* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rhizogoniaceae
Survey
Document related concepts
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
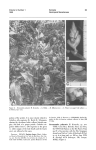
RHIZOGONIACEAE Scott R. Gilmore 1 Rhizogoniaceae Broth., Nat. Pflanzenfam. I, 3: 614 (1904). Type: Rhizogonium Brid. Dioicous, synoicous or monoicous. Plants minute to very large, lax to densely tufted. Stems usually simple, sometimes branched or dendroid. Rhizoids ±papillose. Leaves imbricate to widely spaced, erect-spreading to squarrose, unranked or in ranks of 2 or 4, linear-lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate; margin simple or comprised of elongated cells, ±thickened, entire, dentate, serrate, or with single or paired multicellular teeth; costa strong, ending just below the apex to excurrent, often toothed abaxially; laminal cells usually small and isodiametric, ±thick-walled, smooth. Perichaetia bud-like, basal, lateral or terminal. Calyptra long and thin, usually cucullate. Setae erect, elongate. Capsules erect to cernuous, commonly elongate, often arcuate, short necked, widest at the mouth; operculum ±rostrate. Peristome usually double and well developed. Spores small, globose or ovoid. Rhizogoniaceae comprises eight genera and about 45 species. It is especially diverse in tropical and subtropical regions of the Southern Hemisphere where it grows on bark and decaying wood in moist habitats, also occurring less commonly on rock and soil. Six genera and 15 species are known from near the east coast of Australia. The family has gametophytic affinities with the Bartramiaceae and Calomniaceae, and the sporophyte shows similarity to Mniaceae. Rhizogoniaceae is accepted here in its traditional sense; however, it is likely that future research will result in the segregation of new families. References Eddy, A. (1996), Rhizogoniaceae, Handb. Malesian Mosses 3: 197–214. Koponen, T., Touw, A. & Norris, D.H. (1986), Bryophyte flora of the Huon Peninsula, Papua New Guinea. XIV. Rhizogoniaceae (Musci), Acta Bot. Fenn. 133: 1–24. Manuel, M.G. (1981), Synopsis of Rhizogoniaceae Broth. in Malaya, Cryptog. Bryol. Lichénol. 2: 449–455. Sainsbury, G.O.K. (1955), Notes on Tasmanian mosses from Rodway’s herbarium: IV, Pap. & Proc. Roy. Soc. Tasmania 89: 21–23 (1955). Key to Genera 1 Peristome single (exostome lacking); costa ending below the long hairpointed leaf apex ......................... .................................................................................................................................... HYMENODON 1: Peristome double; costa usually percurrent to excurrent (ending below apex in Goniobryum); leaf apex lacking a long hairpoint ....................................................................................................................... 2 2 2: Laminal cells more than 30 µm long (1:) ................................................................ GONIOBRYUM Laminal cells less than 30 µm long .................................................................................................. 3 3 Marginal teeth paired (2:) ........................................................................................ PYRRHOBRYUM 3: Marginal teeth single ........................................................................................................................... 4 1 7494 Andrea Crescent, Lantzville, British Columbia, Canada V0R 2H0 Cite as: S.R.Gilmore, Australian Mosses Online. 36. Rhizogoniaceae. http://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/Mosses_Online/Rhizogoniaceae.pdf (2012) 4 Leaves neither ranked nor complanate, often with propagula between leaves (3:) ......... LEPTOTHECA 4: Leaves ranked and complanate, lacking propagula between leaves ................................................... 5 5 Leaves 4-ranked; plants 2.5–8.0 cm long; leaf border composed of elongate cells (4:) .. MESOCHAETE 5: Leaves 2-ranked; plants 1–3 cm long; leaf border with or without elongate cells ......... RHIZOGONIUM 2