* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint
Internal rate of return wikipedia , lookup
Investment management wikipedia , lookup
Merchant account wikipedia , lookup
Land banking wikipedia , lookup
Modified Dietz method wikipedia , lookup
Greeks (finance) wikipedia , lookup
Financialization wikipedia , lookup
Stock valuation wikipedia , lookup
Securitization wikipedia , lookup
Continuous-repayment mortgage wikipedia , lookup
International asset recovery wikipedia , lookup
Financial economics wikipedia , lookup
Global saving glut wikipedia , lookup
Time value of money wikipedia , lookup
Business valuation wikipedia , lookup
Present value wikipedia , lookup
Gunduz Caginalp wikipedia , lookup
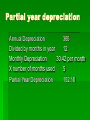
Chapter 8 Accounting for Plant Assets Plant asset record – a sheet that we create when we buy the plant asset and it helps keep track of the depreciation per year, accumulated depreciation, and the book value of the asset PLANT ASSET RECORD No. ________________ General Ledger Acct. No. ____________ Description: Display Case General Ledger Acct. Store Equipment Date Bought: Jan. 2nd 2004 Serial Number:8765309 Original Cost: $1,250 Estimated Useful Life 5 years Estimated Salvage Value: $250 Disposed of: Discarded Sold Date________________________________ Year Annual Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation Depreciation Method: Straight Line Method Traded Disposal Amount:______________________________ Ending Book Value More Definitions Real Property – Land and anything attached to it (that is why we call it real estate) Personal Property – All property not classified as real property Assessed Value – is the value of an asset determined by tax authorities for the purpose of calculating taxes Paid cash for property tax Feb 1. Paid cash for property tax, $3250. Check No. 122 Cash Payments General Date Account Title Ch. No 1-Feb Property Tax Expense 122 Post Ref Debit 3250 Credit Account s Payable Debit Purch Disc Cr Golf Tennis Cash Credit 3250 Section 8-2 Depreciation Original Cost The value the plant asset was to us when we purchased it. Estimated Salvage Value What we believe the asset will be worth when we can not depreciate it any more. Estimated Useful Life How many years we are allowed to depreciate the asset (determined by the government) Straight-line method of depreciation The asset decreases by the same value each year. Original cost -Estimated Salvage Value Estimated Total Depreciation Divided by useful years Annual Depreciation expense Original cost $2000 -Estimated Salvage Value 175 Estimated Total Depreciation $1825 Divided by useful years 5 Annual Depreciation expense $365 per year Our plant asset record would look something like this if we bought the asset at the beginning of the year. year Annual Depreciation Accumulated Depreciation Ending book Value 1 55 55 220 2 55 110 165 3 55 165 110 4 55 220 55 5 55 275 0 Original Cost 275 Now remember at the end of each year we have to adjust or bring our accounts up to date. General Journal Doc No. Date Dec Post Ref Debit Credit Account Title 31 Depr. Exp - Office Equipment Accum Depr.- Office Equipment 11571 11571 Partial year depreciation Annual Depreciation 365 Divided by months in year 12 Monthly Depreciation 30.42 per month X number of months used 5 Partial Year Depreciation 152.10 8-3 Disposing of a plant asset Three ways in which we can dispose of a plant asset Is fully depreciated and has no value to us We sell it for more than book value We sell it for less than book value How do we find out how much it is for us? year Annual Depreciation Accumulated Depreciation Ending book Value 1 55 55 220 2 55 110 165 3 55 165 110 4 55 220 55 5 55 275 0 Original Cost 275 What are things we need to do in order to write off the asset. 1. We need to record any depreciation that has happened up to the point when we sell something. 2. We need to write off the original cost of the asset. 3. We need to write off the accumulated depreciation on the asset 4. We need to record any cash or asset received from the transaction June 30, 2006 Discarded office table: original cost $200; total accumulated depreciation through December 31, 2005, $140; additional depreciation to be recorded through June 30, $20.00 Memorandum 92 What is important about this transaction June 30, 2006 Discarded office table: original cost $200; total accumulated depreciation through December 31, 2005, $140; additional depreciation to be recorded through June 30, $20.00 Memorandum 92 Lets go back to the slide where it tells us what we need to record…… What are things we need to do in order to write off the asset. 1. We need to record any depreciation that has happened up to the point when we sell something. 2. We need to write off the original cost of the asset. 