* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Theory of Plate Tectonics Plates
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
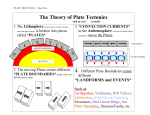
The Theory of Plate Tectonics Plates • Separate sections of Earth’s outer shell, the lithosphere • Plates have jagged edges but fit closely together • Some plates carry the continents or parts of the ocean floor or both Scientific Theory • A well tested concept that explains a wide range of observations J. Tuzo Wilson • Canadian scientist • Observed cracks in continents similar to those in ocean floor The Theory of Plate Tectonics • The theory of plate tectonics is the geological theory that states that the pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant slow motion being driven by the convection currents in the mantle. • The theory of plate tectonics explains the formation, movement and subduction of earth’s plates. • Plate Boundaries - where 2 plates meet, they extend deep into the lithosphere • Fault – breaks in Earth’s crust where rocks have slipped past each other 3 Types of Plate Boundaries 1. Transform 2. Divergent 3. Convergent Transform Boundary • Where 2 plates slip past each other moving in opposite directions • Earthquakes occur frequently along transform boundaries Divergent Boundary • Where 2 plates move apart or diverge • Most occur at the mid-ocean ridge Rift Valley – a deep valley that forms along a divergent boundary on land Convergent Boundary • Where 2 plates come together or collide • The density of the plate determines which one comes out on top Collisions at Convergent Boundaries and their Results: • Oceanic crust + Oceanic crust = deep ocean trench • Continental crust = Continental crust = mountains • Oceanic crust + Continental crust = deep ocean trench and mountains The Continents Slow Dance • The plates move at a slow, steady pace of about 1-10 cm/year • Compare to the rate of fingernail growth • The rate of plate movement is slow, but multiply it over millions of years to understand how Pangaea became Earth’s continents today.