* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Reproduction - holytrinitywhitestone.com
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
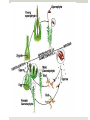
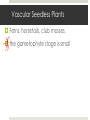
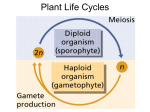
Plant Reproduction Do Now: Write in your notebooks what would happen if an Oyster farmer cut sea stars into pieces and threw them back into the ocean. Humans(animals) and Plants Plant Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Most plants Can be done from seeds, leaves, roots, stems, etc. Sexual Reproduction HOW? Reproductive Organs Female plants produce Egg Male plants produce Sperm Some plants can have BOTH of the reproductive organisms on it. Usually, when this happens the plant cannot create a zygote from itself. Plant Life Cycle Alternation of Generations: life cycle that involves both diploid and haploid stages. Two Stages 1. Gametophyte 2. Sporophyte Gametophyte Gametophyte stage: When the plant cells go through ____________ to produce spores. spores: unicellular haploid cells that divide to become multicellular Then the spores divide by _________ to form plant structures or an entire new plant. Sporophyte Sporophyte stage: fertilization – the joining of two haploid sex cells (sperm and egg). Cells are joined to restore the original number of chromosomes the ___________ number. Seedless Reproduction Do Now: What are the two stages of a plant’s life cycle and how do they differ? How can a plant reproduce without seeds? Spores The sporophyte stage of these plants produces haploid spores in the spore cases When the spore cases break open, spores are released and spread by wind and water Types of Seedless Plants Vascular Have tubelike cells that transport water and nutrients throughout the plant Nonvascular Do not have structures that transport water and nutrients throughout the plant Water and nutrients move from cell to cell Nonvascular Mosses, liverworts, hornworts Sporophyte stage of these plants is small Life Cycle of Moss Gametophyte: green, low growing masses of plant (produces sex cells) Sporophyte: brown stalks growing upwards, does not carry photosynthesis Spore Case: produces millions of spores Life Cycle of Moss 1. The zygote begins the sporophyte stage and develops into an embryo that grows into the stalk and capsule (spore case). 2. Meiosis occurs in the capsule and produces spores. When the spores fall to the ground, they can grow into mature gametophytes Life Cycle of Moss 3. Sex cells are produced in the reproductive structures of the male and female moss gametophytes 4. During heavy rain/dew, the sperm will swim to the egg and fertilization will occur. Vascular Seedless Plants Ferns, horsetails, club mosses. the gametophyte stage is small Life Cycle of Fern Fronds: Leaves Rhizone: underground stem that has Fronds on it, and grows roots that anchor and absorb water/nutrients Sporophytes make their own food through PHOTOSYNTHESIS Sori: structures that produce spores, (underside of fronds) Prothallus: small, green, heart-shaped gametophyte plant Life Cycle of the Fern 1. Meiosis takes place inside each spore case, producing thousands of spores 2. Spores are ejected and fall to the ground, growing into a prothallus 3. Prothallus forms sex cells, it has BOTH male and female reproductive organs Life Cycle of the Fern 4. WATER is needed for sperm to swim to the egg causing fertilization producing a zygote. 5. The zygote is the beginning of the sporophyte stage and grows into the fern plant.