* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiac stress testing
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
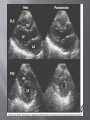
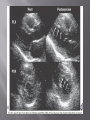
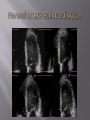
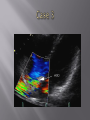
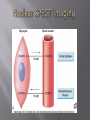
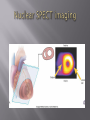
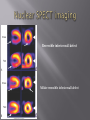
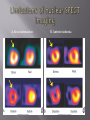
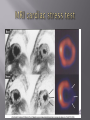
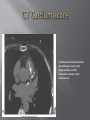
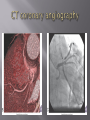
Karam Paul MS, MD, MBA, FACC Community Heart and Vascular ►Know why to undertake a stress test ►Know who should have one ►Know how it is performed ►Understand the limitations ►Understand which to choose ►Know what to do with the result Why do a stress test? ►Elicit abnormalities not present at rest ►Estimate functional capacity ►Estimate prognosis ►Likelihood of coronary artery disease ►Extent of coronary artery disease ►Effect of treatment Who should have one? ►Bayes’ Theorem ►Consider the ‘pre-test risk’ ►Sensitivity & specificity of the test ►Post-test probability of CAD ►Diagnostic power of EST is maximal when the pre-test probability is intermediate. ►Pre-existing coronary artery disease ►Diabetes ►Hypertension ►Smoking history ►Family history ►Renal disease Pre-existing coronary artery disease ►Diabetes ►Hypertension ►Hyperlipidemia ►Smoking history ►Family history ►Renal disease ►Pre-existing coronary artery disease ►Diabetes ►Hypertension ►Hyperlipidemia ►Smoking history ►Family history ►Renal disease How is it done? ►ECG ►Exercise capacity (METS – metabolic equivalent) ►Symptoms ►Blood pressure ►Heart rate response & recovery 1mm planar ST depression 3 consecutive beats ► The normal and rapid upsloping ST segment responses are normal responses to exercise. ► Minor ST depression can occur occasionally at submaximal workloads in patients with coronary disease. ► The slow upsloping ST segment pattern often demonstrates an ischemic response in patients with known coronary disease or those with a high pretest clinical risk of coronary disease. ► Downsloping ST segment depression represents a severe ischemic response. ► ST segment elevation in an infarct territory (Q wave lead) indicates a severe wall motion abnormality and, in most cases, is not considered an ischemic response. (From Chaitman BR: Exercise electrocardiographic stress testing. In Beller GA [ed]: Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease. In Braunwald E [series ed]: Atlas of Heart Diseases. Vol 5. Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease. Philadelphia, Current Medicine, 1995, pp 2.1-2.30 ► Influenced by: Body position Respiration Hyperventilation Drug Rx Myocardial ischemia Necrosis ► Pseudonormalisation: Usually non-diagnostic Consider ancillary imaging ►Peak HR > 85% of maximal predicted for age ►HR recovery >12 bpm (erect) ►HR recovery >18 bpm (supine) Parameters associated with adverse prognosis or multivessel disease ► Duration of symptom-limiting exercise <5 METs ► Failure to increase sBP ≥120mmHg, or a sustained decreased ≥ 10mmHg, or below rest levels, during progressive exercise ► ST segment depression ≥2mm, downsloping ST segment, starting at <5 METs, involving ≥5 leads, persisting ≥5 min into recovery ► Exercise-induced ST segment elevation (aVR excluded) ► Angina pectoris at low exercise workloads ► Reproducible sustained (>30 sec) or symptomatic ventricular tachycardia ► Non-diagnostic ECG changes ► False positives/false negatives ► Women – false positives ► Elderly – more sensitive/less specific ► Diabetics – autonomic dysfunction ► Hypertension ► Inability to exercise ► Drugs – digoxin; anti-anginals ► Anemia ► Cardiomyopathy ► Digoxin ► Glucose load ► Hyperventilation ► Hypokalemia ► Intraventricular conduction disturbance ► Mitral valve prolapse ► Pre-excitation syndrome ► Severe aortic stenosis ► Severe hypertension ► Severe hypoxia ► Severe volume overload (aortic or mitral regurgitation) ► Sudden excessive exercise ► Supraventricular tachycardia's Sensitivity 68% Specificity 77% Echocardiography Radionuclide imaging Compares pre & post: Regional contractility