* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Analysis and Implementation of DSP Based Speed Control of Three
PID controller wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resilient control systems wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Distributed control system wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Control theory wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
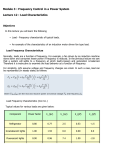
ISSN(Online): 2320-9801 ISSN (Print): 2320-9798 International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering (An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization) Vol. 3, Special Issue 2, March 2015 Analysis and Implementation of DSP Based Speed Control of Three Phase Induction Motor E.Baraneetharan1, P.Raghuraman2 Associate Professor, Cauvery College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, India UG Student, Gnanamani College of Technology, Namakkal, India ABSTRACT: In this paper we analyse the speed control of induction motor in various control techniques and implement the new controller depends on intelligent techniques. In recent years, the field oriented control of induction motor drive is widely used in high performance drive system .It is due to its unique characteristics like high efficiency, good power factor and extremely rugged. These intelligent controllers are used to accomplish the control of preferred speed. Putting into practise of this processor it is interfaced with embedded system. So as real-time control also obtained and the total harmonic distortion diminishes fully by this method. This scheme leads to be able to adjust the speed of the motor by control the frequency and amplitude of the stator voltage. The ratio of stator voltage to frequency should be kept at constant. Associate to other controller like PID, Fuzzy, DTC control, Single Artificial Neuron Network (SANN), Single Pulse Width Modulation inverters (SPWM), Constant V/F methods and Hysteresis Comparators, this method stimulate enhanced operation of preceding modus operandi. By this DSP based controllers we minimize the switching frequencies, Harmonics and need of filter circuits, 50 – 70 % of resonance frequencies and over all time response of the controlling strategy. I.INTRODUCTION In this paper we analyse the speed control of induction motor in various control techniques and implement the new controller depends on intelligent techniques. In recent years, the field oriented control of induction motor drive is widely used in high performance drive system. It is due to its unique characteristics like high efficiency, good power factor and extremely rugged. By controlling of three phase induction motor various techniques are in progress. Still we are lagging to control the three phase induction motor in rural areas. The controlling point, level of voltage and flux will induced other drawbacks in the motor. The efficiency, regulations are getting poor by conventional techniques. To improve switching speed, rising time, settling time & peak over shoot of the response to be achieve by our proposed intelligent modules operation. The THD is 75–80% reduced. So as the resonance also minimized in this technique. The DSP processor (TMS320F28027) is used for our proposal. The accuracy, reliability and compact of this are better when comparing with other. Induction motors are used in many applications such as HVAC, Industrial drives control, automotive control and etc., in recent years there has been a great demand in industry for adjustable speed drives. Recently, Fuzzy logic control has found many applications in the past decade. Fuzzy Logic deals with problems that have vagueness, uncertainty and use membership functions with values varying between 0 and 1. This means that if the reliable expert knowledge is not available or if the controlled system is too complex to derive the required decision rules. Development of a fuzzy logic controller becomes time consuming and tedious or sometimes impossible. In the case that the expert knowledge is available, fine-tuning of the controller might be time consuming as well. Real time implementation of MATLAB interface for speed control of induction motor drive using DSP processor is quite new. The aim of this paper is to show the dynamics response of speed with design the fuzzy logic controller to control a speed of induction motor and to design the real time implementation of MATLAB interface for speed control of induction motor drive by using DSP processor. Copyright to IJIRCCE www.ijircce.com 77 ISSN(Online): 2320-9801 ISSN (Print): 2320-9798 International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering (An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization) Vol. 3, Special Issue 2, March 2015 II.BLOCK DIAGRAM In our scheme, it leads to be able to adjust the speed of the motor by control the frequency and amplitude of the stator voltage. The