* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10102 chief round keroro [
Ulcerative colitis wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Ankylosing spondylitis wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmune encephalitis wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuromyelitis optica wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatoid arthritis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
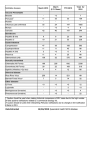
Autoimmune hepatitis 2012 / 02 / 22 GI CR 廖苡君 Introduction • Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a generally unresolving inflammation of the liver of unknown cause. • Onset is frequently insidious with non-specific symptoms but the clinical spectrum is wide, ranging from an asymptomatic presentation to an acute severe disease • Mean incidence is 1 to 2 per 100,000 persons per year • Prevalence is 11 to 17 per 100,000 persons per year DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS: AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES 2010 Pathogenesis • A working model for its pathogenesis postulates: a. environmental triggers b. failure of immune tolerance mechanisms c. genetic predisposition collaborate to induce a T-cell–mediated immune attack upon liver antigens leading to a progressive necro-inflammatory and fibrotic process in the liver DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS: AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES 2010 Pathogenesis Feldman: Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease, 9th ed Clinical manifestation Clinical manifestation Laboratory abnormalities: • serum AST or ALT • Increased serum total IgG or γ-globulin • serological autoantibody (ANA, SMA, anti-LKM 1, or anti LC 1) Diagnosis • The diagnosis requires the presence of characteristic clinical and laboratory features, and the exclusion of other conditions. • The diagnostic criteria for AIH / diagnostic scoring system were codified by an international panel in 1999 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS: AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES 2010 Diagnosis Feldman: Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease, 8th ed Scoring system Alvarez F, Berg PA, Bianchi FB, et al. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Report: review of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol. Nov 1999;31(5):929-38 Simplified score HENNES ET AL. HEPATOLOGY, July 2008 Differential diagnosis A. Other autoimmune liver diseases • Primary biliary cirrhosis • Primary sclerosing cholangitis • Autoimmune cholangiopathy • Overlapping syndrome B. Chronic viral hepatitis • Chronic hepatitis B / C / D / other virus DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS: AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES 2010 Differential diagnosis C. Other • Chronic drug-induced hepatitis • Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency • Wilson's disease • Cholangiopathy related to AIDS • Steatohepatitis (Nonalcoholic or Alcoholic) • Granulomatous hepatitis • Systemic lupus erythematosus • Graft-versus-host disease • Cryptogenic chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS: AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES 2010 Histology • Autoimmune hepatitis is characterized by a chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate. Plasma cells are the prominent cell type. • Biopsies may show evidence for interface hepatitis, bridging necrosis, and fibrosis. • Lobular collapse, best identified by reticulin staining, is a common finding. DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS: AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES 2010 Classification Overlap syndrome Treatment • Regimen Combination therapy Single drug Prednisolone (mg/day) Azathioprine (mg/day) Prednisolone (mg/day) 30 mg x 1 wk 20 mg x 1 wk 15 mg x 2 wk 10 mg until endpoint 50 mg until endpoint 60 mg x 1 wk 40 mg x 1 wk 30 mg x 2 wk 20 mg until endpoint Feldman: Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease, 8th ed End point • 1) 2) 3) 4) Remission No symptom Histologic improvement AST < 2x Gamma Globulin normal • Incomplete response Failure to satisfy remission criteria • Treatment failure Worsening of AST / Bilirubin or histology • Drug toxicity: Cataract, osteopenia, etc Feldman: Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease, 9th ed Treatment result • Average treaatment course: 22 months • Response rate: 65 % in 3 years • 10-year survival: 93% • 9% treatment failure may use high dose Tx : a. Prednisolone alone: 60 mg/day b. Prednisolone 30 mg/day+ Azathiprine 150 mg/day Clinical improvement to high dose Tx: 70% in 2 years Feldman: Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease, 8th ed Prognosis Feldman: Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease, 8th ed Liver transplantation • Effective for decompensated AIH: 5 year survival rate: 83-92% 10 year survival rate: 75% • Recurrence rate: 17%, de-novo AIH: 3-5% Feldman: Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease, 8th ed Thanks for your attention !!