3. We need to write off the accumulated depreciation on the asset 4. We need to record any cash or asset received from the transaction General Journal Doc No. Date Dec Post Ref Debit Credit Account Title 31 Depr. Exp - Office Equipment Accum Depr.- Office Equipment 20 20 What is important about this transaction June 30, 2006 Discarded office table: original cost $200; total accumulated depreciation through December 31, 2005, $140; additional depreciation to be recorded through June 30, $20.00 Memorandum 92 Lets go back to the slide where it tells us what we need to record…… General Journal Date Dec Account Title 31 Depr. Exp - Office Equipment Doc No. Post Ref Debit 20 20 Accum Depr.- Office Equipment Dec 31 Accum Depr.- Office Equipment Loss on Plant Asset Office Equipment Credit 160 40 200 June 30, 2006 Discarded office table: original cost $200; total accumulated depreciation through December 31, 2005, $140; additional depreciation to be recorded through June 30, $20.00 Memorandum 92 Selling a plant asset January 4, 2006, Received Cash from the sale of a fax machine, $185: original cost, $600 total accumulated depreciation through December of 2005 $400 Receipt No. 60 Cash Receipts Journal Because of the date there is no additional accumulated depreciation so there is no need for an adjustment. Date 4-Jan Account Title Accum. Depr- Office Equip Loss on Plant Asset Office Equip Doc No R60 Post Ref General Debit Credit 400 A /R Credit Sales Tax Payable Debit Credit Sales Credit Golf Tennis Sales Discount Debit Golf Tennis Cash Credit 185 15 600 June 27, Paid cash , $850 plus old counter for new store counter: original cost of old counter $1000; total accumulated depreciation through June 27 $765 Memo 130 and Check No. 154 Trading a Plant Asset 1. Remove the original cost of the old plant asset and its related accumulated depreciation 2. Recognizes the cash paid 3. Record the new plant asset at it original cost Cash Receipts Journal Sales Tax Payable General Date 4-Jan Account Title Store Equipment Accum. Depr-Store Equip Store Equipment Doc No R60 Post Ref Debit Credit 1085 A/R Credit Debit Credit Sales Credit Golf Tennis Sales Discount Debit Golf Tennis Cash Credit 850 765 1000 January 2, 2006 Fidelity Company sold land with a building for $97,000 cash; original cost of land $25,000 original cost of building $150,000; total accumulated depreciation on building through December 31, 2005 $85,000 Receipt No. 105 Selling Land and Buildings Cash Receipts Journal Sales Tax Payable General Date 2-Jan Account Title Accum Depr - Building land Building Gain on Plant Asset Doc No R105 Post Ref Debit Credit 85000 A/R Credit Debit Credit Sales Credit Golf Tennis Sales Discount Debit Golf Tennis Cash Credit 97000 25000 150000 7000 8-4 Other methods of Calculating Depreciation Declining – Balance method of depreciation Total Dep / Est. Useful years X 2 = Declining Balance Rate 100% / 5 = 20% x 2 = 40% Year Beginning Book Value DecliningBalance Rate Annual Depreciation Ending Book Value 1 2000 40% 800 1200 2 1200 40% 480 720 3 720 40% 288 432 4 432 40% 172.8 259.2 5 259.2 40% 84.2 175 We can not go below what the estimated salvage value is….. Sum of the years digits We add up all of the years and use it as a fraction of how much should be depreciated over that year. 1+2+3+4+5= 15 Year Beginning Book Value Fraction 1 2000 5/15 1825 608.33 1391.67 2 1391.67 4/15 1825 486.67 905 3 905 3/15 1825 365 540 4 540 2/15 1825 243.33 296.67 5 296.67 1/15 1825 121.67 175 Total Depreciation Annual Depreciation 1825 Ending Book Value Production-Unit Method of Depreciation This method is used when an asset like a truck is used a lot. Orig cost Est. Salvage Value Total Depreciation Estimated Useful life (divide) Depreciation Rate 18,200 -2000 16,200 90,000 Miles .18 per mile Year Beg Book Value Miles Driven Annual Dep Ending Book Value 1 18,200 9000 1620 16,580 2 16,580 23000 4140 12,440 3 12,440 25000 4500 7,940 4 7,940 22000 3960 3,980 5 3,980 8000 1440 2,540 M.A.C.R.S Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System Year Depreciation Rate 1 A depreciation method20% required by the IRS 32% 2 to be used for 3 19.20% income tax 4 11.52% calculation purposes 5 5.76% for most plant assets in service after 1986100% Rates are given by the IRS Annual Depreciation 400 640 384 230.4 115.2 Original Cost 100,000 Estimated Salvage Value -12,250 Estimated Total Value of Coal 87,750 Depletion decrease in coal the value asset Estimated TonsThe of Recoverable divideof a plant 50,000 because theTon removal of a natural resource Depletion Rateofper of Coal $1.755 Last Slide!!!!!!!!!! Tons Recovered Annual Depletion Ending Book Value Year Beg Book Value 1 100000 6000 10530 89470 2 89470 12000 21060 68410 3 68410 13000 22815 45595 4 45595 9000 15795 29800 5 29800 6000 10530 19270