ratio of stator voltage to frequency should be kept at constant. The rectifier circuit and inverter Fig 1.1 Block diagram of DSP based control circuits are used to give the correct variations of pulse signals to the corresponding PWM generators. MATLAB based DSP TMS320 series processor is used here to give continues and non varying switching pulses to reduce the switching losses in the resonance part. We are implemented three phase induction motor for the efficient control of speed in this trial. IC Voltage Regulators Voltage regulators comprise a class of widely used ICs. Regulator IC units contain the circuitry for reference source, comparator amplifier, control device, and overload protection all in a single IC. IC units provide regulation of either a fixed positive voltage, a fixed negative voltage, or an adjustable set voltage. The regulators can be selected for operation with load currents from hundreds of Milli amperes to tens of amperes, corresponding to power ratings from milliwatts to tens of watts. A fixed three-terminal voltage regulator has an unregulated DC input voltage, VI, applied to one input terminal, a regulated DC output voltage, Vo, from a second terminal, with the third terminal connected to ground. The series 78 regulators provide fixed positive regulated voltages from 5 to 24 volts. Similarly, the series 79 regulators provide fixed negative regulated voltages from 5 to 24 volts. For IC’s, Micro Controller, LCD ---------------- 5 volts. For alarm circuit, op-amp, relay circuits ----- 12 volts. Induction Motor One of the mature control systems of induction motor is the field oriented control method. The FOC method is widely used and presents some high standards in modern industrial drives. A continuous trend in IM drives is to increase the reliability of the drive system. One solution is to decrease the amount of normally used sensors. Because of noises and other disadvantages the troublesome device in some of industrial drive system is the speed sensor. Therefore, in most modern IM drives speed sensor elimination is required. Instead of a speed sensor, different methods for speed calculation are proposed in the literature. Comprehensive reviews of the IM sensor less drives are given, indicating that some problems with the sensor less control are persistent, so new solutions are still needed. Current work efforts are dedicated particularly to zero or very low speed range or to very high performance drives. Another problem in electrical drives is system sensitivity to inaccuracy and changes of motor equivalent circuit parameters. Most of the FOC systems Copyright to IJIRCCE www.ijircce.com 78 ISSN(Online): 2320-9801 ISSN (Print): 2320-9798 International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering (An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization) Vol. 3, Special Issue 2, March 2015 are very sensitive to that inaccuracy so some parameters should be estimated on-line. Also, robust structures of the control and estimation schemes are generally researched. The integral part of numerous FOC systems is the stator current controller. Different methods for current control are presented in the literature. Good results of current control are reported for predictive current based controllers. In this paper PCC is implemented in the IM speed sensor less system with field oriented control method. In the FOC system instead of linear PI current controllers, predictive current controllers may be used. The current control algorithm previously presented was modified by using the observer system instead of simple load model [5]. With such approach, better results were recorded. To avoid the system complication for the PCC, the back EMF calculation was integrated to flux and speed observer for FOC IM drive.In this project, new results as well as the new solution for integration of a motor choke in the current controller are presented. The proposed drive is speed sensor less and robust on motor parameters changes. The obtained results confirm that the system works properly without parameters estimation, even in very low speed ranges. Both simulation and experimental investigations for 5.5 kW IM drive is presented.The project circuit module is shown in above figure. The 230V AC Supply step- Downed by 12V AC supply by use of step down transformer. The 12V AC supply given to the Bridge Rectifier.This Circuit has four diode named as D1 to D4 which is responsible for the rectification of 12V AC to 12V DC supply. After this rectification the output DC supply given to the filter circuit. For purpose of filter is reducing the Harmonics. It reduce the Harmonics and given to the voltage regulator. The process of Voltage Regulator 7805, Regulate the 12V DC into 5V DC supply. Hence this rectified and regulated voltege which operates the DSP Processor (TMS320F28027). So 5V supply given to the DSP Processor. Normally DSP Processor working at 5V DC supply. That’s why here we implementing the Voltage Regulator and it regulate the output DC supply through the rectifier. DSP Processor using a SVPWM Algorithm (Space Vector Pulse Width Modulator).In DSP Processor inputs (VCC) are given to the voltage regulator output. Another input of DSP Processor (XTAL1, XTAL2) given to the crystal oscillator. Crystal oscillator is used to given the clock frequency in DSP controller. This DSP Processor Based Speed control of Induction Motor fully depends or based on MATLAB Programming. III. