* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Outline 4
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
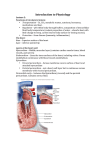
I. Anatomy of the Heart A. Heart Wall 1. Location – Mediastinum 2. Gross Anatomy a. Base b. Apex 3. Pericardium – Pericardial Sac a. Fibrous Pericardium b. Serous Pericardium 1) Parietal Pericardium 2) Visceral Pericardium – Epicardium c. Pericardial Cavity 1) Serous Fluid d. Clinical Application: Pericarditis 4. Layers a. Epicardium b. Myocardium 1) Cardiocytes (Cardiac muscle cells) a. Uninucleated and Branched b. Intercalated discs 1) Cardiac (Fibrous) Skeleton of the Heart c. Endocardium 1) Continuous with Endothelium of vessels B. External and Internal Anatomy of the Heart 1. Atria – Receiving chambers a. Right Atrium 1) Receives Blood from a) Superior Vena Cava b) Inferior Vena Cava c) Coronary Sinus b. Left Atrium 1) Receives Blood from a) Pulmonary Veins* - Oxygenated blood - Usually 4 vessels (3-5) 2. Ventricles – Pumping chambers a. Right Ventricle 1) Pumps blood for Pulmonary Circuit a) Pulmonary Trunk 1] Right and Left Pulmonary Arteries* - Deoxygenated blood b. Left Ventricle 1) Pumps blood for Systemic Circuit a) Aorta 3. External Anatomy a. Auricle b. Coronary Sulcus (Atrioventricular Groove) c. Anterior Interventricular Sulcus d. Posterior Interventricular Sulcus e. Ligamentum arteriosum – Adult relic 1) Ductus arteriosus – Fetal bypass 4. Internal Anatomy a. Interatrial Septum 1) Fossa ovalis – Adult relic a) Foramen ovale – Fetal bypass b. Interventricular Septum c. Pectinate Muscles d. Trabeculae carneae e. Moderator band (Septomarginal band) 1) Passes electrical signals from septum to muscles in the right ventricle f. Heart Valves 1) Atrioventricular (AV) Valves a) Tricuspid Valve b) Bicuspid Valve (Mitral Valve) 1] Clinical Application: Mitral Valve Prolapse c) Chordae tendineae d) Papillary muscles 2) Semilunar Valves a) Aortic Semilunar Valve b) Pulmonary Semilunar Valve C. Coronary Circulation 1. Right Coronary Artery (RCA) a. Located in Coronary Sulcus (Atrioventricular Groove) b. Branches to 1) Atrial arteries 2) Marginal Arteries a) Right Ventricle 3) Posterior Interventricular Branch a) Located in Posterior Interventricular Sulcus b) Supplies Right and Left Ventricles and Interventricular Septum 2. Left Coronary Artery (LCA) a. Located in Coronary Sulcus (Atrioventricular Groove) 1) Branches to a) Anterior Interventricular Branch 1] Located in Anterior Interventricular Sulcus 2] Supplies Right and Left Ventricles and Interventricular Septum a) Circumflex Artery (Branch) 1] Located in Coronary Sulcus 2] Supplies Left ventricle and Left Atrium 3] Gives off Marginal arteries to Left Ventricle 3. Coronary Sinus a. Empties into Right Atrium b. Principal Tributaries 1) Great Cardiac Vein a) Anterior Drainage 2) Middle Cardiac Vein a) Posterior Drainage of RCA 3) Small Cardiac Vein a) Drain Right Marginal Region 4) Posterior Cardiac Vein a) Posterior Drainage of LCA 4. Anterior Cardiac Veins a. Empty into Right Atrium Directly 5. Anastomoses a. Arterial Anastomosis 6. Clinical Application: Myocardial Infarction (MI) D. Conducting System 1. Nodal cells 2. Sinoatrial (SA) node – Intrinsic Pacemaker a. Located inferior to where Superior Vena Cava enters Right Atrium b. Self-excites faster than other nodal cells 3. Atrioventricular (AV) node a. Located in the lower medial floor of right atrium b. Slows Conduction Velocity (100 msec) 1) Allows time for Atria to contract 4. Atrioventricular (AV) bundle – Bundle of His a. Located in the Interventricular Septum b. Conduction Velocity increases to highest speed 5. Right and Left Branches a. Moderator band (from Right Branch) conducts directly to Papillary muscle 6. Purkinje fibers a. Within the muscle bundles of the ventricular walls b. Distributes electrical impulse to cardiocytes 1) Ventricles contract