* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sedation Pharmacology ()
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
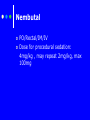
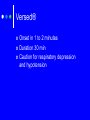
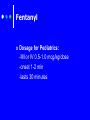
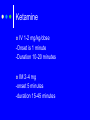
Procedural Sedation Pharmacology Deb Updegraff R.N., P.N.P, C.N.S. Clinical Nurse Specialist LPCH Pediatric Intensive Care Unit Procedural Sedation The phrase “procedural sedation” refers to techniques of managing a patient’s pain and anxiety to facilitate appropriate medical care in a safe, effective and humane fashion. Sedation Pharmacolgy Individual responses are dependant on: Age Concurrent disease states Concurrent drug therapy Chloral Hydrate Hypnotic“Short term sedative and hypnotic given prior to nonpainful procedures Chloral Hydrate Usually given to Outpatients due to relative low risk profile. For nonpainful procedures only. EEGs MRI/CT Scans Echocardiograms Chloral Hydrate PO/Rectal Dose: 50mg/kg give 30-60 minutes prior to procedure. Can repeat x1 25mg/kg Not to exceed 100mg/kg in a 24 hour period Chloral Hydrate Expect a moderate decrease in heart rate and blood pressure in patients ASA I-II For infants < 6 months there is ↑ risk for apnea and hypoxia. Age a limiting factor. High failure rate in children > 4 years. Pentobarbital : Nembutal® Barbituate- Non elective central nervous system depressants primarily used as Hypnotic sedative for non painful procedures. Nembutal PO/Rectal/IM/IV Dose for procedural sedation: 4mg/kg , may repeat 2mg/kg, max 100mg Nembutal: precautions Rapid IV injection ie, can cause respiratory depression, apnea, laryngospasm, bronchospasm and hypotension Recommended to infuse IV dose over 10-30 minutes. Can significantly decrease cardiac output and should be avoided with CHF Benzodiazepines Midazolam- Versed® Lorazepam - Ativan® Induce anterograde amnesia (not retrograde) May have some opioid sparing effect by ↓ anticipatory pain response Midazolam -® Versed Most commonly used Benzo for preoperative and pre-procedural sedation. Undergoes hepatic metabolism and renal excretion and prolonged effects seen with dysfunction of either system Sedative, amnestic and anxiolytic with no analgesic properties Commonly used with an opioid analgesic such as Fentanly® Versed® Onset in 1 to 2 minutes Duration 30 min Caution for respiratory depression and hypotension Dosage for children having procedures: PO; 0.5 mg/kg/dose may repeat once with 0.25mg/kg/dose. Max dose: 20mg. IV: 0.05-0.1 mg/kg dose. May repeat over several minutes to a max dose of 0.1-0.2 mg/kg. Intranasal: 0.2-0.3 mg/kg. May repeat in 15 min Adults: 0.5 mg to 2mg slow push over at least 2 min. Usual dose needed is 2.5 – 5 mg . > 5mg generally not needed. Fentanyl- Sublimaze® Used in combination with Versed for many years due to rapid onset and effectiveness Synthetic opioid Metabolized by the liver Short duration of effect Pure analgesic (should not be used alone) Least histamine release of opiates Caution: Chest rigidity with rapid infusion and hypotension Fentanyl Dosage for Pediatrics: -IM or IV 0.5-1.0 mcg/kg/dose -onset 1-2 min -lasts 30 minutes Etomidate Classified as a General Anesthetic Ultra short acting nonbarbiturate hypnotic used for the induction of Anesthesia Used for Sedation in Adults 0.2mg/kg IV given over 30-60 seconds Onset <1minutes Duration 3-5 minutes Limited data, Action too short for some procedures Ketamine-Ketalar® Classified as a general anesthetic Rapid acting dissociative anesthetic that produces a profound analgesic effect Gaining favor in children due to reliable effects and strong safety profile Ketamine When patients are on ketamine they may appear awake. Eyes may remain open, they may have nystagmus. Ketamine is a potent phencyclidine deriviative Produces potent analgesia and rapid sedation while it preserves respiratory drive and airway protective reflexes Ketamine IV 1-2 mg/kg/dose -Onset is 1 minute -Duration 10-20 minutes IM 2-4 mg -onset 5 minutes -duration 15-45 minutes Ketamine Caution: Nystagmus can occur along with hypersecretions, agitation Delirium, vomiting , myoclonus and laryngospasm PropofolClassified as a general anesthetic -Lower doses sedation hypnosis Anmestic, anxiolytic, antiemetic, and antiepileptic properties No Analgesic effects Propofol Dosing 2.5 -3.5 mg/kg/ dose over 2030 seconds Onset 10-30 seconds Duration 10-20 minutes For prolonged procedures may require continuous infusion 125300mcg/kg/minute. (smaller children may require smaller infusion rates. Propofol Caution Profound Respiratory Depression Profound Irreversible bradycardia Profound Hypotension Avoid with Soy or Egg allergies