* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Operating Systems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
OPERATING SYSTEMS 2 - OVERVIEW
PIETER HARTEL
1
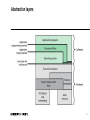
Operating System
Resource manager
Hardware resources
Resources provided by the OS itself (which?)
Objectives
Convenience (why?)
Efficiency (why?)
Evolvability (why?)
Abstraction is the key to managing the complexity
2
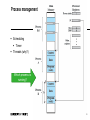
History
Batch
Time sharing
Real-time
Multi-processor
Distributed systems
Electrologica X8 console, 1965
Multi-core (why?)
3
Concepts and abstractions
Concept
Abstraction of
Processes & Threads
Processor
Memory management
Physical memory & disks
Protection and security
Dedicated computer
Scheduling and resource
management
Dedicated computer
4
Abstraction layers
5
Linux example of the Unix API
Output?
gcc Echo.c
./a.out Hello world
strace ./a.out Hello World
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int i;
for(i=0; I < argc; i++) {
printf("%s ", argv[i]);
}
printf("(%d)\n", argc);
return 0;
}
6
Process abstraction
7
Resource sharing (why?)
Deadlock (why?)
Prevention
Detection
Recovery
Avoidance
8
Process management
Scheduling
Timer
Threads (why?)
Which process is
running?
9
Address space management
text
main
etext
data
./a.out
edata
bss
b
extern char etext, edata, end;
int a = 0xaaaa, b;
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
int c = 0xcccc;
int *d_ptr = (int*) malloc(sizeof(int));
int *e_ptr = (int*) alloca(sizeof(int));
b = 0xbbbb;
*d_ptr = 0xdddd;
*e_ptr = 0xeeee;
printf("%p:a=%0x\n", &a, a); …
}
low
end
heap
heap
gcc AddressSpace.c
a
d
brk
stack
Output?
stack
e
argc
c
high
10
Memory management
Paging (why?)
MMU!
Swapping (why?)
11
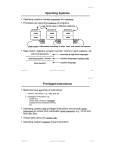
Protection and Security
Processes vs the OS (how?)
Processes vs other Processes (how?)
Privileged processes (why?)
Access control matrix
12
I/O management
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define N 41
Output?
gcc Wrap.c
strace ./a.out Wrap.c junk
Find the system calls for:
fgets()
fputs()
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
if(argc >= 3) {
FILE *from = fopen(argv[1], "r");
FILE *to = fopen(argv[2], "w");
char buf[N];
while (fgets(buf,N,from) != NULL) {
fputs(buf,to); fputc('\n',to);
}
fclose(from);
fclose(to);
return 0;
} else {
printf("usage %s from to\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
}
13
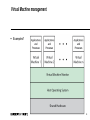
Virtual Machine management
Examples?
14
Summary
Operating systems are large, hence abstraction to manage complexity:
Processes and threads
Memory
Files and peripherals
User accounts
Management issues
Fairness
Sharing
Protection
15