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM Fig 2.1 Circuit Diagram of DSP Based Three Phase Induction Motor Copyright to IJIRCCE www.ijircce.com 79 ISSN(Online): 2320-9801 ISSN (Print): 2320-9798 International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering (An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization) Vol. 3, Special Issue 2, March 2015 The output terminal of DSP Processor (PC0, PC1, PC2, PC3, PC4, and PC5) thoroughly connected with driver system. In This driver system consist of Opto coupler driver’s. Thus the output of a DSP haves 8 ePWM modulator. For our convenience, here we are use 6 ePWM and it is triggered with the 5V supply from the processor to the Opto coupler. When the opto coupler receives the trigger the 12V DC supply is drived by Opto coupler by use of Rectifier. The purpose of this supply is used to give the working process of Opto coupler producing 15V DC output supply. This output given by the MOSFET for a triggering purpose. The input side of inverter the 230V AC supply is given. That 230V AC supply converted by 230V DC supply by use of Bridge rectifier. At the period of conversion some resonance losses will occurred, that will controlled by resonance controller (Inductor). After, this conversion the Single Phase voltage will convert the Three Phase Voltage by the use of MOSFET. Finally, the output 3Ф 440V is given to the induction motor. In between of this inverter and Induction Motor switching losses (resonance) will produce that will controlled by resonance controller in each phase. The induction motor speed rate will feed backed by using of tacho generator. This tacho generator placed on DSP Processor (PA0). In the DSP Processor PI comparator also used. That willcompare input speed and output speed of a both MATLAB and Induction Motor. In that have any Variation means it will correct that and run the motor with preferred speed. That means it will reduce the whole resonance and harmonics losses and give the pure form of Output speed. Finally, our prospect output of an induction motor will get. Fig 2.2 MATLAB circuit for our proposal DSP Processor The F2802x Piccolo family of microcontrollers provides the power of the C28x core coupled with highly integrated control peripherals in low pin-count devices. This family is code-compatible with previous C28x-based code, as well as providing a high level of analog integration. An internal voltage regulator allows for single-rail operation. Enhancements have been made to the HRPWM module to allow for dual-edge control (frequency modulation). Analog comparators with internal 10-bit references have been added and can be routed directly to control the PWM outputs. The ADC converts from 0 to 3.3-V fixed full-scalrange and supports ratio-metric VREFHI / VREFLO references. The ADC interface has been optimized for low overhead and latency. Copyright to IJIRCCE www.ijircce.com 80 ISSN(Online): 2320-9801 ISSN (Print): 2320-9798 International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering (An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization) Vol. 3, Special Issue 2, March 2015 IV. RESULT In this system we observed a performance in both MATLAB and Hardware kit. All over that it is flexible for future enhancement. Experimental results shows that greater Peak Over Shoot, Less Ripples, Good Transient and also avoid the Total Harmonics Distortion (THD) and Resonance Frequencies. Competently, it will control the Induction Motor Speed with a perfect controlling operation. Motor Speed at 1300 RPM Motor Speed at 950 RPM Motor Speed at 600 RPM Copyright to IJIRCCE www.ijircce.com 81 ISSN(Online): 2320-9801 ISSN (Print): 2320-9798 International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering (An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization) Vol. 3, Special Issue 2, March 2015 What ever the speed which is given as the input to the Real time matlab simulator the processor makes the motor to revolute at the given constant speed at any various load changes. This DSP controller can perform large and complex computation with any desired degree of accuracy at very high speed, easily programmable so they are more versatile. It have better resolution. It eliminates the number of firing circuits and power electronics components. So fast response & simple to construct. The Efficiency is improved. So