* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mutations Mutation: a random change in the sequence of
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
E. coli long-term evolution experiment wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
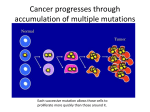
Mutations Mutation: a random change in the sequence of nucleotides in DNA mutagen: a factor in the environment that causes a mutation examples: radiation (nuclear, X-rays) chemicals (tobacco) UV rays (can cause skin cancer) 2 types of mutation: 1. chromosomal mutations: involve entire chromosome 2. gene mutations: involve individual genes Chromosomal Mutations: 1. deletion: a piece of a chromosome breaks off and is lost 2. duplication: extra copy of part of a chromosome Usually, chromosomal mutations have huge effects. Most deletions are lethal. Gene Mutations: 1. frameshift mutation: nucleotides are lost or gained, disrupting the codon sequence Pat the bad cat. (delete 1 letter) Ptt heb adc at nonsense! So if you’re reading codons and one base is lost, it can change all the amino acids that are coded for after the deletion. It could give an entirely different protein, or no protein at all. 2. Point Mutation: a change that occurs in only one nucleotide Ex. DNA has bases ATA mutation ATC When the DNA is transcribed to mRNA, the mutation can affect what amino acid is coded for. DNA: mRNA: codes for: ATA UAU tyrosine mutation ATC UAG STOP codon 1. 2. 3. 4. Mutations: The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly Sometimes mutations can have almost no effect on an organism. Sometimes mutations can kill an organism. Sometimes mutations can be harmful to an organism but not kill it. Sometimes mutations can be helpful to an organism, giving it a new gene that is an advantage. examples: a mutation in a deer thaqt results in better hearing a mutation in a rabbit that gives it thicker fur in the winter a mutation in a squirrel that gives it bigger mouth pouches to carry food How is each one of these mutations helping the organism to survive?