* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Femoral triangle
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
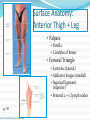
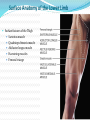
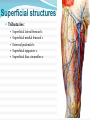
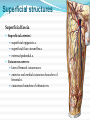
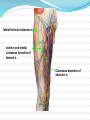
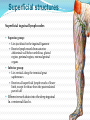
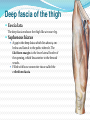
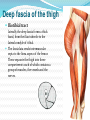
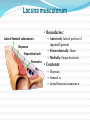
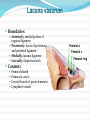
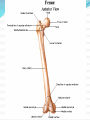
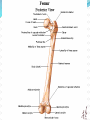
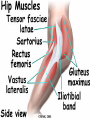
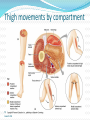
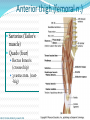
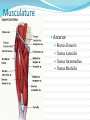
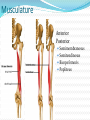
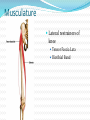
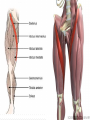
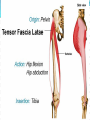
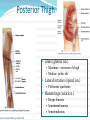
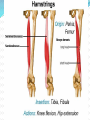
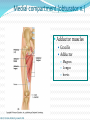
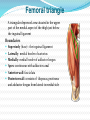
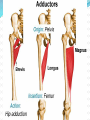
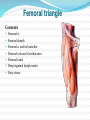
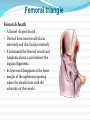
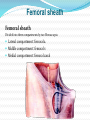
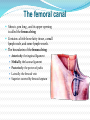
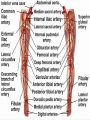
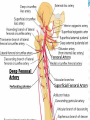
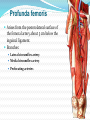
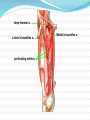
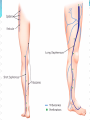
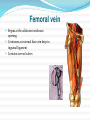
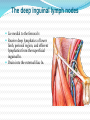
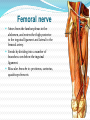
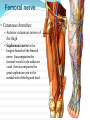
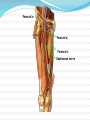
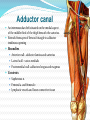
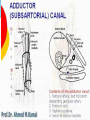
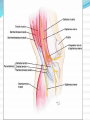
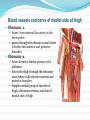
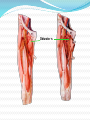
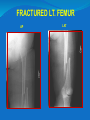
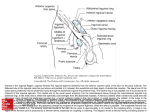
Dr. S. Nishan Silva (MBBS) Surface Anatomy: Anterior Thigh + Leg Palpate Patella Condyles of femur Femoral Triangle Sartorius (lateral) Adductor longus (medial) Inguinal ligament (superior) Femoral a + v, lymph nodes pg 785 Frolich, Human Anatomy, Lower LImb Surface Anatomy of the Lower Limb Surface features of the Thigh Sartorius muscle Quadriceps femoris muscle Adductor longus muscle Hamstring muscles Femoral triange 12-3 Superficial structures Great saphenous vein Drains the medial end of dorsal venous arch of foot Passes upward directly in front of the medial malleolus. Then ascends on medial side of the leg. Passes behind the knee and curves forward around the medial side of the thigh. Passes through the saphenous hiatus in the deep fascia and joins the femoral vein about 4 cm below and lateral to the pubic tubercle. Superficial structures Tributaries: Superficial lateral femoral v. Superficial medial femoral v. External pudendal v. Superficial epigastric v. Superficial iliac circumflex v. Varicose veins Superficial structures Superficial fascia Superficial arteries: superficial epigastric a. superficial iliac circumflex a. external pudendal a. Cutaneous nerves: lateral femoral cutaneous n. anterior and medial cutaneous branches of femoral n. cutaneous branches of obturator n. lateral femoral cutaneous n. anterior and medial cutaneous branches of femoral n. Cutaneous branches of obturator n. Superficial structures Superficial inguinal lymph nodes Superior group: Lies just distal to the inguinal ligament Receive lymph vessels from anterior abdominal wall below umbilicus, gluteal region, perineal region, external genital organs Inferior group: Lies vertical along the terminal great saphenous v. Receives all superficial lymph vessels of lower limb, except for those from the posterolateral part of calf Efferent vessels drain into the deep inguinal ln. or external iliac ln. Deep fascia of the thigh Fascia lata The deep fascia encloses the thigh like a trouser leg. Saphenous hiatus A gap in the deep fasica which lies about 4 cm below and lateral to the pubic tubercle. The falciform margin is the lower lateral border of the opening, which lies anterior to the femoral vessels. Filled with loose connective tissue called the cribriform fascia Deep fascia of the thigh Iliotibial tract laterally the deep fascia forms a thick band, from the iliac tubercle to the lateral condyle of tibial. The fascia lata sends intermuscular septa to the linea aspera of the femur. These separate the thigh into three compartments each of which contains a group of muscles, the vessels and the nerves. Lacuna musculorum Boundaries: Lateral femoral cutaneous n. Iliopsoas Iliopectinal arch Femoral n. Anteriorly: lateral portion of inguinal ligament Posterolaterally: ilium Medially: iliopectinal arch Contents: Iliopsoas femoral n. lateral femoral cutaneous n. Lacuna vasorum Boundaries: Anteriorly: medial portion of inguinal ligament Posteriorly: fascia of pecteineus and pectineal ligament Medially: lacunar ligament Laterally: iliopectinal arch Contents: Femoral sheath Femoral a. and v. Genital branch of genitofemoral n. Lymphatic vessels Femoral a. Femoral v. Femoral ring Anterior/Posterior compartments ANTERIOR POSTERIOR COMPARTMENT COMPARTMENT MOVEMENT Extension Flexion MUSCLES Quads Shin Hamstrings Gastrocs NERVES