* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BF961 N–Channel Dual Gate MOS-Fieldeffect Tetrode
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
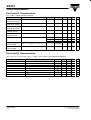
BF961 Vishay Semiconductors N–Channel Dual Gate MOS-Fieldeffect Tetrode, Depletion Mode Electrostatic sensitive device. Observe precautions for handling. Applications Input- and mixer stages especially for FM- and VHF TV-tuners up to 300 MHz. Features D Integrated gate protection diodes D High cross modulation performance D Low noise figure D High AGC-range D Low feedback capacitance D Low input capacitance 3 G2 D 4 2 G1 94 9307 96 12647 1 BF961 Marking: BF961 Plastic case (TO 50) 1=Drain, 2=Source, 3=Gate 1, 4=Gate 2 S 12623 Absolute Maximum Ratings Tamb = 25_C, unless otherwise specified Parameter Drain - source voltage Drain current Gate 1/Gate 2 - source peak current Total power dissipation Channel temperature Storage temperature range Test Conditions Type Tamb ≤ 60 °C Symbol Value VDS 20 ID 30 ±IG1/G2SM 10 Ptot 200 TCh 150 Tstg –55 to +150 Unit V mA mA mW °C °C Symbol RthChA Unit K/W Maximum Thermal Resistance Tamb = 25_C, unless otherwise specified Parameter Test Conditions Channel ambient on glass fibre printed board (40 x 25 x 1.5) mm3 plated with 35mm Cu Document Number 85002 Rev. 3, 20-Jan-99 Value 450 www.vishay.com 1 (7) BF961 Vishay Semiconductors Electrical DC Characteristics Tamb = 25_C, unless otherwise specified Parameter Drain - source breakdown voltage Gate 1 - source breakdown voltage Gate 2 - source breakdown voltage Gate 1 - source leakage current Gate 2 - source leakage current Drain current Test Conditions ID = 10 mA, –VG1S = –VG2S = 4 V Gate 1 - source cut-off voltage Gate 2 - source cut-off voltage VDS = 15 V, VG2S = 4 V, ID = 20 mA VDS = 15 V, VG1S = 0, ID = 20 mA Type Symbol V(BR)DS Min 20 ±IG1S = 10 mA, VG2S = VDS = 0 ±V(BR)G1SS ±IG2S = 10 mA, VG1S = VDS = 0 ±V(BR)G2SS Typ Max Unit V 8 14 V 8 14 V ±VG1S = 5 V, VG2S = VDS = 0 ±IG1SS 100 nA ±VG2S = 5 V, VG1S = VDS = 0 ±IG2SS 100 nA –VG1S(OFF) 20 10.5 20 3.5 mA mA mA V –VG2S(OFF) 3.5 V Max Unit mS pF pF fF pF dB dB dB VDS = 15 V, VG1S = 0, VG2S = 4 V BF961 BF961A BF961B IDSS IDSS IDSS 4 4 9.5 Electrical AC Characteristics VDS = 15 V, ID = 10 mA, VG2S = 4 V, f = 1 MHz , Tamb = 25_C, unless otherwise specified Parameter Forward transadmittance Gate 1 input capacitance Gate 2 input capacitance Feedback capacitance Output capacitance Power gain AGC range Noise figure www.vishay.com 2 (7) Test Conditions VG1S = 0, VG2S = 4 V GS = 2 mS, GL = 0.5 mS, f = 200 MHz VG2S = 4 to –2 V, f = 200 MHz GS = 2 mS, GL = 0.5 mS, f = 200 MHz Symbol y21s Cissg1 Cissg2 Crss Coss Gps DGps F Min 12 Typ 15 3.7 1.6 25 1.6 20 50 1.8 2.5 Document Number 85002 Rev. 3, 20-Jan-99 BF961 Vishay Semiconductors Typical Characteristics (Tamb = 25_C unless otherwise specified) 22 Y21S – Forward Transadmittance ( mS ) P tot – Total Power Dissipation ( mW ) 300 250 200 150 100 50 20 18 20 40 60 80 14 12 10 8 2V 1V 2 VG1S – Gate 1 Source Voltage ( V ) 96 12162 Figure 4. Forward Transadmittance vs. Gate 1 Source Voltage 4.0 C issg1 – Gate 1 Input Capacitance ( pF ) VG1S= 0.6V 20 18 ID – Drain Current ( mA ) 3V 0 –2.0–1.5–1.0–0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 22 0.4V 16 14 0.2V 12 10 0 8 –0.2V –0.4V –0.6V –0.8V 6 4 2 0 0 2 4 6 3.5 3.0 VDS=15V VG2S=4V f=1MHz 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 –2.0 –1.5 –1.0 –0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 VDS – Drain Source Voltage ( V ) 96 12160 VG1S – Gate 1 Source Voltage ( V ) 96 12163 Figure 2. Drain Current vs. Drain Source Voltage Figure 5. Gate 1 Input Capacitance vs. Gate 1 Source Voltage 4.0 24 22 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 VDS=15V IDS=10mA C issg2 – Gate 2 Input Capacitance ( pF ) Y21S – Forward Transadmittance ( mS ) 0V 4 Figure 1. Total Power Dissipation vs. Ambient Temperature VG1S=0.5V 0V –0.5V –2 96 12161 4V 6 100 120 140 160 Tamb – Ambient Temperature ( °C ) 96 12159 VG2S=5V 16 0 0 VDS=15V f=1MHz –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 VG2S – Gate 2 Source Voltage ( V ) Figure 3. Forward Transadmittance vs. Gate 2 Source Voltage Document Number 85002 Rev. 3, 20-Jan-99 3.6 VDS=15V VG1S=0 f=1MHz 3.2 2.8 2.4 2.0 1.6 1.2 0.8 0.4 0 –2 6 96 12164 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 VG2S – Gate 2 Source Voltage ( V ) Figure 6. Gate 2 Input