* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE CRUSADES
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
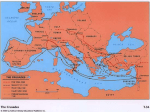
THE CRUSADES A Quest for the Holy Land Crusades • A long series or Wars between Christians and Muslims • They fought over control of Jerusalem which was called the Holy Land because it was the region where Jesus had lived, preached and died Causes of the Crusades Muslim Turks captured Jerusalem from the Byzantine Empire Muslims stopped Christians from Visiting Holy Land Christian pilgrims were attacked Byzantine Empire feared attack on Constantinople The Call to Arms • Pope Urban II called for the defeat of the Turks, returning the Holy Land to the Christians Who Answered the Call? •Feudal Lords •Knights •Peasants The First Crusade (1096-1099) • Peasant army – Untrained – Lacked military equipment – Many killed by Muslim Turks • Knights – Succeeded in capturing Jerusalem Second Crusade (1147-1149) • After victory many Christians went back home. • The Turks eventually took back much of the territory. • King of France and Emperor of Germany sent troops to stop the Turks. Second Crusade (1147-1149) • Saladin leads the Muslim Turks to victory, defeating the Christians • * He was considered a very wise ruler. He was known for his sometimes kind treatment of fallen enemies. Many Christians saw him as a model of knightly chivalry. Third Crusade (1189-1192) • King Richard of England convinces the Turks to allow Christians to visit the Holy Land Crusades Continue Through 1200’s • Several more crusades attempted with no victories for the Christians • Children’s crusade, - 30,000 soldiers many of them under 12 years old – Never made it to the Holy Land The Fall of Constantinople • in 1204, the Crusaders attacked, conquered, and pillaged the city of Constantinople, a goal that the Muslims had been trying achieve for centuries Conquered by the Ottoman Turks • In 1453, the city was finally and permanently conquered by the Ottoman Turks and renamed Istanbul. Byzantine culture, law, and administration came to its final end. Contribution to Western Civilization • Throughout the early Middle Ages, the Byzantine Empire remained a protective barrier between western Europe and hostile Persian, Arab, and Turkish armies. • The Byzantines were also a major conduit of classical learning and science into the West down to the Renaissance. While western Europeans were fumbling to create a culture of their own, the cities of the Byzantine Empire provided them a model of a civilized society. Emperor Suleiman • Leader of Ottoman Empire from 15201566. • Sets out on military conquests and takes over land in the Middle East and Western Europe. • Takes over trade in Red and Mediterranean Seas. Cultural and Social Impact • Sponsored the arts and encouraged artists from Muslim areas to mix with Turkish and European arts. • Promoted poetry and wrote poems under different names. • Sponsors projects to beautify Constantinople and rebuilds Muslim monuments in Jerusalem. Legacy of Suleiman • Ottoman Empire takes control of major Muslim cities and becomes largest power in world. • Shakespeare and other Renaissance authors are inspired by him. • Legal reforms earned him the title “Law Giver”. Results of the Crusades • I.F. Turks Traveled they would Trade • I = Improvements – Ships, Maps, Explorers • F = Feudalism declines because Feudal lords die or spend too much money on military. • T = Turks still rule the Holy Land • T = Travel – Europeans want to travel more • T = Trade – Europeans want product from the East such as sugar, cotton, silk, spices, etc.