114/en/. Accessed November 20, 2015. 3.World Health Organization Fact sheet N°100 Updated March 2014 – Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs100/en/. Accessed November 20, 2015. 4.Tomich N, ed. The Global Vaccine Shortage: The Threat to Children and What to Do About It. New Canaan, Conn: The Albert B. Sabin Vaccine Institute; 2003:26. Available at: http://www.sabin.org/files/attachment/entiredoc.pdf. Accessed December 2, 2011 5.Wilde H. What are today's orphaned vaccines? CID [serial online]. 2001; 33:648-650, Available at: http://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/pdf/10.1086/322705. Accessed November 20, 2015. 6.World Health Organization Fact sheet N°117 Revised May 2015 – Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs117/en/. Accessed November 20, 2015. 7.Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA. Vaccines. 4th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: W.B. Saunders; 2004:1 8.World Health Organization. 2004 immunization data. Available at: http://www.euro.who.int/data/assets/pdf_file/0017/84302/Seven_Key_Reasons.pdf. Accessed April 17, 2014. 9.Path. The Cornerstone of Public Health. Publication date: April 2015 – Available at: http://www.path.org/publications/detail.php?i=1937. Accessed November 20, 2015. 10.World Health Organization. Expanded program on immunization (EPI). Update: diphtheria epidemic in the newly independent states of the former USSR, January 1995-March 1996. WER [serial online].1996;71(33):245-252. Available at: http://www.who.int/docstore/wer/pdf/1996/wer7133.pdf.Accessed November 20, 2015. 11.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles Cases Outbreaks. http://www.cdc.gov/measles/casesoutbreaks.html. Accessed November 20, 2015 12.World Health Organization Fact sheet N°114 Updated October 2015 – Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs114/en/. Accessed November 20, 2015. 26 PRESS KIT