Capacitance vs. Gate 2 Source Voltage www.vishay.com 3 (7) BF961 Vishay Semiconductors C oss – Output Capacitance ( pF ) 3.0 2.5 10 VG2S=4V f=1MHz VDS=15V VG2S=4V f=50...700MHz 5 0 Im ( y21 ) ( mS ) 2.0 1.5 1.0 f=50MHz ID=5mA 10mA 20mA –5 –10 100MHz 200MHz 300MHz –15 400MHz –20 0.5 500MHz 600MHz –25 700MHz 0 0 –30 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 VDS – Drain Source Voltage ( V ) 96 12165 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 Figure 7. Output Capacitance vs. Drain Source Voltage Figure 9. Short Circuit Forward Transfer Admittance 18 f=700MHz 16 Im ( y11 ) ( mS ) 12 Im ( y22 ) ( mS ) 600MHz 14 500MHz 10 400MHz 8 300MHz 6 VDS=15V VG2S=4V ID=5...20mA f=50...700MHz 200MHz 4 2 100MHz 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Figure 8. Short Circuit Input Admittance www.vishay.com 4 (7) 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 f=700MHz 96 12168 600MHz ID=5mA 500MHz ID=20mA 400MHz 300MHz VDS=15V VG2S=4V ID=5...20mA f=50...700MHz 200MHz 100MHz 0 10 Re (y11) ( mS ) 96 12166 Re (y21) ( mS ) 96 12167 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 Re (y22) ( mS ) Figure 10. Short Circuit Output Admittance Document Number 85002 Rev. 3, 20-Jan-99 BF961 Vishay Semiconductors VDS = 15 V, ID = 5 to 20 mA, VG2S = 4 V , Z0 = 50 W S12 S11 j 90° 120° j0.5 60° j2 150° j0.2 ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ 0 30° j5 0.2 0.5 1 2 1 5 600 700MHz 180° 0.04 0.08 0° 50 100 –j0.2 300 –j5 700 MHz 500 –j0.5 300 –150° –30° –j2 –120° –j 12 920 –60° –90° 12 921 Figure 11. Input reflection coefficient Figure 13. Reverse transmission coefficient S21 S22 j 90° 120° 60° j0.5 30° 400 j0.2 200 700MHz 50 180° j2 0.8 1.6 0° 0 j5 ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ 0.2 0.5 1 2 5 100 ID= 20mA 10mA –30° 5mA –30° –150° 300 500 –j0.2 12 922 –j2 –60° –90° Figure 12. Forward transmission coefficient Document Number 85002 Rev. 3, 20-Jan-99 –j5 700 MHz –j0.5 –120° 1 12 923 –j Figure 14. Output reflection coefficient www.vishay.com 5 (7) BF961 Vishay Semiconductors Dimensions in mm 96 12242 www.vishay.com 6 (7) Document Number 85002 Rev. 3, 20-Jan-99 BF961 Vishay Semiconductors Ozone Depleting Substances Policy Statement It is the policy of Vishay Semiconductor GmbH to 1. Meet all present and future national and international statutory requirements. 2. Regularly and continuously improve the performance of our products, processes, distribution and operating systems with respect to their impact on the health and safety of our employees and the public, as well as their impact on the environment. It is particular concern to control or eliminate releases of those substances into the atmosphere which are known as ozone depleting substances ( ODSs ). The Montreal Protocol ( 1987 ) and its London Amendments ( 1990 ) intend to severely restrict the use of ODSs and forbid their use within the next ten years. Various national and international initiatives are pressing for an earlier ban on these substances. Vishay Semiconductor GmbH has been able to use its policy of continuous improvements to eliminate the use of ODSs listed in the following documents. 1. Annex A, B and list of transitional substances of the Montreal Protocol and the London Amendments respectively 2 . Class I and II ozone depleting substances in the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990 by the Environmental Protection Agency ( EPA ) in the USA 3. Council Decision 88/540/EEC and 91/690/EEC Annex A, B and C ( transitional substances ) respectively. Vishay Semiconductor GmbH can certify that our semiconductors are not manufactured with ozone depleting substances and do not contain such substances. We reserve the right to make changes to improve technical design and may do so without further notice. Parameters can vary in different applications. All operating parameters must be validated for each customer application by the customer. Should the buyer use Vishay-Semiconductors products for any unintended or unauthorized application, the buyer shall indemnify Vishay-Semiconductors against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal damage, injury or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized use. Vishay Semiconductor GmbH, P.O.B. 3535, D-74025 Heilbronn, Germany Telephone: 49 ( 0 ) 7131 67 2831, Fax number: 49 ( 0 ) 7131 67 2423 Document Number 85002 Rev. 3, 20-Jan-99 www.vishay.com 7 (7)