* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CSS307-System Programming
Distributed operating system wikipedia , lookup
Process management (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Ubuntu (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
Spring (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
Berkeley Software Distribution wikipedia , lookup
Mobile operating system wikipedia , lookup
Plan 9 from Bell Labs wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Linux kernel wikipedia , lookup
Caldera OpenLinux wikipedia , lookup
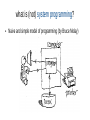
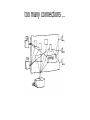
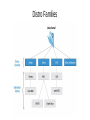
CSS307-System Programming Suleyman Demirel University Fall 2014 by Konstantin Latuta & EN3([ABCDEF]|KZ)04 Outline ● What is system programming? ● Grading Policy of CSS307 ● Introduction to Linux... ● Books what is (not) system programming? ● Naive and simple model of programming (by Bruce Molay) typical program in simple model reality is little bit more complicated... reality... ● Lots of programs ● Lost of users ● Lots of disk files ● Lots of devices and somehow they are connected too many connections ... the role of the operating system ● To manage all resources and connect the various devices to the correct programs the role of the operating system ● To provide services to programs: – Programs request services from the OS. The OS contains code to provide services we will use the services provided by the OS ● Input/Output ● Process management ● Memory ● Devices ● Timers ● IPC (interprocess communication) ● Network our goal is to understand Unix/Linux services by ● Seeing how they are used ● Learning about the system calls to invoke the services ● Writing our own versions of various system programs BUT before doing so We'll have a crash course on Linux (latest till the midterm) ● Linux philosophy and concepts ● Linux Structure and Installation ● Command Line Operations ● Linux Documentation ● File Operations ● User Environment ● Bash Shell Scripting and many more... Tentative Syllabus and Grading Policy ● Linux Crash Course 30% Labs and Quizzes Course Page: http://linux.sdu/~konst/ – ● Linux System Programming 30% Labs (C programming) 20% Creative Project (T-Shirt) 20% Final Exam 100% Linux History ● ● ● Linux is a free open source operating system initially intended for Intel x86-based PCs 1991, Linus Torvalds, a student in Helsinki started writing his own OS kernel, known as Linux kernel 1992, Linux was re-licensed with General Public License (GPL) by GNU (a project of Free Software Foundation which promotes free software) ● Mid-90s, Linux distributions emerged ● 1998, major companies announced support Linux Philosophy ● ● ● ● ● Linux is a free and open source version of UNIX Linux is maintained by a network of developers from all over the world Hierarchical filesystem with the top node / (aka root) Everything is a file (or a file-like object) Fully multitasking and multiuser OS https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H7Uz692S6T4 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RaFNXQ8Dat0 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_C-GAkLPAAc Linux Distributions ● ● Linux kernel is the core of a computer operating system (www.kernel.org) Linux distribution = kernel + some software tools – File management, user management, software package management tools ● commercially supported distributions: Red Hat, SUSE, Ubuntu ● free: CentOS, Fedora, Ubuntu, openSUSE ● And many others like Scientific Linux, Oracle Linux etc. Distro Families Debian Family Key Facts ● ● ● ● ● The Debian family is upstream for Ubuntu, and Ubuntu is upstream for Linux Mint and others. The Linux kernel 3.13 is used in Ubuntu 14.04. It uses the DPKG-based apt-get package manager (we cover in more detail later) to install, update, and remove packages in the system. Ubuntu has been widely used for cloud deployments. While Ubuntu is built on top of Debian, it uses the Unity graphical interface, is GNOME-based and differs quite a bit visually from the interface on standard Debian as well as other distributions. Fedora Family Key Facts ● ● ● ● ● The Fedora family is upstream for CentOS, RHEL, and Oracle Linux. The Linux kernel 2.6.32 is used in RHEL/CentOS 6.x It supports hardware platforms such as x86, x86-64, Itanium, PowerPC, and IBM System z. It uses the RPM-based yum package manager (we cover in more detail later) to install, update, and remove packages in the system. RHEL is widely used by enterprises which host their own systems. SUSE Family Key Facts ● ● ● ● ● SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) is upstream for openSUSE. The Linux kernel 3.11 is used in openSUSE 12.3. It uses the RPM-based zypper package manager to install, update, and remove packages in the system. It includes the YaST (Yet another System Tool) application for system administration purposes. SUSE is widely used in the retail sector. Summary ● Linux borrows heavily from the UNIX operating system, with which its creators were well versed. ● Linux accesses many features and services through files and file-like objects. ● ● ● ● ● ● Linux is a fully multitasking, multiuser operating system, with built-in networking and service processes known as daemons. Linux is developed by a loose confederation of developers from all over the world, collaborating over the Internet, with Linus Torvalds at the head. Technical skill and a desire to contribute are the only qualifications for participating. The Linux community is a far reaching ecosystem of developers, vendors, and users that supports and advances the Linux operating system. Some of the common terms used in Linux are: Kernel, Distribution, Boot loader, Service, Filesystem, X Window system, desktop environment, and command line. A full Linux distribution consists of the kernel plus a number of other software tools for file-related operations, user management, and software package management. There are three major distribution families within Linux: Fedora, SUSE and Debian. Readings ● The Linux Programmer’s Toolbox, John Fusco, 2006 ● Linux Essentials, LPI Introductory Programme, 2012 ● Understanding UNIX/Linux Programming, Bruce Molay, 2002 ● Computer Systems: A Programmers Perspective, Randal E. Bryant & David R. O’Hallaron, 2010 Credits ● ● Linux Foundation for pictures and material on Linux Bruce Molay for picture and introduction to system programming