* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Answer as a group before you watch the video
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
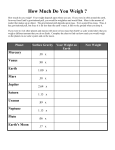
MOVEMENT IN SPACE https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E43-CfukEgs Answer as a group before you watch the video: If you dropped a feather and a bowling ball from the same height, which would hit the ground first? WHY? After you watch the video: Reevaluate your answer from above, what parts were correct? What parts were incorrect? What caused the result you saw the second time the objects were dropped? WEIGHT MASS Weight is a measure of the pull of gravity on Mass is the amount of matter in an object an object. Weight on Earth is based on the pull of gravity Mass is the same no matter where the object is toward the center of Earth. located as long as the object does not gain or lose any of its matter. Your weight would change on different planets based on how much gravitational pull they have Your mass would not change if you could travel to another planet FORCE OF GRAVITY: *a ______________ between all objects in the universe. *This is influenced by … 1. the mass of the objects 2. the distance between them Effects of Mass and Distance on Gravitational Force A _____________ massive object has greater gravitational pull on ____________ massive objects Ex. The Sun is the most massive object in the solar system and so it has the greatest pull on objects, like planets, in the solar system The __________________ the distance between objects the greater the gravitational pull Ex. The Moon has a greater effect on Earth’s tides than the Sun because it is closer to Earth. These two factors of gravitational force cause distinct motions between and among celestial bodies – such as the Sun, planets and their moons Understanding Check Circle which planet has a greater gravitational pull on the other? How do you know? Which moon has a greater pull on the planet, Moon 1 or Moon 2? Why? 100,000 km 200,000 km Effects of Gravity on Planetary Orbits The Sun’s gravitational pull, plus the planet’s ______________________ (Inertia means continual forward motion), keeps the planets moving in elliptical orbits (Earth’s orbit is slightly oval) and determines how fast they orbit. Planets __________________ to the Sun move/orbit faster than planets farther from the Sun because the gravitational attraction is greater. When a planet is farther from the Sun, the gravitational attraction between them decreases and the planet moves/orbits ____________________. Orbits may change due to the gravitational effects from, or collisions with, other objects in the solar system. Understanding Check: Which planet has the fastest orbit? _________________________ Which planet has the slowest orbit? _________________________