* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Practice questions for centripetal motion
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
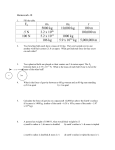
Practice Questions for Centripetal Motion 1. In the Bohr-Rutherford model of the hydrogen atom, the electron, of mass 9.1×10-31kg, revolves around the nucleus. The radius of the orbit is 5.3×10-11m and the period of revolution of the electron around the nucleus is 1.5×10-16s. a) Find the magnitude of the acceleration of the electron. b) Find the magnitude of the electric force acting on the electron. 2. James Bond is trying to escape in a car with mass 432kg moving at 160km/h. He is approaching a corner that forms part of a circle of radius 15.0m. The force of static friction is μs = 0.27. Will he be able to make the turn without sliding? 3. A chestnut of mass 10g is tied to a 1.3 m long string is being swung in a vertical circle. The chestnut makes 10 full rotations in 6.2 seconds. The radius is 0.55m. a) What is the tension in the string at the top? What is the tension at the bottom? b) At what speed should you swing the chestnut in order to have zero tension at the top (so that gravity is doing all the work at the top)? 4. A roller coaster has a circular loop with radius 20.4m. How fast should the cars go so that the passengers feel a normal force of 2.5mg at the top (where m is the mass of the passenger)? 5. A 77kg student is riding a Ferris Wheel of radius 67m that makes one rotation every 65 seconds. top far right bottom FN FN FN fs FG FG *I chose positive direction upwards* FG a) What is the student’s velocity at the top? b) What is the normal force of the seat on the student at the top? c) What is the normal force of the seat on the student at the top? d) What force is acting on the student at the far right, to accelerate him towards the centre? 6. An 82kg student rides a Ferris Wheel. At the top, the normal force of the seat on him is 620N. What will the normal force be if the velocity is doubled? 7. A car of mass 938kg travels around a banked curve of radius 91m. The banking is at an angle of 19° to the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the road and the tires is 0.32. a) What forces provide the centripetal acceleration? What constant speed must the car maintain to travel safely around the curve? b) How does the required speed for a more massive vehicle, such as a truck, compare with the speed required for this car? 8. A child with mass 35.1kg is swinging on a swing. The circular path of the swing has a radius of 3.67m. At the lowest point, the tension in each of the chains is 205N. What is the child’s speed at this point? 9. A yo-yo on a frayed string is swinging in a vertical circle. Where is the most likely place for the yo-yo to be when the string breaks? 10. What happens to the acceleration if the radius is doubled and the period remains the same? . 11. What happens to the acceleration if the radius is doubled and the velocity remains the same? 12. What happens to the acceleration if the velocity is doubled? 13. A plane is flying in a vertical loop of radius 2.1km. If the air exerts a force of 0N on the plane at the top of the loop, what is the plane’s speed?