Femoral n. (lumbar plexus) Sciatic n. (sacral plexus) Frolich, Human Anatomy, Lower LImb BONY ANATOMY OF THE FEMUR BONY ANATOMY OF THE FEMUR Thigh movements by compartment Frolich, Human Anatomy, Lower LImb Anterior thigh (femoral n.) Sartorius (Tailor’s muscle) Quads (four) Rectus femoris (crosses hip) 3 vastus mm. (vast-big) Frolich, Human Anatomy, Lower LImb Musculature Anterior Rectus Femoris Vastus Lateralis Vastus Intermedius Vastus Medialis Musculature Anterior Posterior Semimembranosus Semitendinosus Biceps femoris Popliteus Musculature Lateral restrainers of knee Tensor Fascia Lata Iliotibial Band Posterior Thigh Frolich, Human Anatomy, Lower LImb Gluts (gluteal nn.) Maximus—extensor of thigh Medius--pelvic tilt Lateral rotators (spinal nn.) Piriformis syndrome Hamstrings (sciatic n.) Biceps femoris Semimembranous Semitendinous Medial compartment (obturator n.) Frolich, Human Anatomy, Lower LImb Adductor muscles Gracilis Adductor Magnus Longus brevis Femoral triangle A triangular depressed area situated in the upper part of the medial aspect of the thigh just below the inguinal ligament Boundaries Superiorly (base) : the inguinal ligament Laterally: medial border of sartorius Medially: medial border of adductor longus Apex: continuous with adductor canal Anterior wall: fascia lata Posterior wall: consists of iliopsoas, pectineus and adductor longus from lateral to medial side Femoral triangle Contents Femoral n. Femoral sheath Femoral a. and its branches Femoral vein and its tributaries. Femoral canal Deep inguinal lymph nodes Fatty tissue Femoral triangle Femoral sheath A funnel- shaped sheath Derived from transversalis fascia anteriorly and iliac fascia posteriorly It surroumds the femoral vessels and lymphatic about 2.5cm belower the inguinal ligamemt. Its lower end disappears at the lower margin of the saphenous opening where the sheath fuses with the adventitia of the vessels. Femoral sheath Femoral sheath Divided into three compartments by two fibrous septa Lateral compartment: femoral a. Middle compartment: femoral v. Medial compartment: femoral canal The femoral canal About 1.3cm long , and its upper opening is called the femoral ring Contains: a little loose fatty tissue, a small lymph node, and some lymph vessels. The boundaries of the femoral ring Anteriorly: the inguinal ligament Medially: the lacunar ligament Posteriorly: the pecten of pubis Laterally: the femoral vein Superior: covered by femoral septum Femoral hernia If a loop of intestine is forced into the femoral ring, it expands to form a swelling in the upper part of the thigh. Such a condition is known as a femoral hernia . A femoral hernia is more common in women than in men (possibly because their wider pelvis and femoral canal ). Femoral artery Femoral a. Continuation of the external iliac a. Begins midpoint of inguinal ligament Ends at the adductor tendinous opening by entering the popliteal fossa as the popliteal artery Principal branch-deep femeral a. arises from the posterolateral surface of the femoral artery about 5 cm below the inguinal ligament. Medial femoral circumflex lateral femoral circumflex Four perforating arteries Profunda femoris Arises from the posterolateral surface of the femoral artery about 5 cm below the inguinal ligament. Branches: Lateral circumflex artery. Medial circumflex artery. Perforating arteries deep femeral a. Lateral circumflex a. perforating arteries Medial circumflex a. Femoral vein Begins at the adductor tendinous opening Continues as external iliac vein deep to inguinal ligament Contains several valves The deep inguinal lymph nodes Lie medial to the femoral v. Receive deep lymphatics of lower limb, perineal region, and efferent lymphatics from the superficial inguinal ln. Drain into the external iliac ln. Femoral nerve Arises from the lumbar plexus in the abdomen, and enters the thigh posterior to the inguinal ligament and lateral to the femoral artery. It ends by dividing into a number of branches 2 cm below the inguinal ligament. Muscular branche to: pectineus, sartorius, quadriceps femoris Femoral nerve Cutaneous branches: Anterior cutaneous nerves of the thigh Saphenous nerve is the longest branch of the femoral nerve. It accompanies the femoral vessels in the adductor canal, then accompanies the great saphenous vein to the medial side of the leg and food. Femoral n. Femoral a. Femoral v. Saphenous nerve Adductor canal An intermuscular cleft situated on the medial aspect of the middle third of the thigh beneath the sartorius. Extends from apex of femoral triangle to adductor tendinous opening Boundies Anterior wall: adductor lamina and sartorius Lateral wall : vastus medialis Posteomedial wall: adductors longus and magmus Contents Saphenous n. Femoral a. and femoral v. lymphatic vessels and loose connective tissue Blood vessels and nerve of medial side of thigh Obturator a. Arises from internal iliac artery in the lesser pelvis passes through the obturator canal where it divides into anterior and posterior branches. Obturator n. Arises from the lumbar plexus in the abdomen. Enters the thigh through the obturator canal where it divides into anterior and posterior branches. Supplies medial group of muscles of thigh, obturator externus, and skin of medial side of thigh Obturator n. Strains-hamstring Strains- groin FRACTURED LT. FEMUR AP LAT