we may isolate the circuit for any other applications also. The rejection of disturbance signals gives more accuracy. The overall stability of the system is improved sensitively. It is Used as speed regulators. There is a absence of distortion and ripples. So we may use these controllers for the accuracy of all types of control circuits in remote areas. The time delay of the circuit is better. Therefore it may utilize for all type of power full loads. Also used in pumps and turbines for improve the efficiency and in conveyors in all type of industries. ANALYSIS & DISCUSSION Time (sec) S.No Type of Controller 1. PI Controller Settling time Rising time % THD Point of view The PI controller has low precision of speed regulator debases the performance of the whole system. 3.2 1.5 54.42 2 1.2 59.82 0.58 0.48 62.74 4. DTC Technique 0.6 0.4 77.53 5. SPWM Technique 0.6 0.4 83.74 6. V/F Characteristics 2.5 1.5 50 7. Hysteresis Comparator 1.5 1.3 61 0.45 0.40 52.61 2. PID Controller 3. 8. Fuzzy Logic Controller (FLC) SVPWM Inverter With DSP Based Controller V. Time consuming is high comparing other controllers & techniques Time consuming retuning even if applied to a similar plant in other location It needs an external DSVM technique with two equal time intervals and 12 new voltage vectors. (DSVM = Discrete Space Vector Modulation). Resonance Frequency Losses will Highly Induced This V/Fcomparator producing time delay Highly Hysteresis comparator technique which is using sensor less control of BLDC motor drive of an automotive fuel Pumps only. More compact for all type of loads in different swift. CONCLUSION The progress in science and technology is a non-stop processes a new things and new technology being invented. As the technology grows day by day, we can imagine about the future in which thing we may occupy every place. The proposed system based on DSP processor is found to be more compact, user friendly and less complex, which can readily be used in order to perform. Though it is designed keeping in mind about the need for industry, it can extended for other purpose such as commercial and research applications. MATLAB 12b is used for better simulation and make to simulate the process effectively. This is more suitable for three phase induction motors with 2 HP, 440 v, 50 Hz Copyright to IJIRCCE www.ijircce.com 82 ISSN(Online): 2320-9801 ISSN (Print): 2320-9798 International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering (An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization) Vol. 3, Special Issue 2, March 2015 ratings. This is implemented and got effective result in Hardware kit shown in pictures. Due to probability of high technology (DSP Processor) used this Analysis and Implementation of DSP Based Speed Control of Three Phase Induction Motor is fully software controlled with less hardware circuit. The feature makes this system is the base for future system.The principle of the development of science is that “nothing is impossible”. So we shall look forward to a dazzling and erudite world. REFERENCES 1. ArunimaDey, Bhim Singh, BarathiDwivedi and dinesh Chandra, 2009. Vector Control of Three-Phase Induction Motor using Artificial Intelligent Technique, Allahabad, Vol-4, No-4, ISSN 1819-6608. 2. P.Tripura and Y.srinivasa Kishore babu, 2011. Fuzzy Logic Speed Control of Three-Phase Induction Motor Drive, Guntur. Vol-60, ISSN: 2011-12-20. 3. Marwan A. Badran, Mostafa A. Hamood, Waleed F. Faris, 2013. Fuzzy Logic Based Speed Control System for Three-Phase Induction Motor, Resita, NR.1, ISSN 1453-7397. 4. A.Abbou, T.Nasser, H.Mahmoudi, M.Akherraz, A.Essadki, 2012. Induction Motor Controls and Implementation using dSPACE, Morocco.ISSN: 2224-2856. 5. BrahimMetdji, LotfiBaghli, ToufikRekioua,Seddikbacha, 2012. Low-Cost Direct Torque Control Algorithm for Induction Motor without AC Phase Current Sensors. IEEE,Vol-27, no 9. 6. Rajendra S. Soni, S.S.Dhamal, 2013. Direct Torque Control of Three Phase Induction Motor Using Fuzzy Logic, Bhopal, ISSN: 978-82702-276 7. C.S.Sharma, TaliNagwani, 2013. Simulation and Analysis of PWM Inverter Fed Induction Motor Drive, IJSETR, vol-2, ISSN: 2278-7798. 8. Amit Kumar Sharma, Tushar Deep Saxena, Shirazul Islam and Arun Kumar Yadav, 2013. Performance Analysis of Three Phase PWM Voltage Source Inverter Fed Three Phase Induction Motor Drive, Vol-2, No-2, ISSN: 2278-8948. 9. Yashasvi V M and BasawarajAmarapur, 2012. Digital Signal Processing Based Speed Control of Induction Motor Drive System, Vol-1, ISSN: 2278-8948. 10. OpasRuksaboon and chaiyaponThongchaisuratkrul, 2013. Fuzzy PID Control Compensation System for Speed of VVVF Induction Motor Drive, Vol-5, No-6. 11. I.Takahashi and T. Noguchi, “A new quick-response and high-efficiency control strategy of an induction motor,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl.,vol.IA-22, no. 5, pp. 820–827, Sep./Oct. 1986. Copyright to IJIRCCE www.ijircce.com 83