Overall systolic function Volumes Pressure gradients Filling pressures Pulmonary pressures Valvular function Factors which effect image quality: Body habitus Lung disease Breast implants ►54 year old bank project manager ►Exertional chest pain & dyspnea ►Ex-smoker ►TC = 6.7mmol/L ►Stress ECG – 2mm ST segment depression in 5 leads ►62 year old female ►Chest pain & dyspnea ►Treadmill exercise test – non-diagnostic sub-maximal Hypertension No ECG changes ►Exercised 7½ minutes (9.4 METS) ►No chest pain ►ECG changes ►24 year old female engineer ►Exertional dyspnea ►Palpitations Inducible dyspnea ►ECG partial right bundle branch block no ischemic changes ►43 year old male - airline catering ►Chest pain ►Dyspnea ►Inducible dyspnea ►Non-specific T wave changes ►No ST segment shift ►Global deterioration in left ventricular function ►Radio-tracer injection ►Isotopes: Thallium-201 Technetium 99m (sestamibi) ►Myocardial uptake ►Photon emission captured by gamma camera ►Rest & redistribution phases ►Pharmacologic protocols available ►Digital presentation Reversible inferior wall defect Milder reversible inferior wall defect ►Time-consuming ►Artifacts ►Balanced ischemia ►Radiation Normal apical thinning. A. Breast attenuation B. Anterior ischemia ►Risk of iatrogenic malignancy ►Linear no-threshold model ►Consider: age gender background Einstein, A. J. et al. Circulation 2007;116:1290-1305 Useful for: ►Patients unable to exercise ►ECG uninterpretable ►Unsuitable for DSE And…. ►No radiation But… ►Not currently available ►45 year old diabetic man ►Anterior chest discomfort with exertion ►Exercised for 2 mins 30 secs (4.6 METs) ►95% maximal predicted heart rate ►Mild chest pain ►BP increased from baseline to 180/80mmHg ►1mm ST depression in leads II, III, aVF, V4-6 1. Pre-test risk is intermediate 2. Post-test probability for cardiac events is high 3. The ECG changes are non-diagnostic 4. The ECG changes are false-positive in the setting of hypertension 5. Chest pain is not a useful symptom in diabetics 1. Pre-test risk is intermediate 2. Post-test probability for cardiac events is high 3. The ECG changes are non-diagnostic 4. The ECG changes are false-positive in the setting of hypertension 5. Chest pain is not a useful symptom in diabetics Parameters associated with adverse prognosis or multivessel disease ► Duration of symptom-limiting exercise <5 METs ► Failure to increase sBP ≥120mmHg, or a sustained decreased ≥ 10mmHg, or below rest levels, during progressive exercise ► ST segment depression ≥2mm, downsloping ST segment, starting at <5 METs, involving ≥5 leads, persisting ≥5 min into recovery ► Exercise-induced ST segment elevation (aVR excluded) ► Angina pectoris at low exercise workloads ► Reproducible sustained (>30 sec) or symptomatic ventricular tachycardia ►Pre-test risk of disease ►Sensitivity & specificity of the test ►Value of supplementary data ►AND JUST ONE MORE TIP…….. So….which one to choose? ►Remember Bayes’ theorem ►Consider the pre-test risk ►Be aware of the sensitivity & specificity of the test ►Apply the post test probability ►Correlates with presence & extent of CAD ►Strong negative predictive value ►Cannot predict functional significance ►Higher scores can predict events ►Recommended for asymptomatic with intermediate risk Calcification of the left anterior descending coronary artery (large arrow) and left circumflex coronary artery (small arrow). Score description RR 0 nil 1 – 99 mild 1.9 100 – 399 moderate 4.3 400 – 999 severe 7.2 >1000 extensive 10.8 ► Indicated – asymptomatic with intermediate risk ► Not for low risk/population screening ► High risk – use current guidelines ► Do not reduce Rx if intermediate risk & ‘0’ score ►2-dimensional & 3dimensional reconstructions ►Relies on slow, regular heart rate ►High negative predictive value (‘rule out’ ability) ►Lower positive predictive value (over-estimation tendency) ►Grading of stenosis limited ►Does not evaluate functional significance ►Radiation exposure ►Role not yet clearly defined ►Potential for those with intermediate likelihood of disease: Where stress testing not possible Stress test equivocal/uninterpretable Acute chest pain/no ECG changes/normal enzymes ►Role in anomalous anatomy