* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Functional Foods - University of Kentucky
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
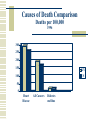
The Diet and Cancer Connection Dr. Sandra Bastin, RD, LD University of Kentucky Cooperative Extension Service Objectives What are functional foods? Connections science has confirmed between some foods and health benefits. Specific nutrients and non-nutrients found in functional foods thought to be of benefit to overall wellness. The importance of a balanced diet and plenty of physical activity. The Value of a Varied Diet! Causes of Death Comparison Deaths per 100,000 1996 300 250 200 150 KY US 100 50 0 Heart Disease All Cancers Diabetes mellitus Kentucky Cancer Burden 2000 Deaths per 100,000 persons 70 60 50 40 KY US 30 20 10 0 Lung Breast Coloretal Prostate Definition of Antioxidants Antioxidants are compounds typically found in foods that significantly decrease the adverse effect of oxidants on body functions. Oxidative stress is damage inflicted on cells in the body. Free radicals are unstable, highly reactive molecules that cause oxidative stress. The Theory of Antioxidants & Disease Oxygen free radical Fatty acids, DNA, or cholesterol Vitamin E stops the chain reaction by changing the nature of the free radical. Vitamin E Common Antioxidants Carotenoids found in fruits & vegetables ~ carrots, fresh tomatoes, tomato products, green vegetables, peppers, squash Vitamin C found in oranges & orange juice, peppers, tomatoes, & many other fruits & vegetables Common Antioxidants Vitamin E found in nuts, fats & oils, Wheat germ & green leafy vegetables. Selenium mostly found in seafood & organ meats Top Antioxidant Fruits & Vegetables Prunes Raisins Blueberries Blackberries Strawberries Raspberries Plums Oranges Red Grapes Cherries Kale Spinach Brussels sprouts Broccoli Beets Red bell pepper Onion Corn Eggplant Epidemiological Trends Age-related Blindness Arthritis Cancer Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes Kidney Disease Kentuckians Not Eating Enough Fruits & Vegetables 85 84 83 82 81 Percentages 80 79 78 77 1990 1994 1996 1997 1998 Definition of Phytochemicals Also known as phytonutrients. Phytochemicals are substances found in plants that may act as disease-fighting substances or cause other health benefits when eaten as part of a varied diet. Dietary Fiber Insoluble fiber in wheat bran Betaglucan & saponins in oats Soluble fiber in oats, psyllium & whole cereal grains Benefits of Soyfoods Soy protein may reduce the risk of heart disease. Isoflavones may reduce menopausal symptoms. Saponins may lower cholesterol and fight against cancer. Omega-3 Fatty Acids Probiotics Fructooligosaccharides Catechins Tannins Sulfides Plant Sterols The Diet Cancer Connection Functional Foods Functional foods are foods that provide a specific health benefit above and beyond their inherent nutritional value.