* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Triangle Angle Sum Theorem ppt.
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
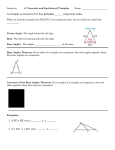
Classifying Triangles www.pleasanton.k12.ca.us/.../Powerpoints/4.1_Triangles_and_Angle. .. Equilateral Isosceles Scalene 3 congruent sides At least 2 congruent sides No congruent sides Equilangular Acute Obtuse 3 congruent angles 3 acute angles 1 obtuse angle Right 1 right angle Adjacent Sides: two sides of a triangle sharing a common vertex Hypotenuse: side of the triangle across from the right angle Legs: sides of the right triangle that form the right angle Base: the non-congruent sides of an isosceles triangle Vertex: the point where two sides of a triangle meet Label the following on the right triangle: Vertices Hypotenuse Legs Vertex Hypotenuse Leg Vertex Vertex Leg Label the following on the isosceles triangle: Base Congruent adjacent sides Legs Adjacent side Adjacent Side Leg Leg m<1 = m<A + m<B Base Interior Angles: angles inside the triangle (angles A, B, and C) 2 B 1 Exterior Angles: angles adjacent to the interior angles (angles 1, 2, and 3) A C 3 The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a triangle is 180o. B A <A + <B + <C = 180o C B A 1 The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of two nonadjacent interior angles. m<1 = m <A + m <B The acute angles of a right triangle are complementary. B A m<A + m<B = 90o www.pleasanton.k12.ca.us/.../Powerpoints/4.1_Triangles_and_Angle...