* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download I Have AIDS* On My Mind - AYD XAVIER
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
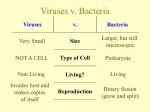
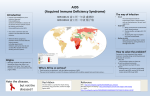
I Have AIDS… On My Mind World AIDS Day - December 1 What is AIDS? • • • • • • Stands for Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome Acquired – one becomes infected with this ailment Immuno Deficiency– it weakens the body’s ability to fight off disease Syndrome – a group of health problems that make up a disease It is caused by a virus called HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus); if these antibodies are found in your blood, the person is declared “HIV-Positive” It is essentially the final and most extreme stage of the HIV infection in which the immune system is extremely damaged Where does it come from? • • Scientists have theorized that HIV originated from a species of chimpanzee in Western Africa and humans were exposed to the virus when they hunted and ate infected animals. HIV is found in specific human body fluids; which infect another person when the fluids enter your body • • • • • • • • Blood Semen Breast Milk Vaginal Fluids Rectal Mucous It is not truly possible to “get” AIDS, but rather have AIDS develop if you are HIV-Positive The infection can be transferred from anyone who is infected with HIV (regardless of whether or not they appear sick or have tested positive) It is possible to acquire HIV by having sexual intercourse with an infected person, sharing a (drug) needle with an infected person, and even being born or drinking the milk of a woman who is infected with the virus. HIV • • • • • HIV Symptoms Include: Fever Headache Sore Muscles and Joints Stomach Ache • • • • Swollen Lymph Glands A Skin Rash for 1-2 Weeks Night Sweats Diarrhea • HIV weakens your immune system by destroying the cells that fight disease and infection. The virus reproduces itself by taking over a cell in the body of its host. The HIV virus multiplies within the body over weeks and months before the immune system responds. In this period, you will not test HIV-Positive, but can infect others with the virus The damage to your immune system is measureable through the number of CD4 (“T-helper”) cells you have in your body – initiate the body’s response to fight diseases HIV causes the count of this cell to decrease • • • Signs and Symptoms AIDS • • • • HIV develops into AIDS when your immune system is greatly damaged ; specifically if you have less than 200 CD4 cells or if your CD4 percentage is less than 14% Having a weakened immune system due to AIDS makes one more vulnerable to an “opportunistic infection” – an organism that does not usually cause disease but grows to be able to cause disease when the immune system is impaired Related diseases include serious weight loss, brain tumors, etc. which can lead to death if left untreated There is currently NO CURE for this disease, however drugs have been developed which slow down the HIV virus and the damage it causes to your immune system What does AIDS look like? • • • • • • • 33.4 million people around the world are currently living with HIV/AIDS AIDS has claimed the lives of over 25 million people since reported cases began in 1981 An estimated 2.6 million people become newly infected with the virus annually Approximately 97% of those with the virus are living in lowmiddle income countries such as sub-Saharan Africa It is estimated that 20-26% of the population between the ages of 15 and 49 are living with AIDS in countries such as Namibia, Zimbabwe , and Botswana This epidemic does not only affect the health of individuals but also impacts households, communities, and the development and economy of a nation through other issues such as other infectious diseases (ie: opportunistic diseases) and food insecurity The total number of children born with HIV has decreased by 24 % with the implementation of treatments in a broader sense of the world The Stigma • • • • Without a cure, HIV/AIDS is a deadly disease that many people fear Many myths include being infected with the virus through casual contact such as sharing a drinking glass or sharing a toilet seat Some may even believe that the person with the disease is at fault and that they deserve the suffering Those diagnosed with AIDS are often discriminated against • They are denied medical care at hospitals or other facilities • They are denied child custody, the right to adopt, or the right to be a foster parent • They are asked unlawful questions or harassed by their employers when applying for a job • They are evicted from a rental property • Information about their condition is exposed at school/work/within a health care institution http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rv0yIICeg-E http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TgKNZrbV42I